A personal area network (PAN) is a short-range network connecting devices around an individual, and understanding what it is can empower you to optimize your digital life. Need a quick answer and free advice? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we can help you with your concerns about network setup, wireless technology, and more. Learn about PANs, how they work, and their advantages in this comprehensive guide, along with information about wireless PAN (WPAN) and wired PAN setups.
1. What Is a Personal Area Network (PAN)?
A personal area network (PAN) is a network that connects devices within a short distance, typically a few meters, centered around an individual. It facilitates communication and resource sharing between devices in a small office or home office (SOHO) environment, either wirelessly or through wired connections.
A PAN typically includes devices such as laptops, smartphones, tablets, wearables, personal digital assistants (PDAs), printers, and entertainment devices. While PANs don’t directly connect to the internet, devices within a PAN are interconnected using wireless technologies like Bluetooth or wired technologies like USB.
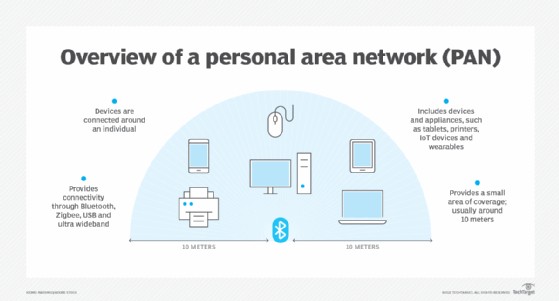 This image shows the items included in a personal area network.
This image shows the items included in a personal area network.
2. What Are the Key Characteristics of a Personal Area Network?
Here are some key characteristics:
- Short Range: PANs operate over a limited distance, usually within 10 meters.
- Personal Focus: They are centered around an individual and their devices.
- Device Interconnectivity: PANs enable seamless communication and data sharing between devices.
- Wireless or Wired: PANs can be implemented using wireless technologies (WPAN) or wired connections.
- Low Power Consumption: Wireless PANs often use low-power technologies like Bluetooth.
3. What Is a Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN)?
A wireless personal area network (WPAN) is a PAN that uses wireless technologies to connect devices. It is designed for a single person, SOHO, or small workgroup, characterized by limited distance, throughput, peripheral sharing, and low volume.
WPANs use low-powered, short-distance wireless technologies such as:
- Infrared Data Association (IrDA)
- Bluetooth
- Ultra-Wideband (UWB)
- Zigbee
- Wireless USB
Conceptually, a PAN differs from a wireless local area network (LAN) in that a PAN is centered around one person, while a LAN connects multiple users. A PAN also differs from a wide area network (WAN), which serves and connects multiple users over a larger geographical area.
4. What Is a Wired PAN?
While wireless communication is more common in PANs, a PAN can also be wired. Wired PANs use technologies such as USB, FireWire (IEEE-1394), or Thunderbolt hardware interfaces to connect devices within a user’s immediate vicinity.
Wired PANs provide a reliable option for connecting devices that are in close proximity to a user and their workspace, ensuring stable data transfer and secure connections.
5. What Are Common Examples and Use Cases of a Personal Area Network?
A PAN has several use cases and applications. Here are some common examples:
- Body Area Network (BAN): This type of mobile computer network moves with a person and is typically established when a person connects their smartphone and Bluetooth headphones. Communication takes place entirely within, on, and in the immediate proximity of a person. A medical sensor used in healthcare with wireless connections implanted in the human body to monitor vital signs is an example of a BAN.
- Wearable Technology: Wearable computer devices, including smart clothing, fitness trackers, and smartwatches with accelerometers, can monitor daily activities and exchange digital information. These devices often use the electrical conductivity of the human body as a data network.
- Offline Network (Home Network): Users can establish this type of network in their home offices. Multiple devices, including printers, TVs, game systems, laptops, and other home appliances, are integrated through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, forming a small, single-space network. The electronic devices in this network aren’t connected to the internet.
- Small Office/Home Office (SOHO): This type of network is set specifically for work purposes and is separate from other home networks. Using an internet connection, this virtual network is typically a small setup of connected devices that are used solely for office work and might incorporate a virtual private network (VPN).
- Infrared (IR) Devices: A PAN can also be established by using infrared communication for remote control of TVs and other home electronics.
- USB Connections: USB ports can be used to connect various devices to a computer, such as printers, webcams, or external hard drives. USB connections are also used to charge smartphones and tablets.
6. What Is the Difference Between a PAN and a LAN?
PANs and LANs differ primarily in their scope and purpose. A PAN connects devices within the short range of a person, whereas a LAN connects devices at a single site, typically an office building. Similar to a PAN, a LAN can be both wired and wireless.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between PANs and LANs:
| Feature | Personal Area Network (PAN) | Local Area Network (LAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Short range, around a person | Single site, typically an office building |
| User Focus | Single user | Multiple users |
| Data Rate | Low to medium | High |
| Connectivity | Wireless or wired | Wireless or wired |
| Common Use Cases | Wearables, Bluetooth devices, SOHO | Offices, schools, homes |
7. What Are the Advantages of Using a Personal Area Network?
Using a PAN offers several benefits:
- No Wires Required: Connecting devices in a PAN only requires Bluetooth or other wireless technologies to be enabled, eliminating the need for extra wires. This reduces the need for cable management and wasted floor space, making it a cost-effective network.
- Reliable and Secure: A PAN network ensures a reliable and stable connection if it’s established within the specified range. The limited transmission range provides a high level of security due to the short network range.
- Easy Data Synchronization: A PAN provides easy data synchronization between different devices. All devices connected within a PAN can be used to exchange, download, and upload data with each other.
- Portability: A PAN provides extreme portability, as it’s typically wireless, and users can transport devices and exchange data wherever they want.
- Lower Power Consumption: Low-power wireless PANs that are carried over technologies including Bluetooth, wireless USB, or Zigbee are ideal for portable devices due to their minimal energy usage and low data transmission costs.
8. What Are the Disadvantages of Using a Personal Area Network?
Despite its advantages, a PAN also has some limitations:
- Short Network Range and Slow Data Transfer: A PAN often uses Bluetooth communication that doesn’t span beyond a limited range, making long-distance data sharing difficult and slowing down the rate of data transfers.
- No Broadcasting Option: A key drawback of PANs is their inability to simultaneously broadcast messages to all connected devices. This limitation renders them impractical for large-scale applications with many devices or long-range connections.
- Signal Interference: The Bluetooth and IrDA rays used for transmission in a PAN can cause interference with radio signals, which can severely interrupt and degrade the quality of communication between devices.
- Cost: Using a PAN can be expensive, as most built-in WPAN devices are costly. Also, most devices used for creating a PAN have a higher price tag, such as smartphones and laptops.
- Line of Sight Propagation: PANs operating on IrDA technology require a direct line of sight between devices. Unlike radio-based communications, IrDA devices must be aligned to work, limiting their flexibility.
- Less Reliable: PANs can be less reliable than wired networks, especially when managing multiple connections or clusters of devices.
9. How Does a Personal Area Network Work?
A personal area network works by establishing a connection between devices within a short range, typically around an individual. This connection can be achieved through wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Zigbee, or infrared, or through wired connections like USB or FireWire.
Here’s a breakdown of how a PAN works:
- Device Discovery: The devices in the PAN use a specific protocol to discover each other. For example, Bluetooth devices use a discovery process to find other Bluetooth-enabled devices in the vicinity.
- Connection Establishment: Once the devices are discovered, they establish a connection. This usually involves a pairing process, where the devices authenticate each other to ensure a secure link.
- Data Transmission: After the connection is established, devices can transmit data between each other. The data is transmitted using the protocol supported by the PAN technology, such as Bluetooth for wireless PANs or USB for wired PANs.
- Resource Sharing: The devices can share resources like internet connections, files, printers, and other peripherals. This sharing enhances productivity and convenience for the user.
- Network Management: The PAN is managed by the devices themselves, with each device having the ability to join or leave the network. This decentralized management makes the PAN flexible and easy to use.
10. What Technologies Are Commonly Used in Personal Area Networks?
Several technologies are commonly used in personal area networks, each with its own advantages and use cases:
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth is one of the most popular technologies for WPANs. It provides short-range wireless communication between devices, such as smartphones, headphones, keyboards, and mice. Bluetooth is known for its low power consumption and ease of use.
- Zigbee: Zigbee is a low-power, low-data-rate wireless technology often used in IoT devices and home automation systems. It is suitable for applications that require long battery life and can support a large number of devices in a network.
- Infrared (IrDA): Infrared technology uses infrared light to transmit data between devices. It requires a direct line of sight between the devices and is commonly used in remote controls for TVs and other home electronics.
- Ultra-Wideband (UWB): UWB is a wireless technology that uses a wide range of radio frequencies to transmit data over short distances. It is known for its high bandwidth and low power consumption, making it suitable for applications like location tracking and secure communication.
- Wireless USB: Wireless USB is a wireless communication protocol that allows devices to connect to a computer without the need for USB cables. It provides a convenient way to connect peripherals like printers, scanners, and external hard drives.
- NearLink: NearLink is a short-range wireless communication technology that offers high data transmission rates and low latency. It is often used in applications that require real-time data transfer, such as augmented reality and virtual reality.
- USB (Wired): USB is a wired connection standard that allows devices to connect to a computer or other devices for data transfer and power charging. It is widely used in PANs for connecting peripherals like printers, webcams, and external storage devices.
- FireWire (IEEE 1394) (Wired): FireWire is a high-speed wired connection standard that is commonly used for connecting digital video cameras and external hard drives to a computer. It provides a reliable and fast data transfer rate.
- Thunderbolt (Wired): Thunderbolt is a high-speed wired connection standard that combines PCI Express and DisplayPort into a single interface. It is often used for connecting high-performance devices like external GPUs and storage arrays to a computer.
Here’s a table summarizing these technologies:
| Technology | Type | Range | Data Rate | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth | Wireless | Up to 100m | Up to 3 Mbps | Headphones, keyboards, mice, smartphones |
| Zigbee | Wireless | Up to 100m | Up to 250 Kbps | IoT devices, home automation |
| Infrared (IrDA) | Wireless | Up to 1m | Up to 4 Mbps | Remote controls |
| Ultra-Wideband | Wireless | Up to 10m | Up to 480 Mbps | Location tracking, secure communication |
| Wireless USB | Wireless | Up to 10m | Up to 480 Mbps | Printers, scanners, external hard drives |
| NearLink | Wireless | Short range | High | Augmented reality, virtual reality |
| USB | Wired | Cable length | Up to 40 Gbps | Printers, webcams, external storage |
| FireWire | Wired | Cable length | Up to 800 Mbps | Digital video cameras, external hard drives |
| Thunderbolt | Wired | Cable length | Up to 40 Gbps | External GPUs, storage arrays |
11. What Security Measures Should Be Taken When Using a Personal Area Network?
When using a personal area network, it’s crucial to implement security measures to protect your devices and data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Here are some key security measures to consider:
- Enable Bluetooth Security Features: Bluetooth devices have security features like pairing and encryption that should be enabled to prevent unauthorized access. Always set a strong PIN or passphrase for pairing devices.
- Use Strong Passwords: Protect your devices with strong, unique passwords. Avoid using default passwords, and regularly update them to maintain security.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that your devices have the latest software updates and security patches. These updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Use a Firewall: Enable a firewall on your devices to monitor and control network traffic. A firewall can help prevent unauthorized access to your PAN and protect against malware and other cyber threats.
- Be Cautious of Public Wi-Fi: Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks to connect your PAN devices, as these networks are often unsecured and can be vulnerable to eavesdropping and hacking.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable any unnecessary services or features on your devices that could create security vulnerabilities. For example, if you’re not using Bluetooth, turn it off to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install and regularly update antivirus software on your devices to protect against malware and other malicious software.
- Monitor Network Activity: Keep an eye on your network activity for any signs of suspicious behavior. If you notice anything unusual, investigate it immediately and take steps to mitigate any potential threats.
- Secure IoT Devices: If your PAN includes IoT devices like smart home appliances, make sure to secure them with strong passwords and keep their firmware updated. IoT devices can be vulnerable to hacking if they’re not properly secured.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Consider segmenting your PAN into different zones to isolate sensitive devices and data. This can help prevent attackers from gaining access to your entire network if one device is compromised.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices for protecting your PAN. Educate yourself and others about the risks and how to mitigate them.
By implementing these security measures, you can help protect your personal area network and keep your devices and data safe from cyber threats.
12. How Can a Personal Area Network Be Used in Healthcare?
Personal area networks (PANs) have significant applications in healthcare, improving patient care, remote monitoring, and overall efficiency. Here are some ways PANs are used in healthcare:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: PANs enable remote patient monitoring by connecting wearable sensors and medical devices to a central system. These devices can track vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, and transmit the data to healthcare providers in real-time. This allows for early detection of health issues and timely intervention.
- Medication Adherence: PANs can be used to improve medication adherence by reminding patients to take their medications and tracking their compliance. Smart pill bottles and wearable devices can send reminders to patients and record when medications are taken, helping healthcare providers monitor and manage medication adherence.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: PANs can support rehabilitation and physical therapy by providing real-time feedback on patient movements and progress. Wearable sensors can track joint angles, muscle activity, and other biomechanical data, allowing therapists to monitor patient performance and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Fall Detection: PANs can be used to detect falls in elderly or disabled patients. Wearable sensors can detect sudden movements and impacts, triggering an alert to caregivers or emergency services. This can help reduce the risk of serious injury and improve patient safety.
- Chronic Disease Management: PANs can help patients manage chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and asthma by providing tools for self-monitoring and education. Wearable devices can track activity levels, diet, and other health metrics, while mobile apps can provide personalized feedback and support.
- Hospital Patient Monitoring: PANs can be used to monitor patients in hospitals, providing real-time data on their vital signs and activity levels. This can help healthcare providers detect early signs of deterioration and respond quickly to emergencies.
- Mental Health Support: PANs can provide mental health support by connecting patients to therapists and counselors remotely. Wearable devices can track mood, sleep patterns, and other indicators of mental health, while mobile apps can provide access to therapy sessions and support groups.
By leveraging PAN technology, healthcare providers can deliver more personalized, proactive, and efficient care, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
13. How Do Personal Area Networks Contribute to the Internet of Things (IoT)?
Personal area networks (PANs) play a crucial role in the Internet of Things (IoT) by providing connectivity for devices within an individual’s immediate vicinity. PANs enable various IoT applications, connecting sensors, wearables, and other smart devices to facilitate data exchange and automation.
Here’s how PANs contribute to the IoT:
- Connectivity for Wearable Devices: PANs are essential for connecting wearable devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smart clothing to smartphones or other central hubs. These wearables collect data on health, activity levels, and environmental conditions, which is then transmitted via PANs to be analyzed and used for various applications.
- Home Automation: PANs enable home automation by connecting smart home devices such as smart lights, thermostats, and security systems. These devices communicate with each other via PANs to automate tasks, optimize energy consumption, and enhance security.
- Healthcare Monitoring: PANs facilitate remote healthcare monitoring by connecting medical sensors and devices to healthcare providers. Wearable sensors can track vital signs, monitor medication adherence, and detect falls, transmitting the data via PANs to enable timely intervention and improve patient outcomes.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): PANs are used in industrial settings to connect sensors and devices for monitoring equipment performance, tracking inventory, and optimizing processes. These devices communicate via PANs to enable real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance.
- Retail Applications: PANs are used in retail environments to connect devices for tracking inventory, monitoring customer behavior, and providing personalized shopping experiences. Sensors and beacons communicate with smartphones via PANs to deliver targeted promotions and enhance customer engagement.
- Smart Agriculture: PANs are used in agriculture to connect sensors and devices for monitoring soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. These devices transmit data via PANs to enable precision farming, optimize irrigation, and improve crop yields.
By providing connectivity for a wide range of devices, PANs enable the IoT to reach its full potential, transforming industries and improving people’s lives.
14. What Are Some Emerging Trends in Personal Area Network Technology?
Personal area network (PAN) technology is constantly evolving, with several emerging trends shaping its future:
- Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Technology: UWB is gaining traction as a PAN technology due to its high bandwidth, low power consumption, and precise location tracking capabilities. UWB is being used in applications like indoor navigation, secure access control, and contactless payments.
- 5G Connectivity: The integration of 5G technology with PANs is enabling faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and improved reliability. This is opening up new possibilities for applications like augmented reality, virtual reality, and real-time remote monitoring.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI is being integrated into PANs to enable intelligent device management, personalized user experiences, and proactive security. AI algorithms can analyze data from PAN devices to optimize performance, predict maintenance needs, and detect security threats.
- Energy Harvesting: Energy harvesting technologies are being developed to power PAN devices, reducing the need for batteries and extending their lifespan. Energy harvesting can be achieved through solar, thermal, or kinetic energy, making PAN devices more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is being used in PANs to process data locally on devices, reducing the need to transmit data to the cloud. This improves latency, enhances security, and enables offline operation.
- Wearable Medical Devices: The market for wearable medical devices is growing rapidly, driven by the increasing demand for remote patient monitoring and chronic disease management. These devices use PANs to transmit data to healthcare providers, enabling timely intervention and improving patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Security: Security is becoming an increasingly important consideration in PAN design, with new technologies being developed to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. These technologies include advanced encryption, biometric authentication, and intrusion detection systems.
- Seamless Device Integration: Efforts are being made to improve the interoperability and seamless integration of devices in PANs. This includes the development of standardized protocols and APIs that allow devices from different manufacturers to communicate and work together more effectively.
These emerging trends are driving innovation in PAN technology, enabling new applications and improving the performance, security, and sustainability of PAN devices.
15. How Can I Troubleshoot Common Issues with My Personal Area Network?
Troubleshooting a personal area network (PAN) involves identifying and resolving common issues that can disrupt connectivity or performance. Here are some steps to troubleshoot common PAN issues:
- Check Device Compatibility: Ensure that all devices in your PAN are compatible with each other and support the same communication protocols. Refer to the device documentation for compatibility information.
- Verify Bluetooth Settings: If you’re using Bluetooth, make sure that Bluetooth is enabled on all devices and that they are discoverable. Check the Bluetooth settings on each device to ensure that they are properly configured.
- Pair Devices Correctly: Follow the correct pairing procedure for each device. This usually involves putting the device into pairing mode and entering a PIN or passphrase. If you’re having trouble pairing devices, try restarting them and repeating the pairing process.
- Check for Interference: Wireless signals can be affected by interference from other devices, such as microwave ovens, cordless phones, and Wi-Fi routers. Try moving your devices away from potential sources of interference or changing the wireless channel on your router.
- Update Device Drivers: Ensure that your devices have the latest drivers installed. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues and performance problems. Visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest drivers for your devices.
- Check Battery Levels: Low battery levels can affect the performance of wireless devices. Make sure that all devices have sufficient battery power or are connected to a power source.
- Restart Devices: Sometimes, simply restarting your devices can resolve connectivity issues. Try turning off all devices in your PAN, waiting a few seconds, and then turning them back on.
- Reset Network Settings: If you’re still having trouble, try resetting the network settings on your devices. This will restore the devices to their default network configuration and may resolve any software-related issues.
- Test with Different Devices: To isolate the problem, try connecting different devices to your PAN and see if the issue persists. This can help you determine whether the problem is with a specific device or with the network itself.
- Consult Documentation: Refer to the documentation for your devices for troubleshooting tips and solutions to common problems. The documentation may also provide information on how to contact technical support for further assistance.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and resolve common issues with your personal area network and ensure that your devices are working properly.
Do you have any questions about What Is Personal Area Network? Need quick and free answers? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN now and get the information you need!
Unlock Answers for Free at WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you struggling to find quick, reliable answers to your questions? Do you need expert advice without the hefty price tag? Look no further than WHAT.EDU.VN! We provide a free platform where you can ask any question and receive prompt, accurate responses from knowledgeable individuals.
Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free to Use: Ask as many questions as you like without spending a dime.
- Fast Responses: Get answers quickly so you can move forward with your day.
- Expert Knowledge: Connect with a community of experts ready to share their insights.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is simple and intuitive, making it easy to ask and find answers.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Join the WHAT.EDU.VN community today and start getting the answers you deserve!
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn
Get your free answers now!
