What is ringworm exactly, and how can you protect yourself and your loved ones from it? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide the answers you need to understand this common fungal infection, offering solutions to your health concerns. Knowing the causes and preventive measures is crucial, so let’s dive into comprehensive information to ensure you stay informed. We’ll cover fungal infections, dermatophytes, and tinea corporis to give you a complete understanding.
1. Understanding Ringworm: The Basics
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by worms but by fungi. These fungi, scientifically known as Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton, are the primary culprits. Understanding these fungi is the first step in preventing and treating ringworm effectively.
- What causes ringworm? Ringworm is caused by fungal pathogens, not worms.
- Common fungi: The most common types include Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton.
- Nail infections: Fungi can enter under the nail through small cracks, leading to fungal nail infections.
2. How Ringworm Spreads: Transmission Methods
Ringworm is highly contagious and can spread through several ways. Knowing these methods can help you take the necessary precautions to protect yourself and others.
- Skin-to-skin contact: Direct contact with infected individuals or animals.
- Shared objects: Transmission via contaminated towels, bed sheets, and clothing.
- Shared surfaces: Contact with infected surfaces like locker room floors and public showers.
3. Activities That Increase Ringworm Risk
Certain activities can heighten your risk of contracting ringworm. Being aware of these risk factors allows you to make informed decisions and take preventive measures.
- Public showers and locker rooms: Walking barefoot in these areas.
- Contact sports: Participating in sports like wrestling where skin-to-skin contact is common.
- Tight clothing: Wearing tight shoes and socks that trap moisture.
- Excessive sweating: Creating a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Animal contact: Close contact with animals that carry the infection.
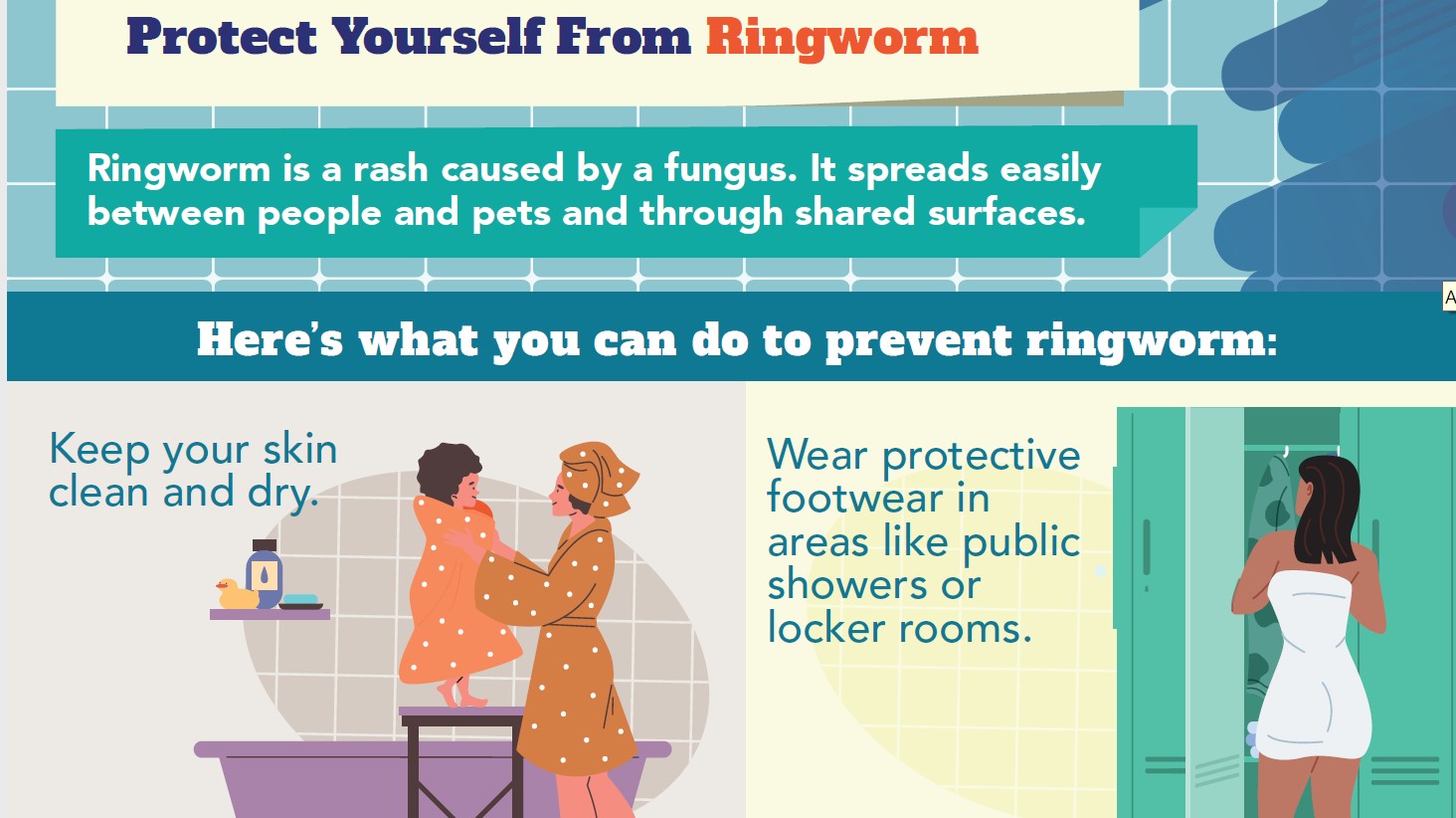
4. Effective Prevention Methods: Keeping Ringworm at Bay
Preventing ringworm involves simple yet effective practices. Incorporate these methods into your daily routine to minimize your risk.
- Keep skin clean and dry: Regularly wash and thoroughly dry your skin.
- Breathable footwear: Wear shoes that allow air to circulate, especially around your feet.
- Protective footwear: Use sandals or shoes in public showers and locker rooms.
- Nail hygiene: Keep fingernails and toenails short and clean.
- Daily changes: Change socks and underwear at least once a day.
- Avoid sharing: Do not share clothing, towels, sheets, or personal items.
5. Ringworm Prevention for Athletes: Staying Safe on the Field
Athletes are at a higher risk of ringworm due to close contact and shared facilities. Specific measures can help prevent outbreaks in sports environments.
- Post-activity showers: Shower immediately after practices, matches, or games.
- Clean sports gear: Regularly clean and disinfect sports equipment.
- No sharing: Avoid sharing sports gear like helmets with other players.
- Locker room footwear: Wear shoes or sandals in locker rooms and public showers.
6. Managing Ringworm Outbreaks in Schools and Daycare Centers
Ringworm can spread rapidly in environments like schools and daycare centers. Early detection and preventive measures are crucial.
- Pediatrician consultation: Consult a pediatrician if your child shows ringworm symptoms.
- Inform authorities: Notify the school or teacher to help prevent further spread.
- Avoid sharing items: Teach children not to share personal items like clothing and hairbrushes.
- Attendance guidelines: Check with the school about attendance and participation in activities.
- Local health department: Contact your local health department for additional information and guidance.
7. Disinfectants: Killing Fungal Spores Effectively
Using the right disinfectants can help kill fungal spores and prevent the spread of ringworm.
- Common disinfectants: Use diluted chlorine bleach (1/4 cup per gallon of water), benzalkonium chloride, or strong detergents.
- Safe mixing: Never mix different cleaning products, as this can create harmful gases.
- Application: Apply disinfectants to surfaces and items that may be contaminated.
8. Risk Factors: Who Is More Susceptible to Ringworm?
While anyone can get ringworm, certain individuals are more susceptible due to weakened immune systems or other health conditions.
- Weakened immune systems: People with compromised immune systems are at higher risk.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to fungal nail infections.
- Travelers: Those traveling to regions with resistant forms of ringworm are at increased risk.
9. Understanding Resistant Forms of Ringworm
Some severe forms of ringworm are resistant to common antifungal medications, posing a greater challenge for treatment.
- Global spread: These resistant forms are becoming more widespread in certain parts of the world.
- Ineffective treatments: Standard antifungal medications may not be effective against these strains.
- Travel precautions: Travelers should be aware of the risk and take extra precautions.
10. Ringworm and Pets: Protecting Your Furry Friends
Ringworm can affect pets, making it essential to take preventive measures to protect both your animals and yourself.
- Veterinary care: Take your pet to the vet immediately if you suspect they have ringworm.
- Protective gear: Wear gloves and long sleeves when handling infected pets.
- Hand hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly after contact with your pet.
- Home hygiene: Vacuum and disinfect areas your pet frequents.
- Multiple pets: Check all pets in the household if one is infected.
11. Special Precautions for Those with Weakened Immune Systems
If you have a weakened immune system, extra precautions are necessary when dealing with animals to avoid contracting ringworm.
- Avoid contact: Do not handle animals with ringworm if you have a compromised immune system.
- High-risk conditions: This includes individuals with advanced HIV, those undergoing cancer treatment, or taking immunosuppressant medications.
- Healthy practices: Follow strict hygiene practices when visiting petting zoos or animal exhibits.
12. Ringworm Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
Knowing the symptoms of ringworm can help you identify and treat the infection early, preventing further spread. Look out for these key indicators:
- Circular rash: A ring-shaped rash that is often red, itchy, and raised.
- Scaly skin: Patches of skin that appear scaly or crusty.
- Hair loss: In cases affecting the scalp, hair loss in circular patterns.
- Nail changes: Thickening, discoloration, or brittleness of nails.
13. Ringworm Treatment Options: What Works Best?
Several treatment options are available for ringworm, depending on the severity and location of the infection.
- Topical antifungal creams: Over-the-counter creams like clotrimazole or terbinafine.
- Prescription medications: Stronger antifungal creams or oral medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Home remedies: Natural remedies like tea tree oil, though scientific evidence may vary.
- Hygiene practices: Maintaining good hygiene to prevent recurrence.
14. How Long Does Ringworm Last? Understanding the Timeline
The duration of a ringworm infection can vary, depending on the treatment and individual factors.
- Topical treatments: Mild cases may clear up in 2-4 weeks with consistent use of topical creams.
- Oral medications: More severe cases requiring oral medications may take several weeks to months to resolve.
- Recurrence: Ringworm can recur if proper hygiene and prevention measures are not followed.
15. Ringworm vs. Other Skin Conditions: Accurate Diagnosis
Ringworm can sometimes be confused with other skin conditions. Knowing the differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Eczema: Often causes widespread, inflamed skin that may not have the distinct ring shape.
- Psoriasis: Typically presents with thick, scaly patches that are not necessarily circular.
- Other fungal infections: Differentiating between different types of fungal infections requires professional diagnosis.
16. Living with Ringworm: Practical Tips for Comfort
Living with ringworm can be uncomfortable, but these practical tips can help manage symptoms and prevent spread.
- Keep the area clean and dry: Regularly wash and dry the affected area.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching can worsen the infection and spread it to other areas.
- Wear loose clothing: Opt for loose-fitting clothing to reduce irritation.
- Isolate personal items: Keep towels, clothing, and bedding separate to prevent transmission.
17. Ringworm in Children: Special Considerations
Ringworm is common in children, particularly in school and daycare settings. Specific considerations are necessary to manage and prevent its spread.
- Early detection: Regularly check children for signs of ringworm.
- School policies: Be aware of school policies regarding attendance and treatment.
- Communication: Maintain open communication with teachers and caregivers.
- Preventive education: Teach children about the importance of hygiene and avoiding shared items.
18. What to Do If You Suspect Ringworm: First Steps
If you suspect you or someone you know has ringworm, taking prompt action is essential.
- Consult a healthcare provider: Seek professional diagnosis and treatment.
- Isolate affected items: Avoid sharing personal items to prevent spread.
- Follow treatment plan: Adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen.
- Maintain hygiene: Practice good hygiene to prevent recurrence.
19. Debunking Ringworm Myths: Facts vs. Fiction
Several misconceptions surround ringworm. Let’s debunk some common myths to ensure accurate understanding.
- Myth: Ringworm is caused by worms. Fact: Ringworm is caused by fungi.
- Myth: Ringworm is a sign of poor hygiene. Fact: Anyone can get ringworm, regardless of hygiene practices.
- Myth: Ringworm will go away on its own. Fact: Ringworm typically requires treatment to clear up.
20. Natural Remedies for Ringworm: Are They Effective?
Some natural remedies are touted as effective treatments for ringworm. However, it’s crucial to approach them with caution.
- Tea tree oil: Known for its antifungal properties, but effectiveness varies.
- Apple cider vinegar: May help balance skin pH, but lacks strong scientific evidence.
- Garlic: Contains compounds with antifungal effects, but can cause skin irritation.
- Consultation: Always consult a healthcare provider before trying natural remedies.
21. Long-Term Effects of Untreated Ringworm: Potential Complications
Leaving ringworm untreated can lead to several complications and long-term effects.
- Spread of infection: The infection can spread to other parts of the body or to other people.
- Secondary infections: Open sores can become infected with bacteria.
- Scarring: Severe cases can lead to scarring or permanent skin damage.
- Nail deformities: Fungal nail infections can cause permanent nail deformities.
22. The Role of Diet in Preventing Ringworm: Nutritional Support
While diet alone cannot prevent or cure ringworm, certain nutrients can support overall skin health and immune function.
- Vitamin D: Supports immune function and skin health.
- Probiotics: Promote a healthy gut microbiome, which can support immune function.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Reduce inflammation and support skin health.
- Balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
23. Environmental Factors and Ringworm: Controlling Your Surroundings
Environmental factors can play a significant role in the spread of ringworm. Controlling your surroundings can help minimize risk.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in damp areas like bathrooms and locker rooms.
- Regular cleaning: Clean and disinfect surfaces regularly, especially in shared spaces.
- Dry environment: Keep skin and clothing dry to prevent fungal growth.
- Avoid overcrowding: Reduce overcrowding in living and recreational spaces.
24. Emerging Research on Ringworm: What’s New?
Ongoing research continues to explore new ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat ringworm.
- New antifungal medications: Researchers are developing new antifungal drugs to combat resistant strains.
- Diagnostic tools: Advanced diagnostic tools can help identify fungal species more accurately.
- Preventive strategies: Studies are exploring new preventive strategies to reduce the spread of ringworm.
- Vaccine development: Some research focuses on developing vaccines to prevent fungal infections.
25. Ringworm and Mental Health: Addressing the Psychological Impact
Living with ringworm can have psychological effects, especially if the infection is visible or persistent.
- Self-esteem: Visible skin conditions can affect self-esteem and body image.
- Social isolation: Concerns about spreading the infection can lead to social isolation.
- Stress and anxiety: Dealing with a persistent infection can cause stress and anxiety.
- Support networks: Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can help.
26. Traveling and Ringworm: Staying Safe on the Go
Traveling can increase your risk of contracting ringworm, especially in regions with different hygiene standards or resistant fungal strains.
- Hygiene practices: Maintain strict hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing and showering.
- Protective clothing: Wear protective clothing in public areas like showers and locker rooms.
- Footwear: Use sandals or shoes in shared bathing facilities.
- Avoid sharing: Avoid sharing personal items like towels and clothing.
27. Seasonal Variations in Ringworm Infections: When Are You Most at Risk?
Ringworm infections can vary with the seasons, depending on environmental conditions and lifestyle factors.
- Summer: Hot, humid weather can create a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Winter: Indoor activities and close contact can increase transmission in winter months.
- Sports seasons: Increased participation in sports can lead to higher infection rates during certain seasons.
- Preventive measures: Adjust preventive measures based on seasonal risks.
28. The Economic Burden of Ringworm: Costs and Consequences
Ringworm infections can have economic consequences, including the cost of treatment, lost productivity, and other related expenses.
- Treatment costs: Expenses for medications, doctor visits, and diagnostic tests.
- Lost productivity: Time off work or school due to infection.
- Public health costs: Costs associated with managing outbreaks and implementing preventive measures.
- Preventive investments: Investing in preventive measures can reduce the long-term economic burden.
29. The Future of Ringworm Management: Innovations and Strategies
The future of ringworm management involves ongoing research, innovative strategies, and a focus on prevention.
- Precision medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual factors and fungal species.
- Public health campaigns: Educating the public about ringworm prevention and management.
- Integrated approaches: Combining medical treatments with preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments.
- Global collaboration: Collaborating internationally to address resistant strains and emerging threats.
30. Ringworm and the Elderly: Special Considerations
Elderly individuals may face unique challenges when dealing with ringworm infections due to age-related factors and potential comorbidities.
- Compromised immune function: Aging can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible.
- Skin fragility: Elderly skin may be more prone to injury and infection.
- Medication interactions: Potential interactions between antifungal medications and other drugs.
- Assisted living facilities: Increased risk of transmission in shared living environments.
Understanding “what is ringworm” is the first step in effective prevention and management. By knowing the causes, transmission methods, and preventive measures, you can protect yourself and your community. For more information and personalized advice, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. Do you have more questions or need further assistance? Our team at WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide you with free answers. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Don’t hesitate—ask your questions today and get the answers you need! Visit our website at what.edu.vn for more details. Let us help you navigate your health concerns with expert guidance and support.