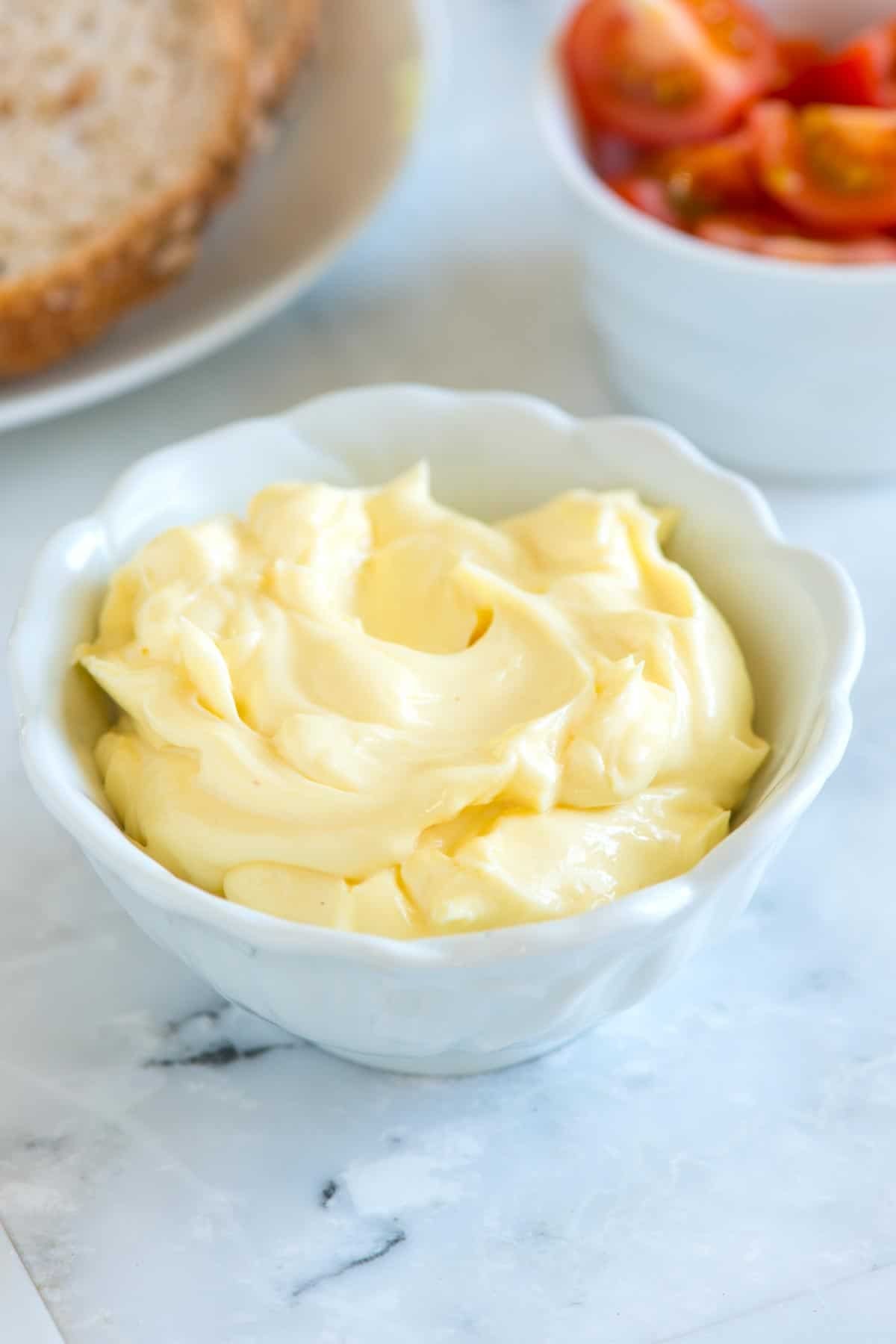
What Is Mayo Made Of? Explore the creamy condiment’s essential components and learn how WHAT.EDU.VN provides quick, reliable answers to all your culinary questions. Discover the secrets behind this popular sauce and unlock a world of flavor.
1. Unveiling Mayonnaise: A Culinary Staple
Mayonnaise, often shortened to “mayo,” stands as a cornerstone of global cuisine, gracing sandwiches, salads, and countless other dishes with its creamy texture and tangy flavor. But what exactly goes into this ubiquitous condiment? Understanding the fundamental ingredients and the science behind their combination is key to appreciating the versatility and deliciousness of mayonnaise.
Whether you’re a seasoned chef or a curious home cook, you’ve likely wondered about the essential components that make up this beloved sauce. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing clear, concise answers to all your culinary inquiries. Let’s delve into the world of mayo, exploring its ingredients, variations, and the secrets to making it perfectly.
2. The Core Components: What is Classic Mayo Made Of?
Classic mayonnaise, at its heart, is an emulsion – a stable mixture of two liquids that don’t typically combine, like oil and water. This emulsion is achieved through the careful combination of a few key ingredients:
- Egg yolk: This is the emulsifier, binding the oil and water-based components together. The lecithin in egg yolks is what makes this possible.
- Oil: A neutral-flavored oil, such as canola, soybean, or safflower, forms the bulk of the mayonnaise, providing its richness and creamy texture.
- Acid: Vinegar (white, apple cider, or wine vinegar) or lemon juice adds tanginess and helps to stabilize the emulsion.
- Seasoning: Salt is essential for flavor, and other seasonings like mustard, sugar, or spices can be added to customize the taste.
These simple ingredients, when combined in the right way, create the creamy, tangy condiment we all know and love. Each component plays a vital role in the final product, contributing to its flavor, texture, and stability.
3. A Closer Look: The Role of Each Ingredient
To truly understand what mayo is made of, it’s essential to examine the function of each ingredient:
3.1. Egg Yolk: The Emulsifier
Egg yolk is the star of the show when it comes to making mayonnaise. It contains lecithin, a phospholipid that acts as an emulsifier. Emulsifiers have a unique molecular structure with both water-loving (hydrophilic) and oil-loving (hydrophobic) properties. This allows lecithin to bridge the gap between the oil and water-based ingredients, creating a stable emulsion where tiny droplets of oil are suspended throughout the water phase.
Without an emulsifier like egg yolk, the oil and vinegar would quickly separate, resulting in a greasy, unappetizing mess. The lecithin in egg yolk ensures that the mayonnaise remains smooth, creamy, and stable over time.
3.2. Oil: The Foundation of Creaminess
The type of oil used in mayonnaise significantly impacts its flavor and texture. Neutral-flavored oils, such as canola, soybean, or safflower, are commonly used because they allow the other ingredients to shine through. Olive oil can be used, but its strong flavor can be overpowering for some palates.
The oil is added slowly and gradually to the egg yolk, creating the emulsion. As the oil is incorporated, it forms tiny droplets that are surrounded by the lecithin molecules from the egg yolk. This process creates the characteristic creamy texture of mayonnaise.
3.3. Acid: Tanginess and Stability
Vinegar or lemon juice serves two important purposes in mayonnaise. First, it adds a tangy flavor that balances the richness of the oil. Second, it helps to stabilize the emulsion.
The acid in vinegar or lemon juice lowers the pH of the mixture, which helps to prevent the growth of bacteria. This extends the shelf life of the mayonnaise and reduces the risk of spoilage. The acid also helps to denature the proteins in the egg yolk, further stabilizing the emulsion.
3.4. Seasoning: Enhancing the Flavor Profile
Salt is an essential seasoning in mayonnaise, enhancing the flavors of all the other ingredients. Other seasonings, such as mustard, sugar, and spices, can be added to customize the taste.
Mustard, in particular, is often used in mayonnaise recipes because it contains mucilage, another type of emulsifier that helps to stabilize the emulsion. Sugar adds a touch of sweetness that balances the tanginess of the acid, while spices like white pepper, cayenne pepper, or garlic powder can add depth and complexity to the flavor profile.
4. Variations on a Theme: Exploring Different Types of Mayo
While classic mayonnaise follows the basic recipe outlined above, numerous variations exist, catering to different tastes and dietary needs:
- Light Mayonnaise: Reduced-fat versions use less oil and often incorporate thickeners like cornstarch or modified food starch to maintain a creamy texture.
- Vegan Mayonnaise: Plant-based alternatives replace egg yolk with ingredients like aquafaba (chickpea brine), soy milk, or cashews to achieve the emulsification.
- Flavored Mayonnaise: Infused with herbs, spices, roasted garlic, or chili peppers, flavored mayonnaises add a unique twist to sandwiches and dips.
- Japanese Mayonnaise (Kewpie): Made with egg yolks only (no egg whites), rice vinegar, and a touch of MSG, Kewpie mayonnaise is known for its rich, umami flavor.
These variations demonstrate the versatility of mayonnaise as a base for countless flavor combinations. Whether you’re looking for a healthier option, a plant-based alternative, or a unique flavor profile, there’s a mayonnaise out there to suit your needs.
5. The Science of Emulsification: How Mayo Comes Together
The magic of mayonnaise lies in the process of emulsification. An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable). In the case of mayonnaise, oil is dispersed in a water-based solution (vinegar or lemon juice).
Achieving a stable emulsion requires energy, which is typically provided by whisking, blending, or processing the ingredients. The emulsifier, lecithin in egg yolk, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the mixture by reducing the surface tension between the oil and water phases.
5.1. The Emulsification Process
- Dispersion: The oil is initially dispersed into the water-based solution in the form of large droplets.
- Reduction of Surface Tension: The emulsifier molecules position themselves at the interface between the oil and water droplets, reducing the surface tension.
- Stabilization: The emulsifier molecules create a barrier around the oil droplets, preventing them from coalescing and separating from the water phase.
This process results in a stable emulsion where the oil droplets are evenly distributed throughout the water phase, creating the creamy texture of mayonnaise.
5.2. Factors Affecting Emulsion Stability
Several factors can affect the stability of a mayonnaise emulsion:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can cause the emulsion to break.
- Ingredient Ratios: The ratio of oil to water-based ingredients is crucial for stability.
- Agitation: Excessive agitation can disrupt the emulsion.
- Contaminants: Certain contaminants, such as salt or acids, can destabilize the emulsion.
Understanding these factors can help you troubleshoot common mayonnaise-making problems, such as broken emulsions or thin consistency.
6. Making Mayo at Home: A Step-by-Step Guide
Making mayonnaise at home is surprisingly easy and allows you to customize the flavor to your liking. Here’s a simple recipe:
6.1. Ingredients
- 1 large egg yolk
- 1 tablespoon lemon juice or vinegar
- 1/2 teaspoon Dijon mustard (optional)
- 1/4 teaspoon salt
- 1 cup neutral-flavored oil (canola, sunflower, or safflower)
6.2. Instructions
- Combine Ingredients: In a bowl, whisk together the egg yolk, lemon juice or vinegar, mustard (if using), and salt.
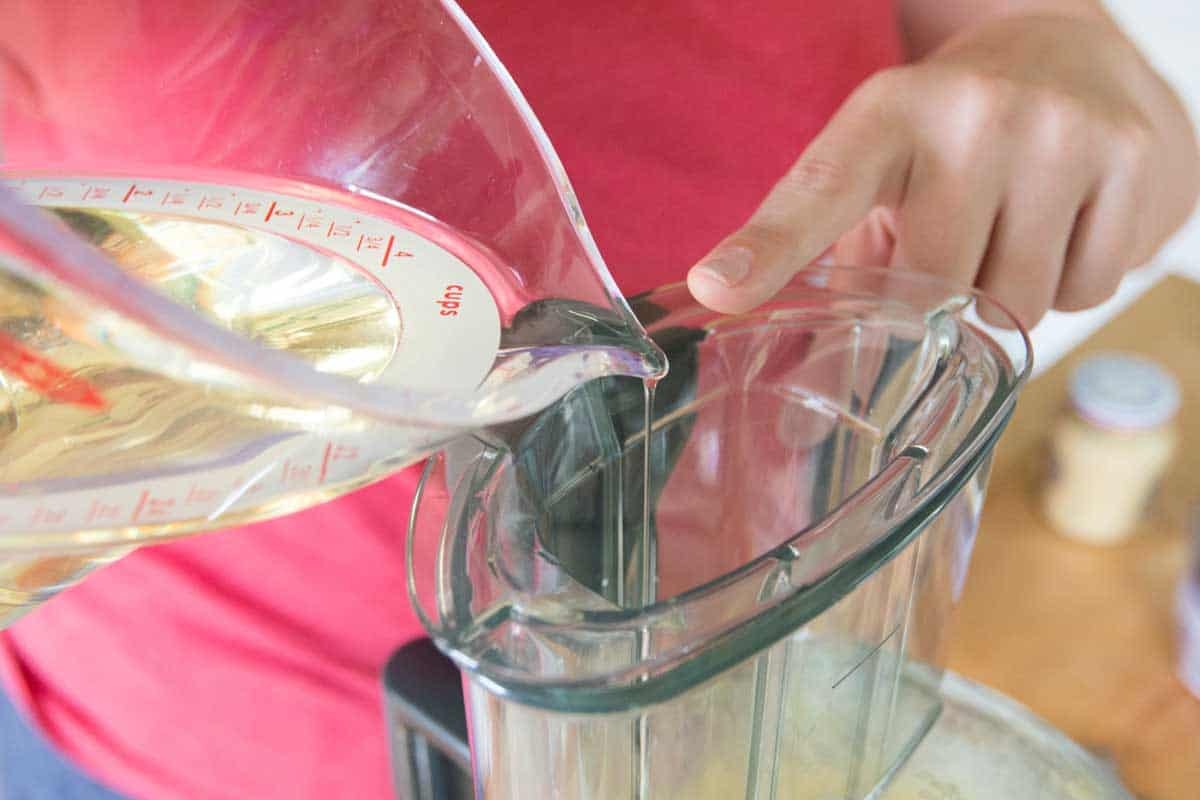
- Add Oil Gradually: Slowly drizzle in the oil, drop by drop at first, while whisking constantly. As the mixture begins to emulsify, you can increase the flow of oil to a thin stream.
- Continue Whisking: Continue whisking until all the oil is incorporated and the mayonnaise is thick and creamy.
- Adjust Seasoning: Taste and adjust the seasoning as needed. Add more salt, lemon juice, or spices to your liking.
- Store: Store the homemade mayonnaise in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to one week.
6.3. Tips for Success
- Use room-temperature ingredients for best results.
- Add the oil very slowly at first to ensure a stable emulsion.
- If the mayonnaise breaks, try whisking in a tablespoon of boiling water or another egg yolk.
Alt text: Video demonstrating the process of making homemade mayonnaise.
7. Troubleshooting Mayo: Common Problems and Solutions
Even with the best intentions, homemade mayonnaise can sometimes go wrong. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
7.1. Broken Emulsion
Problem: The mayonnaise separates and looks curdled.
Solution: This usually happens when the oil is added too quickly. To fix it, try whisking in a tablespoon of boiling water or another egg yolk. You can also try starting over with a fresh egg yolk and slowly whisking in the broken mayonnaise, drop by drop.
7.2. Thin Consistency
Problem: The mayonnaise is too thin and runny.
Solution: This can happen if you use too much acid or not enough oil. To fix it, slowly whisk in more oil until the mayonnaise thickens.
7.3. Bitter Taste
Problem: The mayonnaise has a bitter taste.
Solution: This can happen if you use olive oil with a strong flavor. To avoid this, use a neutral-flavored oil or a light, fruity olive oil.
7.4. Bland Flavor
Problem: The mayonnaise lacks flavor.
Solution: Adjust the seasoning to your liking. Add more salt, lemon juice, mustard, or spices.
8. Health Considerations: Is Mayo Good for You?
Mayonnaise, like any condiment, should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. While it’s high in fat, it also provides some nutrients:
- Fat: Mayonnaise is primarily composed of fat, which is essential for energy, hormone production, and cell function.
- Vitamin E: Mayonnaise contains vitamin E, an antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
- Sodium: Mayonnaise can be high in sodium, so it’s important to be mindful of your intake, especially if you have high blood pressure.
Choosing light or reduced-fat mayonnaise can help to reduce the calorie and fat content. Making your own mayonnaise at home allows you to control the ingredients and customize the nutritional profile.
9. Delicious Uses for Mayo: Beyond the Sandwich
Mayonnaise is a versatile condiment that can be used in a variety of ways:
- Sandwiches and Wraps: A classic spread for adding moisture and flavor.
- Salads: A key ingredient in potato salad, coleslaw, and macaroni salad.
- Dips: A base for creamy dips like ranch, blue cheese, and aioli.
- Sauces: An ingredient in tartar sauce, fry sauce, and other creamy sauces.
- Marinades: Adds moisture and flavor to grilled meats and vegetables.
- Baking: Can be used to add moisture and tenderness to cakes and muffins.
10. Common Questions About Mayonnaise
10.1. What is the difference between mayonnaise and aioli?
Aioli is traditionally made with garlic, olive oil, and salt, while mayonnaise is made with egg yolk, oil, and vinegar or lemon juice. However, modern aioli often includes egg yolk, making it very similar to mayonnaise.
10.2. Can I use olive oil to make mayonnaise?
Yes, you can use olive oil to make mayonnaise, but its strong flavor can be overpowering. Use a light, fruity olive oil or combine it with a neutral-flavored oil.
10.3. How long does homemade mayonnaise last?
Homemade mayonnaise lasts for up to one week in the refrigerator.
10.4. Can I freeze mayonnaise?
Freezing mayonnaise is not recommended, as it can cause the emulsion to break and the texture to become grainy.
10.5. Is mayonnaise gluten-free?
Yes, most mayonnaise is gluten-free. However, it’s always a good idea to check the ingredient list to be sure.
11. Addressing Your Culinary Questions with WHAT.EDU.VN
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of having quick, reliable answers to your culinary questions. Whether you’re wondering about the ingredients in mayonnaise or need help troubleshooting a recipe, our platform is designed to provide you with the information you need.
11.1. Instant Answers at Your Fingertips
Our website offers a vast database of culinary knowledge, covering a wide range of topics from basic cooking techniques to advanced recipes. Simply type your question into the search bar, and you’ll receive instant answers from our team of experts.
11.2. A Community of Knowledge Sharing
WHAT.EDU.VN is more than just a website – it’s a community of passionate cooks and food enthusiasts. Our users can ask questions, share their own tips and recipes, and connect with others who share their love of food.
11.3. Free and Accessible Information
We believe that everyone should have access to high-quality culinary information, which is why our platform is completely free to use. Whether you’re a student, a professional chef, or a home cook, you can rely on WHAT.EDU.VN to provide you with the knowledge you need to succeed in the kitchen.
12. Embrace Your Culinary Curiosity with WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your culinary questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and unlock a world of culinary knowledge. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the information you need to explore new flavors, master new techniques, and create delicious meals for yourself and your loved ones.
Remember, no question is too big or too small. Whether you’re wondering about the science behind mayonnaise or need help perfecting your favorite recipe, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
13. From Our Kitchen to Yours: Addressing Your Food-Related Concerns
We at WHAT.EDU.VN are committed to ensuring you have the necessary resources to navigate the culinary world confidently. Facing difficulties in finding swift, cost-free answers to your food-related questions? Unsure of where to seek reliable information or who to ask? Concerned about consultation expenses? Need a user-friendly platform for posing questions and receiving feedback? Desire insights from knowledgeable individuals?
13.1. Your Culinary Challenges, Our Solutions
- A Free Platform for All Inquiries: WHAT.EDU.VN offers a complimentary platform to ask any culinary question that comes to mind.
- Rapid and Precise Responses: We aim to provide accurate and timely answers to all your queries, ensuring you’re never left waiting.
- Clear and Understandable Information: Our explanations are crafted to be easily digestible, regardless of your culinary expertise.
- A Thriving Community for Knowledge Exchange: Connect with fellow food enthusiasts to share insights, tips, and recipes, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
- Complimentary Consultation for Simple Queries: Receive free guidance on straightforward culinary matters, ensuring you have the support you need.
13.2. Let’s Get Cooking Together!
Unlock your culinary potential with WHAT.EDU.VN. Our user-friendly platform and expert advice will empower you to create delicious dishes and explore the world of food with confidence.
14. Call to Action: Your Culinary Journey Starts Now!
Ready to dive deeper into the world of mayonnaise and other culinary delights? Have questions about ingredients, techniques, or recipes? Don’t hesitate to reach out to the WHAT.EDU.VN community!
Visit us at WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your burning culinary questions and receive free, expert answers. Our platform is designed to be user-friendly and accessible, ensuring that everyone can benefit from our wealth of culinary knowledge.
Join the WHAT.EDU.VN community and embark on a journey of culinary discovery. We’re here to help you every step of the way, providing the information and support you need to become a confident and skilled cook.
Have a question about mayonnaise or any other culinary topic? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the answers you need!
Contact us:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
15. FAQ: Decoding Mayonnaise – Your Questions Answered!
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the shelf life of mayo? | Store-bought mayo can last for several months unopened. Once opened, it’s best to use it within 2-3 months. Homemade mayo, due to the fresh ingredients, should be used within a week. |
| Can I make mayo without mustard? | Yes, you can. Mustard adds flavor and helps stabilize the emulsion, but it’s not essential. If omitting, consider adding a pinch of another emulsifier like turmeric. |
| What oil is best for making mayo? | Neutral-flavored oils like canola, sunflower, or safflower are ideal as they don’t overpower the other flavors. Olive oil can be used, but its distinct taste might not be desirable for all. |
| How can I make low-fat mayo? | Use less oil and incorporate thickeners like cornstarch or Greek yogurt. Some recipes use a base of pureed white beans for a creamy texture with significantly reduced fat. |
| Why did my mayo curdle? | This usually happens when the oil is added too quickly or the ingredients are at different temperatures. Add the oil very slowly, especially at the beginning, and ensure all ingredients are at room temperature. |
| Can I use pasteurized eggs for mayo? | Yes, pasteurized eggs are a safer option, especially for those concerned about salmonella. They won’t affect the taste or texture of the mayo. |
| What flavors can I add to mayo? | The possibilities are endless! Try adding roasted garlic, herbs (dill, chives, parsley), spices (smoked paprika, cayenne pepper), citrus zest, or even a touch of honey or maple syrup for sweetness. |
| Is vegan mayo as stable as regular mayo? | Vegan mayo can be just as stable if made correctly. Ingredients like aquafaba or soy milk contain emulsifying properties similar to egg yolks. Follow a trusted vegan mayo recipe for the best results. |
| How do I store homemade mayo? | Store homemade mayo in an airtight container in the refrigerator. It’s crucial to keep it cold to prevent bacterial growth. Label it with the date of preparation to ensure you use it within a week. |
| What are some creative uses for mayo? | Beyond sandwiches and salads, mayo can be used to make creamy salad dressings, as a marinade for grilled meats, to add moisture to baked goods, or as a base for flavorful dips like aioli or remoulade. |


These FAQs are designed to give a summary of common questions and to help you in your understanding “what is mayo made of”.
With what.edu.vn by your side, mastering the culinary arts has never been easier. Start exploring today and unlock your full potential in the kitchen.