What Is Msp? Discover how Managed Service Providers can transform your IT strategy. WHAT.EDU.VN offers insights into MSP services, helping businesses leverage expert support. Explore cloud computing, IT solutions, and scalable services for optimal efficiency.
1. Understanding the Core of MSP: What is a Managed Service Provider?
A Managed Service Provider (MSP) is essentially a third-party company that takes on the responsibility of managing and maintaining a customer’s information technology (IT) infrastructure and the systems used by end-users. These MSPs allow businesses, especially Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs), nonprofits, and governmental bodies, to outsource specific, routine management tasks. This can cover a range of services including, but not limited to, network and infrastructure management, cybersecurity measures, and continuous monitoring of systems. By leveraging MSPs, organizations can enhance operational efficiency and focus on core business objectives.
MSPs are designed to provide services daily, ensuring that client organizations can concentrate on improving their core offerings without the distraction of worrying about potential system downtimes or operational interruptions. This model is particularly valuable for organizations that may lack the resources or expertise to manage their IT needs effectively in-house.
1.1. The Evolution of the MSP Model
The concept of the Managed Service Provider evolved from earlier models like Application Service Providers (ASPs) in the 1990s. ASPs provided remote application hosting, which paved the way for cloud computing and the idea of remotely supporting IT infrastructure. Initially, MSPs focused on remote monitoring and management (RMM) of servers and networks. Over time, these services have expanded to include a more comprehensive suite of offerings designed to meet the evolving needs of businesses. The shift towards cloud-based services has further blurred the lines between MSPs and cloud service providers, especially when services are delivered over the internet under a service-level agreement (SLA).
1.2. What Distinguishes an MSP?
MSPs stand out because they offer proactive management and maintenance of IT systems. Unlike traditional IT support, which is often reactive and addresses issues as they arise, MSPs focus on preventing problems before they occur. This proactive approach includes regular monitoring, updates, and security measures designed to keep systems running smoothly and securely.
Moreover, MSPs typically operate under a Service Level Agreement (SLA), which outlines the specific services provided, performance metrics, and response times. This agreement ensures that clients have clear expectations and can hold the MSP accountable for delivering the agreed-upon services.
1.3. Common Misconceptions About MSPs
There are several misconceptions about what MSPs do and who they serve. One common myth is that MSPs are only for small businesses. While SMBs do make up a significant portion of the MSP client base, larger enterprises also benefit from outsourcing specific IT functions to MSPs.
Another misconception is that MSPs are only responsible for basic IT tasks. In reality, MSPs can offer a wide range of sophisticated services, including cybersecurity, cloud management, data analytics, and strategic IT consulting.
2. Exploring the Applications: What are MSPs Used For?
MSPs are versatile and can be employed across various industries and organizational sizes to improve IT operations and overall business performance. Here’s a closer look at their typical applications:
2.1. Common Use Cases for MSPs
- Supplementing IT Staff: Many organizations, particularly government agencies and larger enterprises facing budget constraints, use MSPs to augment their in-house IT staff, providing additional expertise and support without the overhead of hiring full-time employees.
- Handling Complex IT Tasks: MSPs are often brought in to manage the complex, time-consuming, and repetitive tasks associated with IT infrastructure and end-user systems. This allows in-house IT teams to focus on strategic projects that drive business growth.
- Enhancing Cybersecurity: MSPs play a critical role in adding and managing cybersecurity software, ensuring that IT systems are protected against a wide range of threats.
- Managing User Access and Compliance: MSPs handle user access accounts, contract management, compliance, and risk management, ensuring that organizations meet regulatory requirements and maintain data security.
- Providing Technical Support: MSPs offer comprehensive technical support to staff, addressing issues promptly and efficiently to minimize downtime and maintain productivity.
2.2. Industry-Specific Applications
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, MSPs ensure that systems comply with HIPAA regulations, protect sensitive patient data, and maintain the reliability of critical systems.
- Finance: Financial institutions rely on MSPs to manage complex IT environments, ensure data security, and meet stringent regulatory requirements.
- Manufacturing: MSPs help manufacturing companies optimize their IT infrastructure, manage industrial control systems, and support advanced technologies like IoT and automation.
- Education: Educational institutions use MSPs to manage networks, support student devices, and provide technical assistance to faculty and staff.
2.3. What specific services do MSPs typically provide?
MSPs can handle a wide array of tasks, including the management of IT infrastructure, offering technical support to staff, adding cybersecurity software to IT systems, managing user access accounts, handling contract management, offering compliance and risk management, and even providing payroll services.
3. Demystifying the Process: How Do MSPs Work?
The engagement between an organization and an MSP typically begins with a thorough assessment to identify gaps and areas for improvement within the IT system. This assessment forms the foundation for developing a tailored service plan that aligns with the organization’s business objectives.
3.1. Initial Assessment and Planning
The first step in working with an MSP is an assessment of the organization’s current IT environment. This assessment helps to identify potential areas for improvement and how IT can better support business goals. It also helps the MSP understand the specific needs and challenges of the organization.
3.2. Different Service Delivery Models
- Technical Support Fix Services: MSPs offer remote troubleshooting and on-site technical support to resolve issues as they arise. This model typically involves charging for time spent troubleshooting and for any parts used in the repair.
- Subscription Services: MSPs offer ongoing maintenance, security, and monitoring services for a fixed monthly fee. This model focuses on maintaining the quality and reliability of the organization’s network, with the MSP proactively addressing issues as part of the agreement.
3.3. Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Maintenance, security, monitoring, reporting, and other services are defined using an SLA that documents what the organization can expect from the MSP. Response times, performance, and security specifications are also included in the service agreement, ensuring that both parties have a clear understanding of the services provided and the expected outcomes.
3.4. The Role of RMM and PSA Tools
MSPs often deploy specialist software platforms that automatically manage functions. These platforms consist of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools and Professional Services Automation (PSA) applications.
- RMM Software: RMM software enables off-site technicians to maintain IT systems, such as networks, servers, desktops, and mobile devices. These tools also enable MSPs to apply patches and other system updates.
- PSA Tools: PSA tools enable an MSP to manage an organization’s projects, billing, assets, and inventory.
4. Classifying MSPs: What are the Types of MSPs?
MSPs can be classified based on several criteria, including the size of their target customers, the scope of their services, and the technologies they specialize in.
4.1. Categorizing MSPs by Service Scope
- Pure-Play MSPs: These smaller providers focus on monitoring networks and application performance, offering their own native services that primarily focus on reporting and alerts.
- Staffing Legacy MSPs: These MSPs generally target mid-level organizations and Fortune 500 companies, offering a wide range of services, including monitoring, reporting, and software installation and upgrades.
- High-Level MSPs: These consist of small and large providers that enable their clients to outsource as much of their IT processes as needed, typically offering a wide range of services.
4.2. Categorizing MSPs by Service Type
- Monitoring MSPs: These MSPs offer real-time monitoring software for different applications, network devices, servers, or websites.
- Remote Support MSPs: These MSPs offer cloud-based software, support remote devices, and remotely troubleshoot technical issues.
- Proactive Support MSPs: These MSPs perform preventative maintenance to stay ahead of any device or network issues that could arise.
- Centralized Management MSPs: These MSPs provide a management console for complex networks, remote monitoring, patch management, and security software.
- Scheduled Maintenance MSPs: These MSPs offer organizations regularly scheduled network maintenance.
- Simplified Billing MSPs: These MSPs handle invoicing, payments, and budgeting via a billing management system.
4.3. Specialized MSPs
Some MSPs specialize in specific technologies, industries, or service types. For example, a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) focuses exclusively on cybersecurity services, while a managed print service provider specializes in managing printers and supplies.
5. Unveiling the Advantages: What are the Benefits of Managed Service Providers?
There are numerous benefits to partnering with a managed service provider, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
5.1. Key Benefits of Using MSPs
- Filling Staff Shortages: MSPs can supplement an organization’s existing IT staff, providing additional resources and expertise as needed.
- Access to Expertise: Hiring a reputable MSP provides an organization with access to expert resources and specialized knowledge.
- Business Continuity: An SLA documents the MSP’s obligations to the business to prepare for or recover from a disaster, ensuring business continuity.
- Constant Network Monitoring: Many MSPs offer 24/7 monitoring services using network monitoring tools that offer system visibility and cloud management.
- Improved Security: Some MSPs provide security software and awareness training to enhance an organization’s security posture.
- Cost Efficiency: Paying a fixed monthly charge for managed services can be more cost-effective than paying hourly for unplanned repairs and support.
5.2. Strategic Advantages
- Focus on Core Business: By outsourcing IT management to an MSP, organizations can focus on their core competencies and strategic initiatives.
- Scalability: MSPs offer scalable services that can grow with the organization, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Access to Latest Technologies: MSPs stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and can help organizations implement and manage these technologies effectively.
5.3. Real-World Examples of Benefits
Consider a small business that lacks dedicated IT staff. By partnering with an MSP, they can ensure that their network is secure, their systems are running smoothly, and their employees have access to technical support when needed. This allows the business owner to focus on growing the business without being bogged down by IT issues.
6. Addressing the Concerns: What are the Challenges of Managed Service Providers?
While MSPs offer numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of the potential challenges and drawbacks.
6.1. Potential Downsides of Using MSPs
- Lack of Security Focus: Not all MSPs have a major focus on cybersecurity, which can leave organizations vulnerable to threats.
- Dependency on Third-Party Organizations: Organizations that depend on an MSP to handle daily tasks may become overly reliant on them. If the MSP fails to follow through on the SLA, the organization could experience system downtime.
- Response Times: It may take time for an MSP to respond to an issue, particularly if the MSP is dealing with multiple clients simultaneously.
- Upselling: An MSP may try and upsell an organization on technology or services they do not need, leading to unnecessary costs.
- Inaccessible Information: An organization’s information may not be freely accessible if the MSP is using a proprietary tool to manage and monitor its infrastructure.
6.2. Mitigation Strategies
- Thorough Vetting: Organizations should carefully vet potential MSPs to ensure they have the expertise and resources needed to meet their specific requirements.
- Clear SLAs: SLAs should be clearly defined and include specific performance metrics, response times, and security requirements.
- Regular Communication: Organizations should maintain regular communication with their MSP to ensure that issues are addressed promptly and that the MSP is meeting their needs.
- Data Ownership: Organizations should ensure that they have clear ownership of their data and that they can access it even if they terminate their relationship with the MSP.
6.3. Overcoming Challenges
To address these challenges, organizations need to conduct thorough research, ask the right questions, and establish clear expectations with their MSP. This includes discussing security protocols, response times, data ownership, and potential upselling practices.
7. Deciphering the Costs: What is the Pricing Model for Managed Service Providers?
Understanding the pricing models used by MSPs is essential for budgeting and ensuring cost-effectiveness.
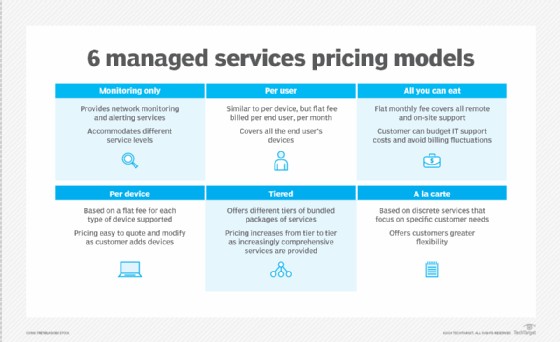
7.1. Common Pricing Models
- Per-Device Pricing: The MSP charges the customer a flat fee for each device it manages.
- Per-User Pricing: The MSP charges a flat fee for each user, accommodating users who use multiple devices.
- All-Inclusive Pricing: Also referred to as the all-you-can-eat model, the MSP charges a flat fee for its IT infrastructure support and management services.
- Tiered Pricing: Organizations can choose the bundle of services that best fits their needs. This is typically a favored pricing model for MSPs.
- Monitoring-Only Pricing: MSPs only offer monitoring and alerting services for an organization’s IT infrastructure.
7.2. Factors Influencing Pricing
The pricing model used by an MSP can depend on several factors, including the size of the organization, the complexity of its IT environment, and the specific services required.
7.3. Budgeting for MSP Services
When budgeting for MSP services, organizations should consider not only the direct costs of the services but also the indirect benefits, such as reduced downtime, improved security, and increased productivity.
7.4. Real-World Pricing Examples
For example, a small business with 20 employees might opt for per-user pricing, paying a flat monthly fee for each employee who requires IT support. A larger enterprise with a complex IT environment might choose tiered pricing, selecting a bundle of services that meets their specific needs.
8. Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of MSPs
The managed services landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing business needs, and emerging threats.
8.1. Key Trends Shaping the Future of MSPs
- Increased Focus on Cybersecurity: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, MSPs are placing greater emphasis on cybersecurity services, offering advanced threat detection, incident response, and security awareness training.
- Cloud Adoption: Cloud computing continues to drive the growth of the MSP market, with MSPs helping organizations migrate to the cloud, manage cloud environments, and optimize cloud spending.
- Automation: Automation is playing an increasing role in managed services, with MSPs using automation tools to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
- Data Analytics: MSPs are leveraging data analytics to gain insights into IT performance, identify potential issues, and optimize IT operations.
- Edge Computing: As edge computing becomes more prevalent, MSPs are expanding their services to manage and support edge infrastructure.
8.2. Predictions for the Future of MSPs
Experts predict that the MSP market will continue to grow in the coming years, driven by the increasing complexity of IT environments, the growing threat of cyberattacks, and the need for specialized IT expertise.
8.3. Staying Ahead of the Curve
To stay ahead of the curve, MSPs need to continuously adapt their services, invest in new technologies, and develop expertise in emerging areas such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics.
9. Real-Life Scenarios: MSP in Action
To further illustrate the value of MSPs, let’s consider a few real-life scenarios where MSPs have made a significant impact.
9.1. Case Study 1: Improving Security for a Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider was struggling to protect sensitive patient data from cyber threats. By partnering with an MSP specializing in cybersecurity, they were able to implement advanced threat detection and incident response capabilities, significantly reducing their risk of a data breach.
9.2. Case Study 2: Optimizing Cloud Infrastructure for a Retail Company
A retail company was struggling to manage its cloud infrastructure and optimize its cloud spending. By working with an MSP experienced in cloud management, they were able to streamline their cloud operations, reduce their cloud costs, and improve the performance of their cloud-based applications.
9.3. Case Study 3: Supporting Remote Workers for a Financial Firm
A financial firm needed to support a growing number of remote workers while maintaining data security and compliance. By partnering with an MSP, they were able to provide secure access to company resources, monitor remote devices, and ensure that remote workers had the support they needed to stay productive.
10. Addressing Your Concerns: FAQ About MSPs
To address any remaining questions or concerns, let’s take a look at some frequently asked questions about MSPs.
10.1. Common Questions About MSPs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between an MSP and an IT consultant? | An MSP provides ongoing management and support for IT systems, while an IT consultant provides advice and guidance on IT strategy and implementation. |
| How do I choose the right MSP for my business? | Consider your specific needs, budget, and technical requirements. Look for an MSP with relevant experience, a strong reputation, and a clear understanding of your business goals. |
| What should I expect from an MSP? | Expect proactive monitoring, maintenance, and support for your IT systems, as well as regular communication, detailed reporting, and strategic guidance. |
| How can I measure the ROI of an MSP? | Measure the impact of the MSP on key metrics such as uptime, security incidents, and IT costs. Also consider the indirect benefits, such as increased productivity and improved business agility. |
| What are the key terms to include in an SLA with an MSP? | Include specific performance metrics, response times, security requirements, and data ownership provisions. |
| How do MSPs handle data security and compliance? | MSPs implement a range of security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. They also ensure that IT systems comply with relevant regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. |
| Can an MSP help with cloud migration? | Yes, many MSPs offer cloud migration services, helping organizations move their IT infrastructure and applications to the cloud safely and efficiently. |
| How do MSPs ensure business continuity? | MSPs implement backup and disaster recovery solutions, providing organizations with the ability to quickly recover from outages and maintain business continuity. |
| What is remote monitoring and management (RMM)? | RMM is a set of tools and technologies that enable MSPs to remotely monitor and manage IT systems, providing proactive maintenance, troubleshooting, and support. |
| What is professional services automation (PSA)? | PSA is a software platform that helps MSPs manage their projects, billing, assets, and inventory, streamlining their operations and improving efficiency. |

10.2. Additional Resources
For more information about MSPs, consider exploring industry publications, attending industry events, and consulting with IT professionals.
10.3. Final Thoughts
MSPs can be a valuable partner for organizations looking to improve their IT operations, reduce costs, and focus on their core business. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and pricing models of MSPs, organizations can make informed decisions and choose the right MSP for their needs.
Feeling overwhelmed by IT challenges? Let WHAT.EDU.VN help you find the perfect MSP solution. Our platform provides expert guidance and connects you with top-rated providers.
Unlock Seamless IT Management: Ask Your Questions at WHAT.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of IT can be daunting, but finding the right solutions shouldn’t be. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in seeking reliable and cost-effective answers to your IT questions. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive expert guidance completely free of charge.
Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Expert Advice: Get access to a wealth of knowledge from experienced IT professionals who are ready to provide you with the insights you need.
- Quick and Accurate Answers: Our platform is designed to deliver prompt and precise responses to your questions, helping you make informed decisions without delay.
- Easy-to-Understand Information: We break down complex topics into simple, digestible formats, ensuring that you understand the solutions available to you.
- Community-Driven Support: Connect with a community of users who share their experiences and insights, fostering a collaborative environment for knowledge sharing.
- Convenient and Accessible: Our platform is available anytime, anywhere, allowing you to get the answers you need on your own schedule.
Our Commitment to You
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to empowering you with the information you need to overcome your IT challenges. Whether you’re a student, a business owner, or simply someone with a curious mind, we’re here to provide you with the support you deserve.
Contact Us
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your IT questions go unanswered. Visit what.edu.vn today and experience the ease and convenience of our free consultation service. We’re here to help you unlock seamless IT management and achieve your goals.