Nativism is a policy or practice of favoring native inhabitants as opposed to immigrants, which often leads to discriminatory practices and exclusionary policies. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear and comprehensive explanations of complex concepts like nativism to help you understand its implications. Explore the roots, effects, and history of nativism, and discover its modern relevance, including anti-immigrant sentiment, xenophobia, and cultural preservation efforts.
1. What is Nativism?
Nativism is the political attitude of favoring native inhabitants over immigrants. It involves a range of beliefs, policies, and actions aimed at protecting the interests of native-born or established inhabitants against those of immigrants. This can manifest as prejudice, discrimination, and even exclusionary laws. Nativism often stems from fears about the economic, cultural, and social impact of immigration on the existing population.
To delve deeper, consider these aspects of nativism:
- Beliefs: Nativists often believe that native inhabitants are superior to immigrants and that immigrants pose a threat to the nation’s cultural identity, economic stability, and social cohesion.
- Policies: Nativist policies can include stricter immigration laws, restrictions on immigrant rights, and efforts to promote the cultural assimilation of immigrants.
- Actions: Nativist actions can range from peaceful protests and political activism to acts of violence and discrimination against immigrants.
Understanding nativism requires examining its historical roots and contemporary manifestations. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply someone curious about this phenomenon, WHAT.EDU.VN offers resources and answers to help you explore this complex topic further.
2. What Are the Key Characteristics of Nativism?
Nativism encompasses several defining characteristics that underscore its nature and impact. These characteristics include ethnocentrism, xenophobia, protectionism, and assimilationism. Understanding these elements is crucial for grasping the multifaceted nature of nativism.
- Ethnocentrism: This is the belief in the inherent superiority of one’s own ethnic group or culture. Nativists often view their culture as superior and perceive immigrants as a threat to their cultural values and traditions.
- Xenophobia: This refers to the fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers. Nativism often involves a fear of immigrants, driven by concerns about their potential impact on society.
- Protectionism: Nativists often advocate for policies that protect the interests of native inhabitants, particularly in the economic sphere. This can include restricting immigration to safeguard jobs and wages for native-born workers.
- Assimilationism: This is the belief that immigrants should assimilate into the dominant culture. Nativists often pressure immigrants to adopt the language, customs, and values of the native population, sometimes to the detriment of their own cultural heritage.
Recognizing these key characteristics helps in analyzing nativist movements and policies, offering a clearer understanding of their motivations and consequences.
3. How Does Nativism Differ From Patriotism?
While both nativism and patriotism involve a sense of attachment to one’s country, they differ significantly in their focus and expression. Patriotism is a love for and devotion to one’s country, often expressed through pride in its history, culture, and values. Nativism, on the other hand, is characterized by hostility toward immigrants and a desire to protect the interests of native inhabitants.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
| Feature | Patriotism | Nativism |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Love and pride for one’s country and its values. | Hostility toward immigrants and a desire to protect the interests of native inhabitants. |
| Attitude | Inclusive, welcoming of diversity, and focused on national unity. | Exclusive, suspicious of outsiders, and focused on maintaining a perceived cultural purity. |
| Motivation | A desire to contribute to the well-being and success of the nation as a whole. | Fear of cultural or economic competition from immigrants and a desire to preserve the status quo. |
| Policies | Policies that promote national unity, civic engagement, and the common good. | Policies that restrict immigration, limit immigrant rights, and promote assimilation. |
| Expression | Celebrating national holidays, supporting national institutions, and promoting national values. | Advocating for stricter immigration laws, protesting against immigration, and expressing anti-immigrant sentiment. |
In essence, patriotism is about loving one’s country, while nativism is about fearing and rejecting those who are not seen as “native.”
4. What Are Some Historical Examples of Nativism in the United States?
The United States has a long history of nativism, with various movements and policies targeting different immigrant groups throughout its history. Here are some notable examples:
-
The Know-Nothing Party (1850s): This anti-immigrant political movement opposed Irish and German Catholic immigrants, advocating for stricter immigration laws and restrictions on the political rights of immigrants.
-
The Chinese Exclusion Act (1882): This federal law prohibited Chinese laborers from immigrating to the United States, reflecting widespread anti-Chinese sentiment and fears about economic competition.
-
The Immigration Act of 1924: This law established quotas that favored immigrants from Northern and Western Europe, while severely restricting immigration from Southern and Eastern Europe, as well as Asia.
-
Japanese American Internment (World War II): Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the U.S. government forcibly removed and incarcerated approximately 120,000 Japanese Americans in internment camps, based on unfounded fears of disloyalty.
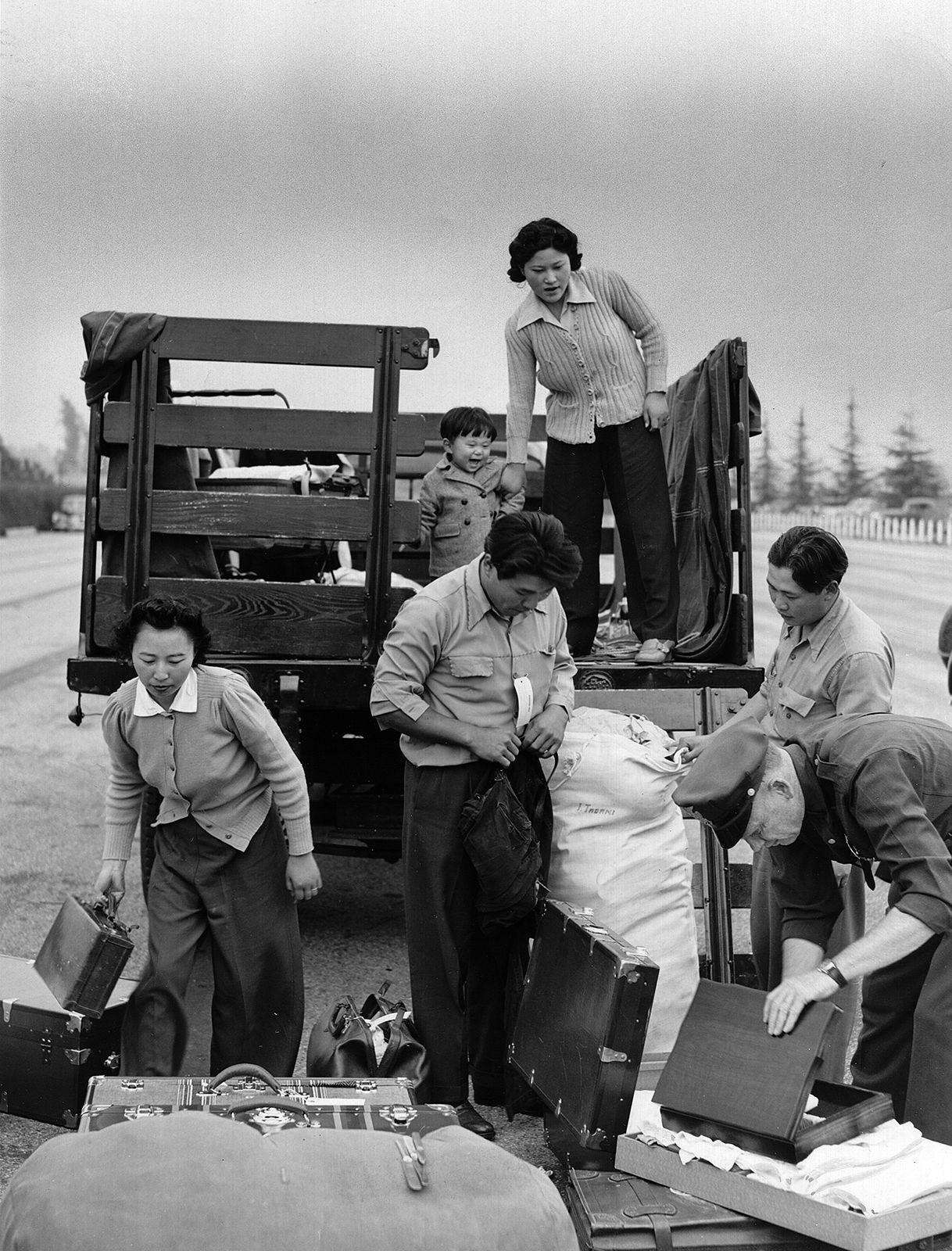 Japanese Americans being removed to internment camps
Japanese Americans being removed to internment camps
These historical examples illustrate the recurring nature of nativism in American history and its profound impact on immigrant communities.
5. What Factors Contribute to the Rise of Nativism?
Several factors contribute to the rise of nativism in society. These include economic anxiety, cultural preservation, political opportunism, and social change. Understanding these drivers is essential for addressing the underlying causes of nativism.
- Economic Anxiety: Economic downturns or periods of high unemployment can fuel nativist sentiment, as native-born workers may feel threatened by competition from immigrants for jobs and resources.
- Cultural Preservation: Nativists often fear that immigration will lead to the erosion of their cultural identity and traditions. They may advocate for policies that promote cultural assimilation and limit the influence of foreign cultures.
- Political Opportunism: Politicians may exploit nativist sentiment to gain support and advance their political agendas. They may use anti-immigrant rhetoric to appeal to voters who feel threatened by immigration.
- Social Change: Rapid social and demographic changes can trigger nativist reactions, as some members of society may feel uncomfortable or threatened by the changing social landscape.
By recognizing these contributing factors, societies can develop strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of nativism and promote greater understanding and inclusion.
6. What Are the Economic Arguments Used by Nativists?
Nativists often employ various economic arguments to justify their stance against immigration. These arguments typically revolve around concerns about job displacement, wage depression, and the strain on public resources. However, many of these claims are often based on misconceptions or lack empirical support.
- Job Displacement: Nativists argue that immigrants take jobs away from native-born workers, leading to higher unemployment rates. However, studies have shown that immigration often has a minimal impact on overall employment and can even create new jobs through increased demand and innovation.
- Wage Depression: Nativists claim that immigrants drive down wages by increasing the supply of labor, particularly in low-skilled occupations. While there may be some localized wage effects, research suggests that the overall impact of immigration on wages is relatively small.
- Strain on Public Resources: Nativists argue that immigrants place a burden on public resources, such as schools, healthcare, and social welfare programs. However, immigrants also contribute to the economy through taxes and consumption, and their net impact on public finances is often positive or neutral.
It’s important to critically evaluate these economic arguments and consider the broader economic benefits of immigration, such as increased productivity, innovation, and entrepreneurship.
7. How Does Nativism Impact Immigrant Communities?
Nativism can have profound and far-reaching impacts on immigrant communities, affecting their social, economic, and psychological well-being. These impacts can manifest in various forms, including discrimination, marginalization, and social exclusion.
- Discrimination: Nativism often leads to discrimination against immigrants in various aspects of life, such as employment, housing, education, and healthcare. Immigrants may face prejudice and bias based on their ethnicity, language, or immigration status.
- Marginalization: Nativism can marginalize immigrant communities, making it difficult for them to fully integrate into society. Immigrants may be excluded from social networks, political processes, and cultural institutions.
- Social Exclusion: Nativism can foster a climate of fear and hostility towards immigrants, leading to social isolation and exclusion. Immigrants may feel unwelcome or unsafe in their communities, leading to mental health issues and reduced social cohesion.
Addressing the negative impacts of nativism requires promoting policies and programs that foster inclusion, respect, and understanding between immigrant and native-born communities.
8. What Role Does Media Play in Shaping Nativist Sentiment?
The media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion on immigration and can either amplify or mitigate nativist sentiment. Media coverage of immigration can influence how the public perceives immigrants and the potential impacts of immigration on society.
- Sensationalism: Some media outlets may sensationalize stories about immigration, focusing on negative aspects such as crime or economic strain, which can fuel nativist fears and prejudices.
- Stereotyping: Media portrayals of immigrants can reinforce negative stereotypes, depicting them as criminals, freeloaders, or threats to cultural values.
- Framing: The way media frames immigration issues can influence public perceptions. For example, framing immigration as a security threat can increase support for stricter border controls and anti-immigrant policies.
However, the media can also play a positive role by providing accurate and balanced coverage of immigration, highlighting the contributions of immigrants to society, and promoting understanding and empathy.
9. What Are Some Contemporary Examples of Nativism Around the World?
Nativism is not unique to the United States and can be observed in various forms around the world. Here are some contemporary examples:
- Europe: The rise of right-wing populist parties in Europe has been fueled by anti-immigrant sentiment, particularly in response to the influx of refugees and migrants from the Middle East and Africa.
- Australia: Australia has a long history of nativism, with restrictive immigration policies and public debates about multiculturalism and national identity.
- Asia: In some Asian countries, there is growing concern about the impact of foreign workers on local economies and cultural traditions, leading to stricter immigration controls and anti-immigrant sentiment.
These examples highlight the global nature of nativism and its potential to shape immigration policies and social attitudes in diverse contexts.
10. How Can Societies Combat Nativism?
Combating nativism requires a multifaceted approach that addresses its underlying causes and promotes inclusion, understanding, and respect for diversity. Here are some strategies that societies can employ:
- Education: Educating the public about the benefits of immigration and the contributions of immigrants to society can help dispel myths and stereotypes and foster greater understanding.
- Dialogue: Encouraging dialogue and interaction between immigrant and native-born communities can promote empathy and break down barriers.
- Policy Reform: Enacting fair and inclusive immigration policies that protect the rights of immigrants and promote their integration into society can help reduce discrimination and marginalization.
- Leadership: Political and community leaders can play a crucial role in combating nativism by speaking out against anti-immigrant rhetoric and promoting a vision of an inclusive and welcoming society.
By implementing these strategies, societies can create a more just and equitable environment for all residents, regardless of their immigration status.
Are you looking for answers to your pressing questions? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for free and reliable information. Our experts are ready to provide you with the insights you need. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or WhatsApp us at +1 (206) 555-7890. Explore WHAT.EDU.VN today!
11. What is the Relationship Between Nativism and Xenophobia?
Nativism and xenophobia are closely related concepts, often reinforcing each other within a society. Xenophobia, the fear or dislike of strangers or foreigners, serves as a key emotional and psychological foundation for nativist ideologies. When people harbor xenophobic attitudes, they are more likely to support nativist policies and movements that aim to restrict immigration and protect the interests of native-born citizens.
The relationship between the two can be understood through the following points:
- Xenophobia as a Driver: Xenophobia acts as a primary driver of nativism. The fear and distrust of foreigners can lead to the belief that immigrants are a threat to national identity, security, or economic stability.
- Nativism as a Manifestation: Nativism is often a political and social manifestation of underlying xenophobic sentiments. It translates these fears into concrete actions, such as advocating for stricter immigration laws or discriminatory practices.
- Reinforcing Cycle: Nativist policies and rhetoric can, in turn, reinforce xenophobia by legitimizing negative stereotypes and creating a climate of hostility towards immigrants.
Understanding this relationship is crucial for addressing both issues effectively. Efforts to combat nativism must also target the root causes of xenophobia, such as misinformation, cultural misunderstandings, and economic anxieties.
12. How Does Nativism Affect Political Discourse and Policy?
Nativism significantly influences political discourse and policy, often leading to the adoption of restrictive immigration laws and the marginalization of immigrant communities. The rise of nativist sentiment can reshape political debates, influence electoral outcomes, and impact the policy-making process.
Here are some key ways nativism affects politics and policy:
- Policy Changes: Nativist movements often advocate for policies that limit immigration, tighten border controls, and restrict access to social services for immigrants. These policies can have profound consequences for immigrant families and communities.
- Political Rhetoric: Nativist rhetoric can become a powerful tool in political campaigns, used to mobilize voters and demonize political opponents. This type of rhetoric can create a divisive and hostile political climate.
- Public Opinion: Nativist sentiment can shape public opinion on immigration, making it more difficult to enact comprehensive immigration reform or promote policies that support immigrant integration.
- Electoral Outcomes: In some cases, nativist movements can gain enough support to influence electoral outcomes, leading to the election of candidates who support anti-immigrant policies.
Addressing the impact of nativism on political discourse and policy requires promoting evidence-based information, fostering constructive dialogue, and advocating for policies that reflect the values of inclusion and respect for diversity.
13. What are the Psychological Roots of Nativism?
The psychological roots of nativism are complex and multifaceted, involving a range of cognitive, emotional, and social factors. Understanding these psychological underpinnings can provide insights into why some individuals and groups are more prone to nativist beliefs and attitudes.
Some of the key psychological factors contributing to nativism include:
- In-Group Bias: People tend to favor members of their own group (in-group) and view outsiders (out-group) with suspicion or hostility. This in-group bias can lead to the belief that native-born citizens are superior to immigrants.
- Threat Perception: Nativism is often fueled by the perception that immigrants pose a threat to national identity, economic stability, or cultural values. This threat perception can be amplified by misinformation or fear-mongering.
- Authoritarianism: Individuals with authoritarian personality traits tend to value conformity, obedience, and social order. They may be more likely to support nativist policies that aim to maintain the status quo and suppress perceived threats from outsiders.
- Social Identity: People’s sense of self-worth and belonging can be closely tied to their national identity. Nativism can be a way of protecting this social identity by excluding those who are seen as different or foreign.
By addressing these psychological factors, societies can work to reduce prejudice, promote empathy, and foster a more inclusive and welcoming environment for immigrants.
14. How Does Nativism Interact With Racism and Other Forms of Prejudice?
Nativism often intersects with racism and other forms of prejudice, creating complex and overlapping systems of discrimination and inequality. While nativism is primarily focused on the distinction between native-born and foreign-born individuals, it can easily become intertwined with racial, ethnic, and religious biases.
Here are some key ways nativism interacts with other forms of prejudice:
- Racial Nativism: In many societies, nativism is closely linked to racial prejudice. Immigrants from certain racial or ethnic groups may face greater discrimination and hostility than those from other groups.
- Religious Nativism: Nativism can also be intertwined with religious prejudice, particularly when immigrants belong to minority religious groups. They may face discrimination based on their religious beliefs and practices.
- Intersectionality: The experience of nativism can be further complicated by other forms of prejudice, such as sexism, classism, and homophobia. Immigrants who belong to multiple marginalized groups may face compounded discrimination and barriers to integration.
Addressing the complex interplay between nativism and other forms of prejudice requires a comprehensive approach that challenges all forms of discrimination and promotes equality and inclusion for all members of society.
15. What Role Do Economic Conditions Play in Nativist Sentiments?
Economic conditions often play a significant role in shaping nativist sentiments within a society. Economic downturns, job losses, and wage stagnation can fuel anxieties and resentments that are often directed towards immigrants.
Here are some key ways economic conditions influence nativism:
- Job Competition: During periods of high unemployment, native-born workers may perceive immigrants as a direct threat to their job prospects. This can lead to increased hostility and support for policies that restrict immigration.
- Wage Depression: Nativists often argue that immigrants drive down wages by increasing the supply of labor. While the economic evidence on this issue is mixed, the perception that immigrants are depressing wages can fuel resentment and anti-immigrant sentiment.
- Strain on Public Resources: Economic hardship can increase concerns about the burden that immigrants place on public resources, such as schools, healthcare, and social welfare programs.
- Scapegoating: In times of economic crisis, immigrants may be scapegoated for broader economic problems, even when there is little or no evidence to support this claim.
Addressing the economic roots of nativism requires policies that promote economic growth, create job opportunities, and ensure that all workers have access to fair wages and benefits. It also requires challenging the narrative that immigrants are to blame for economic problems and highlighting their contributions to the economy.
16. How Can Education Help Combat Nativism?
Education plays a crucial role in combating nativism by promoting understanding, empathy, and critical thinking skills. By providing accurate information and challenging stereotypes, education can help reduce prejudice and foster a more inclusive and welcoming society.
Here are some specific ways education can help combat nativism:
- Promoting Cultural Awareness: Education can help students learn about different cultures, histories, and perspectives, fostering greater understanding and appreciation for diversity.
- Challenging Stereotypes: Education can challenge negative stereotypes about immigrants and other marginalized groups by presenting accurate and nuanced information.
- Developing Critical Thinking Skills: Education can help students develop the critical thinking skills necessary to evaluate information, identify bias, and resist manipulation.
- Fostering Empathy: Education can foster empathy by encouraging students to consider the experiences and perspectives of others, including immigrants and refugees.
- Promoting Civic Engagement: Education can promote civic engagement by encouraging students to participate in democratic processes and advocate for social justice.
By integrating these elements into the curriculum, schools and universities can play a vital role in combating nativism and creating a more informed and inclusive citizenry.
17. What are Some Strategies for Promoting Immigrant Integration and Inclusion?
Promoting immigrant integration and inclusion requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the economic, social, cultural, and political dimensions of integration. Effective integration strategies can help immigrants thrive, contribute to their communities, and foster social cohesion.
Some key strategies for promoting immigrant integration and inclusion include:
- Language Training: Providing access to high-quality language training programs can help immigrants acquire the language skills they need to succeed in education, employment, and civic life.
- Job Training and Placement: Offering job training and placement services can help immigrants find employment that matches their skills and experience.
- Access to Education: Ensuring that immigrants have access to education at all levels, from early childhood education to higher education, can help them achieve their full potential.
- Healthcare Access: Providing access to affordable healthcare can help immigrants stay healthy and productive.
- Civic Engagement: Encouraging immigrants to participate in civic life, such as voting, volunteering, and joining community organizations, can help them feel more connected to their communities.
- Cultural Competency Training: Providing cultural competency training to service providers, employers, and community leaders can help them better understand and serve the needs of immigrant communities.
- Anti-Discrimination Policies: Enacting and enforcing anti-discrimination policies can help protect immigrants from prejudice and discrimination.
By implementing these strategies, societies can create a more welcoming and inclusive environment for immigrants and ensure that they have the opportunity to thrive and contribute to their new communities.
18. How Do Nativist Movements Use Social Media?
Nativist movements have increasingly turned to social media as a tool for spreading their message, recruiting new members, and influencing public opinion. Social media platforms offer nativist groups a powerful means of bypassing traditional media gatekeepers and reaching a wide audience with their ideas.
Here are some ways nativist movements use social media:
- Spreading Propaganda: Nativist groups use social media to spread propaganda, misinformation, and conspiracy theories about immigrants and other minority groups.
- Recruiting New Members: Social media platforms provide nativist groups with a way to connect with like-minded individuals and recruit them into their movements.
- Organizing Protests and Rallies: Nativist groups use social media to organize protests, rallies, and other events designed to promote their cause.
- Harassing and Intimidating Opponents: Nativist activists often use social media to harass and intimidate their opponents, including immigrants, activists, and journalists.
- Influencing Public Opinion: Nativist groups use social media to influence public opinion on immigration and related issues, often by targeting specific demographics with tailored messages.
Addressing the spread of nativist propaganda on social media requires a multi-pronged approach that includes fact-checking, media literacy education, and collaboration between social media platforms and civil society organizations.
19. What is the Role of Leadership in Addressing Nativism?
Leadership plays a crucial role in addressing nativism by setting the tone for public discourse, promoting inclusive policies, and challenging prejudice and discrimination. Leaders at all levels, from political leaders to community organizers, can help to create a more welcoming and inclusive society for immigrants.
Here are some specific ways leaders can address nativism:
- Speaking Out Against Hate Speech: Leaders can use their platforms to speak out against hate speech and discrimination targeting immigrants and other minority groups.
- Promoting Inclusive Policies: Leaders can advocate for policies that promote immigrant integration, such as access to language training, job training, and healthcare.
- Building Bridges Between Communities: Leaders can facilitate dialogue and collaboration between immigrant and native-born communities to build trust and understanding.
- Challenging Stereotypes: Leaders can challenge negative stereotypes about immigrants by highlighting their contributions to society and sharing their stories.
- Promoting Civic Engagement: Leaders can encourage immigrants to participate in civic life by voting, volunteering, and joining community organizations.
By taking these steps, leaders can help to create a more just and equitable society for all residents, regardless of their immigration status.
20. What are the Long-Term Social and Economic Consequences of Nativism?
Nativism can have significant long-term social and economic consequences for societies, including reduced social cohesion, economic stagnation, and diminished cultural diversity. When nativist sentiments become entrenched in a society, they can create a climate of fear and mistrust that undermines social and economic progress.
Here are some potential long-term consequences of nativism:
- Reduced Social Cohesion: Nativism can lead to increased social division and conflict, as immigrant and native-born communities become more isolated from each other.
- Economic Stagnation: Nativism can stifle economic growth by discouraging immigration, reducing innovation, and limiting access to talent.
- Diminished Cultural Diversity: Nativism can lead to the homogenization of culture, as immigrant communities are pressured to assimilate and abandon their cultural traditions.
- Increased Discrimination: Nativism can create a climate of tolerance for discrimination against immigrants and other minority groups, leading to increased inequality and injustice.
- Political Instability: Nativism can destabilize political systems by fueling extremism, polarization, and anti-democratic movements.
Addressing the long-term consequences of nativism requires a sustained commitment to promoting inclusion, diversity, and social justice. It also requires a willingness to challenge prejudice and discrimination in all its forms.
Are you seeking expert insights on pressing issues? WHAT.EDU.VN provides free and reliable answers to your questions. Our team is ready to assist you. Reach out to us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or connect via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN now!
Navigating complex topics like nativism can be challenging. That’s why WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. We provide free, accessible information and expert answers to your questions. Explore our resources and discover a wealth of knowledge. Our services include simplifying complex topics, diverse educational content, and a user-friendly platform.
Ready to explore further? Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or WhatsApp us at +1 (206) 555-7890. Uncover the answers you’ve been searching for at what.edu.vn.