Navigating the complexities of the U.S. House of Representatives can be challenging, but WHAT.EDU.VN is here to offer clarity and simplify your understanding. Grasp the composition, dynamics, and pivotal role of the House in American governance for free. Explore insights into legislative counts and congressional representation, and gain a more profound appreciation of American governance through WHAT.EDU.VN today.
1. Understanding the House of Representatives: An Overview
The House of Representatives, often referred to as the House, is one of the two chambers of the United States Congress, the other being the Senate. Together, they form the legislative branch of the U.S. federal government. The House plays a crucial role in the lawmaking process, representing the interests of citizens across the nation. The structure and function of the House are defined by the Constitution, which establishes its composition, powers, and responsibilities. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for anyone seeking to engage with or analyze American politics.
2. What Is the Composition of the House of Representatives?
The House of Representatives comprises 435 members, each representing a specific congressional district within a state. The number of representatives allocated to each state is based on its population, as determined by the decennial census. This ensures that states with larger populations have greater representation in the House. In addition to the 435 voting members, there are also non-voting members representing the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and other U.S. territories.
3. How Is the Number of Representatives per State Determined?
The apportionment of representatives among the states is based on population, but the process is not as simple as directly assigning representatives based on raw population numbers. Instead, a method called “equal proportions” is used to ensure that each state has fair representation. This method takes into account the principle of one person, one vote, while also recognizing the historical and political realities of the American system.
4. What Role Does the Census Play in Determining Representation?
The census, conducted every ten years, is a comprehensive count of the U.S. population. The data collected by the census is used to determine the number of representatives each state will have for the next decade. Changes in population can lead to shifts in representation, with some states gaining seats while others lose them. This process of reapportionment is a critical aspect of maintaining fair and equitable representation in the House.
5. How Often Does Reapportionment Occur?
Reapportionment occurs every ten years, following the completion of the decennial census. The new apportionment plan takes effect with the next congressional election. States that have experienced significant population growth are likely to gain seats, while those with declining or stagnant populations may lose seats. This can have significant implications for the political landscape, as it can shift the balance of power between states and regions.
6. What Are Congressional Districts?
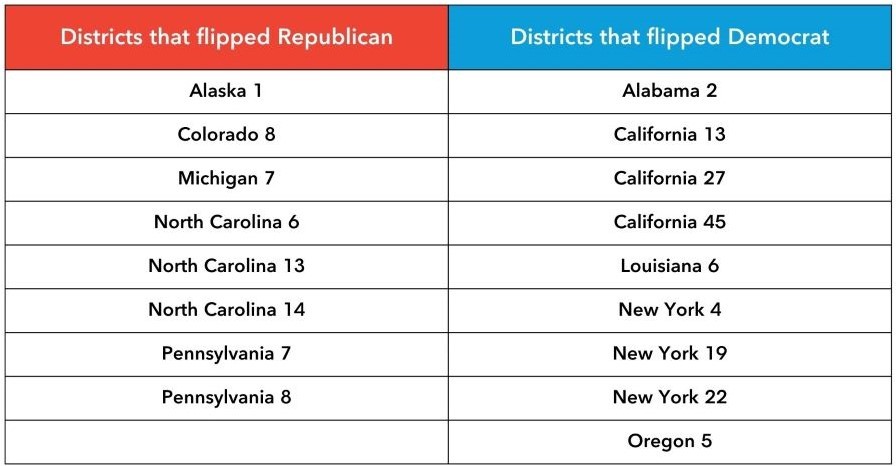
Each state is divided into congressional districts, with each district electing one representative to the House. The boundaries of these districts are drawn by state legislatures, and the process of redistricting can be highly political. Gerrymandering, the practice of drawing district lines to favor one political party or group, is a common concern in redistricting. Fair and impartial redistricting is essential for ensuring that all citizens have equal representation.
7. How Are Congressional District Boundaries Drawn?
The process of drawing congressional district boundaries, known as redistricting, is typically carried out by state legislatures. In some states, independent commissions are responsible for redistricting to reduce the potential for political gerrymandering. The goal of redistricting is to create districts that are roughly equal in population and that comply with the Voting Rights Act, which prohibits discriminatory redistricting practices.
8. What Is Gerrymandering, and Why Is It Controversial?
Gerrymandering is the practice of drawing congressional district boundaries to favor one political party or group over another. This can be done by concentrating voters of one party into a small number of districts, or by spreading them thinly across many districts. Gerrymandering can distort the will of the voters and create districts that are not competitive. It is a controversial practice that has been challenged in courts across the country.
9. What Are the Qualifications for Serving in the House of Representatives?
To be eligible to serve in the House of Representatives, a person must be at least 25 years old, a U.S. citizen for at least seven years, and a resident of the state they represent. These qualifications are set forth in the Constitution and are intended to ensure that representatives are experienced, knowledgeable, and committed to the interests of their constituents.
10. How Long Is a Term in the House of Representatives?
Members of the House of Representatives serve two-year terms. This relatively short term length is intended to keep representatives closely accountable to their constituents. Representatives must stand for reelection every two years, giving voters the opportunity to evaluate their performance and decide whether to return them to office.
11. What Are the Powers and Responsibilities of the House of Representatives?
The House of Representatives has several important powers and responsibilities, including:
- Initiating revenue bills: All bills for raising revenue must originate in the House.
- Impeaching federal officials: The House has the sole power to impeach federal officials, including the President.
- Electing the President in case of an Electoral College tie: If no candidate receives a majority of electoral votes, the House elects the President.
- Passing legislation: The House plays a crucial role in the lawmaking process, considering and voting on bills and resolutions.
- Oversight of the executive branch: The House has the power to oversee the activities of the executive branch and hold it accountable.
12. What Is the Role of the Speaker of the House?
The Speaker of the House is the presiding officer of the House and is elected by the members of the House. The Speaker plays a key role in setting the legislative agenda, controlling the flow of legislation, and representing the House in negotiations with the Senate and the President. The Speaker is typically a member of the majority party and is a powerful figure in American politics.
13. How Are Committee Assignments Determined in the House?
Committee assignments in the House are determined by the party leadership, with input from individual members. The majority party typically controls the committee chairs and has a majority of seats on each committee. Committee assignments are important because they determine which members have the most influence over specific policy areas.
14. What Is the Role of Committees in the House?
Committees play a crucial role in the legislative process in the House. They are responsible for:
- Reviewing and amending bills: Committees review bills referred to them, hold hearings, and make amendments.
- Conducting oversight of the executive branch: Committees oversee the activities of the executive branch and hold hearings to investigate issues of concern.
- Making recommendations to the full House: Committees make recommendations to the full House on whether to pass or reject bills.
15. What Are Some of the Key Committees in the House?
There are many important committees in the House, including:
- Appropriations Committee: Responsible for allocating federal funds.
- Ways and Means Committee: Responsible for tax policy.
- Energy and Commerce Committee: Responsible for energy, healthcare, and telecommunications.
- Judiciary Committee: Responsible for legal and judicial matters.
- Rules Committee: Responsible for setting the rules for debate on the House floor.
16. How Does a Bill Become a Law in the House?
The process of a bill becoming a law in the House involves several steps:
- Introduction: A bill is introduced in the House by a member.
- Committee review: The bill is referred to a committee for review and amendment.
- Floor debate: If the committee approves the bill, it is sent to the House floor for debate.
- Vote: The House votes on the bill.
- Senate consideration: If the House passes the bill, it is sent to the Senate for consideration.
- Presidential action: If the Senate passes the bill, it is sent to the President for signature. If the President signs the bill, it becomes law.
17. What Is a Quorum in the House?
A quorum is the minimum number of members who must be present for the House to conduct business. The quorum in the House is a majority of the members, or 218 members. If a quorum is not present, the House cannot vote on legislation.
18. How Does the House Interact with the Senate?
The House and Senate must work together to pass legislation. Bills must pass both chambers in the same form before they can be sent to the President for signature. If the House and Senate pass different versions of a bill, they must reconcile their differences through a conference committee.
19. What Is a Conference Committee?
A conference committee is a temporary committee composed of members from both the House and Senate. Its purpose is to reconcile differences between the House and Senate versions of a bill. The conference committee produces a compromise bill that is then sent back to both chambers for a vote.
20. What Is a Presidential Veto?
A presidential veto is the President’s power to reject a bill passed by Congress. If the President vetoes a bill, it is sent back to Congress. Congress can override a presidential veto with a two-thirds vote in both the House and Senate.
21. What Is the Significance of the House of Representatives in American Governance?
The House of Representatives is a crucial part of the American system of checks and balances. It represents the interests of citizens across the nation and plays a key role in the lawmaking process. The House’s power to initiate revenue bills and impeach federal officials gives it significant influence over the direction of government policy.
22. How Can Citizens Engage with the House of Representatives?
Citizens can engage with the House of Representatives in several ways:
- Contacting their representatives: Citizens can contact their representatives to express their views on issues of concern.
- Attending town hall meetings: Representatives often hold town hall meetings to hear from their constituents.
- Voting in elections: Citizens can vote in elections to choose their representatives.
- Advocating for legislation: Citizens can advocate for legislation by contacting their representatives and organizing grassroots campaigns.
23. What Are Some of the Current Issues Facing the House of Representatives?
The House of Representatives is currently facing several important issues, including:
- Economic policy: The House is grappling with issues such as tax reform, budget deficits, and trade policy.
- Healthcare: The House is debating the future of the Affordable Care Act and other healthcare issues.
- Immigration: The House is considering immigration reform legislation.
- National security: The House is addressing issues related to terrorism, cybersecurity, and defense spending.
24. How Does the House of Representatives Reflect the Diversity of the United States?
The House of Representatives has become increasingly diverse in recent years, with more women, minorities, and LGBTQ+ members serving in Congress. However, the House still does not fully reflect the diversity of the United States population. Efforts are underway to increase representation for underrepresented groups.
25. What Is the Future of the House of Representatives?
The future of the House of Representatives is uncertain, but it is likely to continue to play a central role in American governance. The House will face challenges such as increasing political polarization, declining public trust in government, and the need to address complex policy issues. However, the House also has the opportunity to adapt to changing circumstances and continue to serve as a voice for the American people.
26. Understanding the Current Count on the House of Representatives
As of today, it’s essential to stay updated on the precise composition of the House. This involves understanding the current party distribution, any recent shifts in seats due to special elections or resignations, and the implications of these changes for legislative priorities.
27. How Do Vacancies Affect the House Count?
When a seat in the House becomes vacant due to resignation, death, or other reasons, a special election is typically held to fill the vacancy. The timing of these elections and the outcome can impact the overall count and party balance in the House.
28. What Is a Majority in the House, and Why Is It Important?
A majority in the House means that one political party holds more than half of the seats (at least 218 out of 435). The majority party controls the House agenda, committee assignments, and the legislative process. Having a majority is crucial for a party to advance its policy priorities.
29. How Does the Party in Power Influence Legislation?
The party in power in the House has significant influence over legislation. The Speaker of the House, who is typically a member of the majority party, controls the flow of legislation and sets the agenda. The majority party also controls the committee chairs, who play a key role in shaping legislation.
30. What Is Bipartisanship, and Why Is It Important in the House?
Bipartisanship refers to cooperation and compromise between members of different political parties. In a closely divided House, bipartisanship is often necessary to pass legislation. When members of both parties work together, it can lead to more effective and sustainable policies.
31. How Do Ideological Differences Affect the House?
Ideological differences between members of the House can make it difficult to reach consensus on policy issues. The House is often divided along ideological lines, with conservative Republicans and liberal Democrats holding very different views on issues such as taxation, healthcare, and social policy.
32. What Role Do Caucuses Play in the House?
Caucuses are groups of members of Congress who share a common interest or goal. There are many different types of caucuses in the House, including ideological caucuses, regional caucuses, and issue-based caucuses. Caucuses can play a significant role in shaping the legislative agenda and influencing policy debates.
33. How Does the House Respond to Public Opinion?
The House is intended to be responsive to public opinion, as members are elected every two years. Representatives often pay close attention to polls, town hall meetings, and other forms of feedback from their constituents. However, the influence of public opinion can be limited by factors such as party loyalty and the influence of special interests.
34. What Are Some of the Challenges Facing the House Today?
The House is facing several challenges today, including:
- Political polarization: The House is more polarized than ever before, making it difficult to reach consensus on policy issues.
- Declining public trust: Public trust in government is at a low point, making it difficult for the House to address complex problems.
- Gridlock: The House is often gridlocked, with little progress being made on important legislation.
- Campaign finance: The role of money in politics is a growing concern, as it can distort the legislative process.
35. What Are Some Potential Reforms for the House?
There are many potential reforms that could improve the functioning of the House, including:
- Campaign finance reform: Reducing the influence of money in politics could make the House more responsive to the needs of ordinary citizens.
- Redistricting reform: Ending gerrymandering could create more competitive districts and make elections fairer.
- Rules reform: Changing the rules of the House could make it easier to pass legislation and reduce gridlock.
- Increased bipartisanship: Encouraging members of different parties to work together could lead to more effective policies.
36. What Resources Are Available to Learn More About the House?
There are many resources available to learn more about the House of Representatives, including:
- The House website: The official website of the House provides information about members, committees, and legislation.
- The Congressional Research Service: The CRS provides nonpartisan research and analysis to members of Congress.
- News organizations: Many news organizations provide coverage of the House and its activities.
- Academic journals: Academic journals publish scholarly articles about the House and American politics.
37. How Can I Contact My Representative?
You can contact your representative by phone, email, or mail. You can find your representative’s contact information on the House website.
38. How Can I Stay Informed About What Is Happening in the House?
You can stay informed about what is happening in the House by following news organizations, reading academic journals, and visiting the House website. You can also sign up for email alerts from your representative.
39. The Count on the House: Understanding Its Significance
The count on the House of Representatives isn’t just a number; it’s a reflection of the nation’s political climate and the balance of power in Congress. This count influences everything from legislative outcomes to committee assignments, and it’s a critical piece of information for anyone seeking to understand American governance.
40. What Is the Role of the House in Impeachment Proceedings?
The House of Representatives has the sole power to impeach federal officials, including the President, Vice President, and federal judges. Impeachment is the process of bringing charges against an official for “treason, bribery, or other high crimes and misdemeanors.” If the House impeaches an official, the Senate then holds a trial to determine whether to remove the official from office.
41. How Does the House Handle Budget Appropriations?
The House plays a crucial role in the federal budget process. All bills for raising revenue must originate in the House, and the House Appropriations Committee is responsible for allocating federal funds to various government agencies and programs. The budget process is often contentious, as members of the House have different priorities and views on how federal funds should be spent.
42. What Is the “Rules Committee” and Its Importance?
The Rules Committee is one of the most powerful committees in the House. It sets the rules for debate on the House floor, including the amount of time allotted for debate, the number of amendments that can be offered, and whether amendments must be germane to the bill. The Rules Committee can use its power to shape the outcome of legislation and advance the priorities of the majority party.
43. Understanding “Ways and Means” Committee
The Ways and Means Committee in the House is primarily responsible for overseeing tax policy and revenue-related matters. Its decisions have a direct impact on the nation’s economy, including issues related to taxation, trade, and various social programs.
44. What is the Role of “Congressional Record”?
The Congressional Record serves as the official record of proceedings and debates in both the House and Senate. It includes transcripts of speeches, roll call votes, and other official actions taken by members of Congress. It is an important resource for researchers, journalists, and anyone interested in following the legislative process.
45. The Count and Representation: Ensuring Fair Governance
The composition of the House is carefully designed to ensure fair representation of the American people. By understanding how the count is determined and how it impacts the legislative process, citizens can become more engaged and informed participants in their democracy.
46. What Are Some Landmark Legislations Passed By the House?
The House has played a significant role in passing landmark legislation throughout American history. Some notable examples include the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Voting Rights Act of 1965, and the Affordable Care Act of 2010. These laws have had a profound impact on American society and reflect the House’s power to shape the nation’s future.
47. How Does Divided Government Affect the House?
Divided government occurs when the President and the majority in one or both houses of Congress are from different political parties. Divided government can lead to gridlock and make it difficult to pass legislation. However, it can also encourage bipartisanship and compromise, as members of different parties are forced to work together to achieve their goals.
48. What Is the Role of the House in Foreign Policy?
While the President has primary responsibility for foreign policy, the House plays a significant role in shaping the nation’s approach to the world. The House has the power to declare war, ratify treaties, and appropriate funds for foreign aid and defense. The House also holds hearings on foreign policy issues and can influence public opinion through its debates and resolutions.
49. The Evolving Count: Historical Shifts in the House
The count on the House of Representatives has changed significantly over time, reflecting shifts in population and political power. Understanding these historical shifts can provide insights into the evolution of American democracy and the changing priorities of the American people.
50. What Is the Impact of Technology on the House?
Technology has had a profound impact on the House, as it has on all aspects of American society. Members of the House now use email, social media, and other online tools to communicate with their constituents, track public opinion, and conduct research. Technology has also made it easier for citizens to follow the activities of the House and engage with their representatives.
51. How Does the House Address Ethical Concerns?
The House has a Committee on Ethics that is responsible for investigating allegations of misconduct by members and staff. The Committee can issue sanctions, including reprimands, censures, and even expulsion from the House. The House also has rules and regulations governing the conduct of members and staff, including restrictions on gifts, lobbying, and financial conflicts of interest.
52. What Is the Significance of Committee Hearings?
Committee hearings are an important part of the legislative process in the House. They provide an opportunity for members to gather information, hear from experts, and debate the merits of proposed legislation. Hearings can also be used to conduct oversight of the executive branch and investigate issues of public concern.
53. The Count and Future Elections: Anticipating Changes
As future elections approach, it’s essential to anticipate potential changes in the count on the House of Representatives. Factors such as demographic shifts, economic trends, and political realignments can all influence the outcome of elections and the composition of the House.
54. What Are the Different Types of Legislation Considered in the House?
The House considers a variety of different types of legislation, including:
- Bills: Bills are the primary means of enacting laws. They can be introduced by any member of the House and must be passed by both the House and Senate to become law.
- Resolutions: Resolutions are used to express the opinion of the House on a particular issue or to make internal rules and procedures. There are several types of resolutions, including simple resolutions, concurrent resolutions, and joint resolutions.
- Amendments: Amendments are changes to bills or resolutions that can be offered by members of the House during floor debate.
55. How Does the House Celebrate or Recognize Special Events?
The House often uses resolutions to celebrate or recognize special events, such as holidays, anniversaries, and achievements. These resolutions can be a way for the House to express its support for a particular cause or to honor individuals or groups who have made significant contributions.
56. What Is the Role of the House Historian?
The House Historian is responsible for preserving the history and traditions of the House of Representatives. The Historian’s office conducts research, publishes books and articles, and provides information to members of the House and the public. The House Historian plays an important role in ensuring that the history of the House is accurately documented and accessible.
57. The Count and Citizen Engagement: Making Your Voice Heard
The count on the House of Representatives is ultimately determined by the choices of American voters. By staying informed, engaging with their representatives, and participating in elections, citizens can make their voices heard and shape the future of the House and the nation.
58. How Can Young People Get Involved in the House?
There are many ways for young people to get involved in the House of Representatives, including:
- Internships: The House offers internships to college students and recent graduates who are interested in learning about the legislative process.
- Page Program: The House Page Program allows high school students to work as messengers and assistants to members of the House.
- Youth Advisory Councils: Some members of the House have Youth Advisory Councils that provide advice and feedback on issues of concern to young people.
- Advocacy: Young people can advocate for legislation by contacting their representatives and organizing grassroots campaigns.
59. What Is the Franking Privilege?
The franking privilege allows members of the House to send official mail to their constituents free of charge. The franking privilege is intended to help members communicate with their constituents and keep them informed about their activities in Congress. However, it has also been criticized as a form of taxpayer-funded campaigning.
60. The Enduring Count: The House as a Pillar of Democracy
The count on the House of Representatives is a dynamic and ever-changing reflection of the American people. As a pillar of democracy, the House plays a vital role in shaping the nation’s future and ensuring that the voices of all citizens are heard.
Staying informed about the count on the House of Representatives is essential for understanding American governance and engaging in the democratic process. Now you know more than ever what to expect.
Have more questions about the House of Representatives or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask on WHAT.EDU.VN! Our community of experts is ready to provide you with fast, accurate, and free answers. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious about the world around you, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for knowledge. We address the difficulties of securing reliable answers promptly and without cost, offering a user-friendly platform that links you to knowledgeable individuals eager to share their insights. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890, or visit our website at what.edu.vn to explore our services. Ask your question today and let us help you find the answers you need! Our LSI keywords include legislative branch, congressional members, and U.S. government.
 US House of Representatives Building
US House of Representatives Building
