What Is Satin fabric? Satin is a luxurious textile celebrated for its smooth, glossy surface and elegant drape, often associated with high-end fashion and home decor. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we unravel the mysteries of this captivating material, from its origins to its diverse applications. Discover the secrets of satin weaves, materials, and the best ways to care for this exquisite fabric.
1. Decoding Satin: More Than Just a Material
Satin isn’t a raw material, such as cotton or wool; it’s a type of weave. Think of it like this: satin is to fabric what a recipe is to a cake. You can’t make satin without specific raw materials, but simply having those materials doesn’t automatically result in satin.
1.1. The Satin Weave Explained
The satin weave is characterized by floating yarns. These floats are warp yarns (running lengthwise) that pass over multiple weft yarns (running widthwise) before being tied down. This creates a minimal number of interlacings, resulting in a smooth surface with a high luster.
1.2. Satin vs. Sateen: What’s the Difference?
While both are known for their sheen, satin and sateen differ in their fiber content. Satin is woven with filament fibers like silk, nylon, rayon, or polyester. Sateen, on the other hand, is typically woven with spun fibers like cotton.
2. A Glimpse into Satin’s History
Satin’s story begins in China around 2,000 years ago in the port city of Quanzhou, known as Zaitun in Arabic—hence the name “satin.” For centuries, the secret of satin weaving remained within the East.
2.1. Satin’s Journey to the West
Satin production spread to Italy in the 12th century and, by the 14th century, became available throughout Europe. However, before the advent of synthetic fibers, satin was exclusively made from silk, making it a luxury affordable only to the wealthy and the church.
2.2. Satin: A Symbol of Status and Elegance
For centuries, satin was more than just a fabric; it was a statement of status and refined taste. Its lustrous beauty and luxurious feel made it a favorite among royalty and the elite.
3. Unveiling the Satin Weave
The satin weave is more intricate than simpler weaves, such as plain or twill weaves. It creates a fabric with long floats on the surface, which are responsible for its characteristic sheen.
3.1. The Technicalities of the Satin Weave
In technical terms, the intersections between the warp and weft yarns are more complex in a satin weave. This results in longer runs of yarn on the surface, which reflect light more effectively, creating the signature satin shimmer.
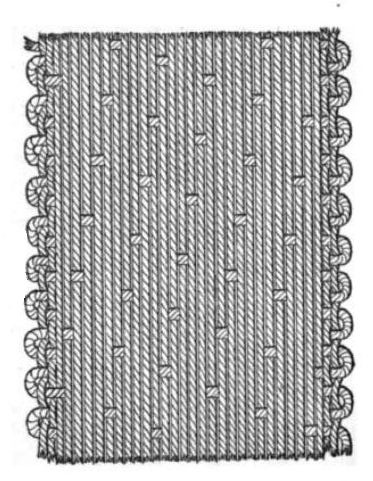 satin weave structure
satin weave structure
The Satin weave structure in silk is complex.
3.2. The Front and Back of Satin
While the front of satin boasts a lustrous, shimmering surface, the back is typically duller. This is a direct result of the weave structure, which concentrates the sheen on one side of the fabric.
4. Satin Materials: From Silk to Synthetics
Satin can be made from a variety of fibers, each contributing unique qualities to the final fabric.
4.1. Silk Satin: The Epitome of Luxury
Silk satin is considered the highest quality satin, known for its exceptional drape, luster, and soft feel. It’s often used in high-end apparel, lingerie, and bedding.
4.2. Synthetic Satins: Affordable Elegance
Nylon, rayon, and polyester are common synthetic fibers used to create satin. These satins offer a more affordable alternative to silk while still providing a beautiful sheen and drape.
4.3. Sateen: A Cotton Alternative
When a satin weave is applied to short-staple fibers like cotton, the resulting fabric is called sateen. Sateen offers a similar luster to satin but with the added comfort and breathability of cotton.
5. Exploring the Diverse Types of Satin
Satin comes in a wide array of types, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The harness refers to how the weft thread goes over and under the warp threads. A four harness satin weave goes over three warp threads and then under one. A five harness weave changes this pattern to four and one, and an eight harness satin weave goes over seven and under one.
5.1. Antique Satin
This heavy satin has a subtle luster and is often used for upholstery and draperies. Its durability and understated elegance make it a popular choice for home decor.
5.2. Baronet Satin
Made from rayon and cotton, baronet satin is a truly luxurious fabric. Its rich texture and sheen make it ideal for special occasion apparel and accessories.
5.3. Charmeuse Satin
Charmeuse is known for its high luster on one side and a duller finish on the other. This lightweight satin drapes beautifully, making it a favorite for dresses, blouses, and lingerie.
5.4. Crepe-Back Satin
This reversible fabric features a satin weave on one side and a crepe weave on the other. This versatility makes it a popular choice for garments that can be styled in multiple ways.
5.5. Duchess Satin
Commonly used in bridal wear, duchess satin is a heavy, stiff satin that holds its shape well. Its ability to be dyed in solid colors makes it a versatile choice for structured gowns and dresses.
5.6. Lucent Satin
Lucent satin is a double-faced sateen with a high-luster finish. Its slippery texture and shiny appearance make it suitable for clothing, bags, and fashion accessories.
5.7. Messaline Satin
This lightweight and soft satin is commonly used in dressmaking. Its delicate drape and subtle sheen make it ideal for flowing garments and linings.
5.8. Monroe Satin
Monroe satin is a medium-weight sateen-fronted weave often used for bags and accessories. Its durability and subtle luster make it a practical and stylish choice.
5.9. Panne Satin
Panne satin has a very high degree of luster, achieved by pressing the fabric with heated rollers. This creates a flattened pile effect, making it a popular choice for dressmaking and evening wear.
5.10. Slipper Satin
Slipper satin features a matte surface and a cotton reverse. Its lightweight and sturdy construction make it suitable for craftwork and accessories.
6. The Allure of Satin: Advantages and Benefits
Satin’s popularity stems from its unique combination of aesthetic appeal and practical properties.
6.1. Luxurious Look and Feel
Satin’s smooth, glossy surface exudes luxury and sophistication. It’s often chosen for garments and home decor items where a touch of elegance is desired.
6.2. Versatility in Design
As demonstrated by the diverse types of satin, this fabric is incredibly versatile. It can be used for everything from bridal gowns to upholstery, adapting to a wide range of design aesthetics.
6.3. Durability and Longevity
Despite its delicate appearance, satin can be surprisingly durable, especially thicker varieties. The tight weave of the fabric contributes to its strength and resistance to wear and tear.
6.4. Wrinkle Resistance
Satin’s inherent wrinkle resistance makes it a practical choice for travel and everyday wear. Garments made from satin tend to maintain their smooth appearance even after prolonged use.
6.5. Printable Surface
Satin’s smooth surface is ideal for printing vibrant colors and intricate designs. This makes it a popular choice for custom fabrics, scarves, and other printed textiles.
7. Addressing the Challenges: Disadvantages of Satin
While satin offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges.
7.1. Sewing Difficulties
Satin’s slippery texture can make it challenging to sew, especially for beginners. The fabric tends to shift and slide, requiring extra care and precision.
7.2. Snagging Potential
Due to the long floats in the satin weave, the fabric is prone to snagging. Care must be taken to avoid sharp objects and rough surfaces that could damage the delicate threads.
8. Caring for Your Satin: Maintenance Tips
Proper care is essential to maintain the beauty and longevity of satin fabrics.
8.1. Washing Guidelines
Synthetic satins and cotton sateens can typically be washed at home on a delicate cycle with cold water. However, silk satins should always be dry cleaned to prevent damage.
8.2. Drying Techniques
After washing (if applicable), satin garments should be laid flat on a clean towel to air dry. Avoid squeezing, hanging, or tumble drying, as these methods can distort the fabric’s shape.
9. Frequently Asked Questions About Satin
Still curious about satin? Here are some frequently asked questions to further enhance your understanding:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary use of satin? | Satin is widely used in clothing (especially evening wear, lingerie, and linings), bedding, upholstery, and accessories due to its smooth texture and lustrous appearance. |
| Is satin a good fabric for summer? | Satin can be comfortable in summer, especially lightweight varieties like charmeuse. However, it may not be as breathable as cotton or linen. |
| How can I tell if a fabric is real satin? | Look for a smooth, glossy surface with a characteristic sheen. The back of the fabric will typically be duller than the front. |
| Does satin shrink when washed? | Silk satin is prone to shrinking, while synthetic satins are generally more resistant to shrinkage. Always follow the care instructions on the garment label. |
| Can I iron satin? | Yes, but use a low heat setting and iron on the reverse side of the fabric. A pressing cloth can also help protect the delicate surface. |
| Is satin environmentally friendly? | The environmental impact of satin depends on the fiber used. Silk production can have environmental concerns, while recycled synthetic satins offer a more sustainable option. |
| What is the cost of satin compared to other fabrics? | Satin is generally more expensive than common fabrics like cotton or polyester, especially if it’s made from silk. Synthetic satins are more affordable. |
| Is satin suitable for people with sensitive skin? | Silk satin is often a good choice for sensitive skin due to its smooth texture and hypoallergenic properties. However, some synthetic satins may cause irritation. |
| How does satin compare to velvet? | Both satin and velvet are luxurious fabrics, but they have different textures. Satin is smooth and glossy, while velvet has a soft, plush pile. |
| What are some modern applications of satin? | Beyond traditional uses, satin is now found in athletic wear, tech accessories, and even sustainable fashion, showcasing its versatility and adaptability. |
10. Unleash Your Curiosity with WHAT.EDU.VN
Do you have burning questions about fabrics, fashion, or anything else under the sun? Don’t hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN! Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with accurate, informative, and engaging answers to all your queries.
Are you struggling to find reliable information online? Do you need help understanding complex topics? WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help! We offer a free question-and-answer platform where you can get the answers you need quickly and easily.
Here’s how WHAT.EDU.VN can help you:
- Ask any question: No matter how big or small, we’re here to answer it.
- Get fast answers: Our team of experts works hard to provide you with timely and accurate information.
- Learn from a community: Connect with other curious minds and share your knowledge.
- It’s completely free: No hidden fees or subscriptions required.
Ready to get started?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your first question! We’re confident that you’ll find our platform to be a valuable resource for all your information needs.
Contact Us:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Join the what.edu.vn community and unlock a world of knowledge!