The Kaaba is a cube-shaped building located in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, and it is the holiest shrine in Islam. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive explanations and insights into the significance of the Kaaba and its role in the Islamic faith, offering clarity on its religious importance and historical context. Understand the essence of the Kaaba, its structure, and its rituals, enriching your knowledge of Islamic traditions and practices.
1. What Is the Kaaba and Where Is It Located?
The Kaaba (also spelled Ka’bah) is a cuboid building in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, and is the most sacred site in Islam. Situated in the center of the Masjid al-Haram (Great Mosque of Mecca), it serves as the qibla, the direction Muslims face during prayer. This location is religiously significant for Muslims worldwide.
1.1. What Is the Significance of Mecca in Relation to the Kaaba?
Mecca’s significance is deeply intertwined with the Kaaba, making it the holiest city in Islam. Mecca is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad, and it is where Islam’s central pilgrimage, the Hajj, takes place. The presence of the Kaaba elevates Mecca to a position of unparalleled importance, attracting millions of Muslims annually for religious observance and spiritual renewal.
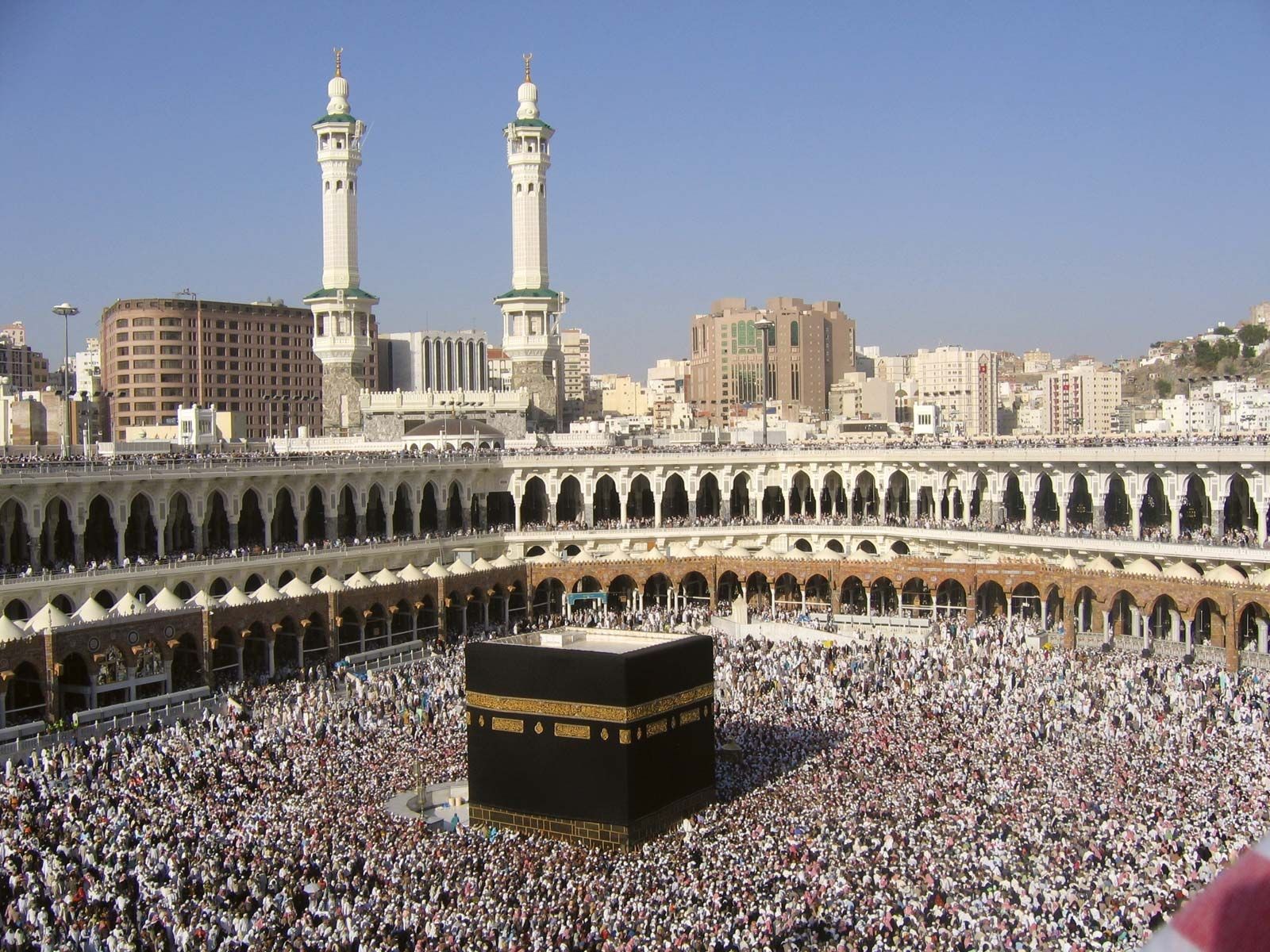 Pilgrims surrounding the Kaaba during Hajj in Mecca, Saudi Arabia
Pilgrims surrounding the Kaaba during Hajj in Mecca, Saudi Arabia
2. What Is the History of the Kaaba?
The history of the Kaaba is rich and dates back to pre-Islamic times, serving as a focal point for polytheistic worship before Islam. Islamic tradition holds that the Kaaba was originally built by Prophet Adam and later rebuilt by Prophet Abraham (Ibrahim) and his son Ishmael (Ismail). Over centuries, it has been reconstructed and renovated multiple times, reflecting its enduring significance across different eras.
2.1. How Has the Kaaba Evolved Through History?
The Kaaba has undergone numerous transformations throughout history, from its early construction to its role as a polytheistic shrine and its eventual dedication to monotheism under the Prophet Muhammad. Key historical events include:
- Pre-Islamic Era: The Kaaba housed numerous idols representing various tribal gods.
- Prophet Muhammad’s Era: In 630 CE, Prophet Muhammad cleansed the Kaaba of idols, rededicating it to Allah.
- Subsequent Reconstructions: The structure has been rebuilt and renovated multiple times due to natural disasters and human actions, each reconstruction adding to its historical narrative.
2.2. What Is the Significance of Abraham and Ishmael in the History of the Kaaba?
Abraham and Ishmael are central figures in the Kaaba’s history. Islamic tradition recounts that they rebuilt the Kaaba under divine guidance, establishing it as a place of monotheistic worship. This narrative underscores the Kaaba’s spiritual heritage and its connection to the Abrahamic faith tradition.
3. What Is the Structure and Design of the Kaaba?
The Kaaba is a cube-shaped structure approximately 15 meters (50 feet) high, with a base measuring about 10 by 12 meters (35 by 40 feet). Constructed from gray stone and marble, its corners are aligned with the cardinal directions. Inside, it features three pillars supporting the roof and suspended silver and gold lamps.
3.1. What Are the Dimensions of the Kaaba?
The Kaaba stands about 15 meters (50 feet) tall. Its base is approximately 10 meters (35 feet) by 12 meters (40 feet), giving it a cuboid shape. These dimensions make it a significant architectural structure within the Great Mosque.
3.2. What Materials Were Used to Construct the Kaaba?
The Kaaba is primarily constructed of gray stone and marble. These materials were chosen for their durability and aesthetic appeal, ensuring the structure’s longevity and visual prominence.
3.3. What Is the Significance of the Black Stone (Hajar al-Aswad)?
The Black Stone (Hajar al-Aswad) is located in the eastern corner of the Kaaba. According to Islamic tradition, it was given to Adam upon his expulsion from paradise to seek forgiveness. Over time, it is believed to have absorbed the sins of pilgrims, turning it black. Touching or kissing the Black Stone is a revered practice during the Hajj, symbolizing a connection to the divine and a renewal of faith.
4. What Is the Kiswah and Its Significance?
The Kiswah is an elaborately decorated black cloth that covers the Kaaba. Adorned with gold and silver embroidery featuring Quranic verses, the Kiswah is replaced annually during the Hajj. This tradition symbolizes purity, renewal, and reverence for the Kaaba.
4.1. How Often Is the Kiswah Replaced?
The Kiswah is replaced once a year, traditionally on the first day of the Islamic month of Muharram. This annual change is a significant event, marking the start of the new Islamic year and symbolizing renewal and respect for the Kaaba.
4.2. What Materials Are Used to Make the Kiswah?
The Kiswah is made from high-quality black silk and adorned with gold and silver threads. The intricate embroidery includes Quranic verses and other Islamic motifs, showcasing exceptional craftsmanship and devotion.
4.3. What Is the Process of Making the Kiswah?
The making of the Kiswah is a meticulous process involving skilled artisans. It includes weaving the black silk, embroidering the Quranic verses with gold and silver threads, and assembling the panels to fit the Kaaba. This process takes several months and reflects the dedication and artistry involved in honoring the Kaaba.
5. What Is the Religious Significance of the Kaaba in Islam?
The Kaaba is the most sacred site in Islam, serving as the qibla, the direction Muslims face during their daily prayers. It is the focal point of the Hajj pilgrimage, where millions of Muslims circumambulate the Kaaba as an act of devotion. The Kaaba symbolizes the oneness of God (Allah) and the unity of the Muslim community worldwide.
5.1. How Is the Kaaba the Qibla for Muslims?
The Kaaba serves as the qibla, the direction that Muslims face during their five daily prayers. This practice unifies Muslims globally, orienting their spiritual focus towards the sacred site. The direction of prayer reinforces the Kaaba’s central role in Islamic worship and spiritual life.
5.2. What Role Does the Kaaba Play in the Hajj Pilgrimage?
During the Hajj pilgrimage, circumambulating the Kaaba (Tawaf) is a central ritual. Pilgrims walk around the Kaaba seven times in a counterclockwise direction, reciting prayers and supplications. This act symbolizes devotion to Allah and unity with the global Muslim community. The Hajj is a mandatory pilgrimage for Muslims who are physically and financially able, underscoring the Kaaba’s pivotal role in Islamic practice.
5.3. What Is Tawaf and Its Significance?
Tawaf is the act of circumambulating the Kaaba seven times in a counterclockwise direction. This ritual is performed during the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages. Tawaf symbolizes the pilgrims’ devotion to Allah and their unity with Muslims worldwide. It is a deeply spiritual act that connects pilgrims to the heart of Islam.
6. What Are the Rituals and Practices Associated with the Kaaba?
Several rituals and practices are associated with the Kaaba, including circumambulation (Tawaf), touching or kissing the Black Stone (Hajar al-Aswad), and praying towards the Kaaba (Qibla). These practices are integral to Islamic worship and pilgrimage, reflecting reverence for the sacred site.
6.1. How Do Muslims Perform Tawaf?
Muslims perform Tawaf by walking around the Kaaba seven times in a counterclockwise direction. Pilgrims start at the Black Stone, reciting prayers and supplications with each circuit. The act symbolizes their devotion to Allah and unity with the global Muslim community.
6.2. What Is the Significance of Touching or Kissing the Black Stone?
Touching or kissing the Black Stone is a revered practice during the Hajj. It is believed to be a means of seeking blessings and forgiveness from Allah. While not mandatory, it is highly encouraged as a way to connect with the divine and emulate the Prophet Muhammad.
6.3. How Does Praying Towards the Kaaba Unify Muslims?
Praying towards the Kaaba, the qibla, unifies Muslims worldwide. Regardless of their location, Muslims face the Kaaba during their daily prayers, creating a sense of global unity and shared devotion to Allah.
7. What Is the Zamzam Well and Its Relation to the Kaaba?
The Zamzam Well is a sacred well located near the Kaaba. According to Islamic tradition, it sprang forth to quench the thirst of Ishmael (Ismail) and his mother Hagar. The water from Zamzam is considered blessed and is often consumed by pilgrims as a symbol of spiritual purification and blessings.
7.1. What Is the Story Behind the Zamzam Well?
The story of the Zamzam Well dates back to when Abraham’s wife, Hagar, was wandering in the desert with her son Ishmael, searching for water. When their water ran out, Ishmael cried out in thirst. In response to Hagar’s desperate prayers, Allah sent the angel Gabriel, who struck the ground and caused a spring of water to emerge, saving them both. This spring became known as the Zamzam Well.
7.2. What Is the Significance of Zamzam Water for Muslims?
Zamzam water is highly revered by Muslims for its historical and spiritual significance. It is believed to have healing properties and is often consumed by pilgrims who visit Mecca. Many Muslims take Zamzam water home to share with family and friends, considering it a blessed and holy gift.
7.3. How Is Zamzam Water Used in Religious Practices?
Zamzam water is used in various religious practices. Pilgrims drink it during the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages, and it is often used to wash the Kaaba during ceremonial cleansings. Muslims believe that drinking Zamzam water can bring blessings, healing, and spiritual purification.
8. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Kaaba?
Several misconceptions surround the Kaaba, including the belief that Muslims worship the Kaaba itself. In reality, Muslims worship Allah and face the Kaaba as a direction of prayer, symbolizing unity and devotion. Another misconception is that the Kaaba has always been a purely Islamic site, overlooking its pre-Islamic history as a polytheistic shrine.
8.1. Do Muslims Worship the Kaaba?
No, Muslims do not worship the Kaaba. Instead, they worship Allah and face the Kaaba as the qibla, the direction of prayer. The Kaaba serves as a focal point that unites Muslims worldwide in their devotion to Allah.
8.2. Has the Kaaba Always Been an Islamic Site?
No, the Kaaba was not always an Islamic site. Before the advent of Islam, it was a polytheistic shrine housing numerous idols representing various tribal gods. Prophet Muhammad cleansed the Kaaba of these idols and rededicated it to Allah in 630 CE.
8.3. Is the Kaaba Just a Building?
While the Kaaba is a physical structure, it is far more than just a building. It is the most sacred site in Islam, symbolizing the oneness of God (Allah) and the unity of the Muslim community worldwide. Its historical and religious significance transcends its physical form.
9. What Is the Kaaba’s Role in Islamic Art and Culture?
The Kaaba is a prominent motif in Islamic art and culture, appearing in paintings, calligraphy, and architectural designs. It symbolizes the heart of Islam and is a source of inspiration for artistic expression and cultural identity.
9.1. How Is the Kaaba Represented in Islamic Art?
The Kaaba is often represented in Islamic art through intricate geometric designs, calligraphy featuring Quranic verses, and depictions of the Hajj pilgrimage. These artistic representations convey reverence for the Kaaba and its central role in the Islamic faith.
9.2. What Cultural Significance Does the Kaaba Hold for Muslims?
The Kaaba holds immense cultural significance for Muslims worldwide. It symbolizes their shared faith, history, and identity. The Kaaba serves as a reminder of their spiritual heritage and the importance of unity and devotion in their lives.
9.3. How Does the Kaaba Influence Islamic Architecture?
The Kaaba influences Islamic architecture by serving as a model for the design of mosques and other religious structures. The concept of orienting buildings towards the qibla (the direction of the Kaaba) is a fundamental principle in Islamic architecture, ensuring that Muslims can pray in the correct direction, no matter where they are.
10. What Are Some Frequently Asked Questions About the Kaaba?
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Kaaba, addressing common queries and misconceptions about this sacred site.
10.1. Who Built the Kaaba?
According to Islamic tradition, the Kaaba was originally built by Prophet Adam and later rebuilt by Prophet Abraham (Ibrahim) and his son Ishmael (Ismail).
10.2. Why Is the Kaaba Covered in Black Cloth?
The Kaaba is covered in black cloth, known as the Kiswah, as a sign of reverence and respect. The Kiswah is adorned with gold and silver embroidery featuring Quranic verses.
10.3. Can Non-Muslims Visit the Kaaba?
Non-Muslims are generally not allowed to enter the city of Mecca or visit the Kaaba. Access is restricted to Muslims as it is considered a holy sanctuary.
11. What Is the Significance of the Kaaba in Contemporary Islamic Society?
In contemporary Islamic society, the Kaaba remains the central symbol of faith and unity. It serves as a reminder of the core principles of Islam and the shared heritage of Muslims worldwide. The Kaaba continues to inspire devotion, artistic expression, and cultural identity.
11.1. How Does the Kaaba Serve as a Symbol of Unity?
The Kaaba serves as a symbol of unity by being the qibla towards which all Muslims pray, regardless of their location. This shared direction of prayer fosters a sense of global unity and shared devotion to Allah.
11.2. What Is the Kaaba’s Impact on Modern Muslim Identity?
The Kaaba has a profound impact on modern Muslim identity by serving as a constant reminder of their shared faith, history, and values. It inspires a sense of belonging to a global community and reinforces the importance of devotion, unity, and spiritual growth.
11.3. How Does the Kaaba Inspire Muslims Today?
The Kaaba inspires Muslims today by serving as a beacon of faith, hope, and spiritual renewal. It reminds them of the importance of seeking closeness to Allah, living according to Islamic principles, and striving for personal and communal betterment.
12. What Are the Ethical Considerations Related to Visiting the Kaaba?
Visiting the Kaaba during the Hajj pilgrimage involves several ethical considerations. Pilgrims are expected to conduct themselves with humility, respect, and kindness towards others. They should also adhere to the rules and regulations set forth by Saudi authorities to ensure a safe and orderly pilgrimage experience.
12.1. What Behaviors Are Expected of Pilgrims Visiting the Kaaba?
Pilgrims visiting the Kaaba are expected to exhibit humility, respect, and kindness towards others. They should avoid engaging in disputes, maintain cleanliness, and adhere to Islamic principles of modesty and piety.
12.2. How Can Pilgrims Ensure a Respectful Visit to the Kaaba?
Pilgrims can ensure a respectful visit to the Kaaba by educating themselves about the rituals and customs associated with the Hajj pilgrimage. They should also be mindful of their behavior, avoid causing disruptions, and treat fellow pilgrims with kindness and compassion.
12.3. What Role Does Intention (Niyyah) Play in Visiting the Kaaba?
Intention (Niyyah) plays a crucial role in visiting the Kaaba. Pilgrims should approach the Hajj pilgrimage with sincere intentions to seek closeness to Allah, purify their hearts, and renew their faith. Their intention should guide their actions and behaviors throughout the pilgrimage experience.
13. How Has the Kaaba Influenced Literature and Poetry?
The Kaaba has significantly influenced literature and poetry, serving as a recurring theme in Islamic writings. Poets and writers often use the Kaaba as a metaphor for spiritual longing, devotion, and the search for divine connection.
13.1. What Are Some Examples of the Kaaba in Islamic Poetry?
Many Islamic poets have written about the Kaaba, expressing their love, reverence, and longing to visit the sacred site. These poems often use vivid imagery and metaphors to convey the spiritual significance of the Kaaba and its impact on the hearts of believers.
13.2. How Is the Kaaba Used as a Metaphor in Literature?
In literature, the Kaaba is often used as a metaphor for the human heart, the search for truth, and the ultimate destination of the soul. It symbolizes the center of one’s spiritual life and the yearning for divine connection.
13.3. What Themes Are Commonly Associated with the Kaaba in Literature?
Common themes associated with the Kaaba in literature include love for Allah, longing for spiritual purification, the journey of self-discovery, and the importance of unity and devotion within the Muslim community.
14. How Does the Kaaba Connect Muslims to Their Spiritual Heritage?
The Kaaba connects Muslims to their spiritual heritage by serving as a tangible link to the prophets Abraham and Muhammad. It reminds them of the origins of Islam and the enduring values of faith, devotion, and unity that have shaped their history and identity.
14.1. How Does the Kaaba Serve as a Link to the Prophets?
The Kaaba serves as a link to the prophets by being the site that, according to Islamic tradition, was built by Prophet Adam and rebuilt by Prophet Abraham and his son Ishmael. It is also the site that Prophet Muhammad cleansed of idols and rededicated to Allah, making it a central part of Islamic history and faith.
14.2. What Lessons Can Be Learned from the History of the Kaaba?
The history of the Kaaba teaches valuable lessons about the importance of faith, perseverance, and unity. It reminds Muslims of the challenges faced by their ancestors and the sacrifices they made to uphold the principles of Islam.
14.3. How Does Visiting the Kaaba Strengthen One’s Faith?
Visiting the Kaaba strengthens one’s faith by providing a deeply spiritual and transformative experience. Pilgrims feel a profound sense of connection to Allah and the global Muslim community. This experience reinforces their commitment to living according to Islamic principles and striving for spiritual growth.
15. What Is the Future of the Kaaba in Modern Society?
The future of the Kaaba in modern society is secure as it remains the central symbol of Islam for Muslims worldwide. Efforts to preserve and maintain the Kaaba are ongoing, ensuring that it continues to inspire and unite Muslims for generations to come.
15.1. How Are Efforts Being Made to Preserve the Kaaba?
Efforts to preserve the Kaaba include regular maintenance and restoration work, as well as measures to protect it from damage and environmental factors. The Saudi government invests significant resources in ensuring the Kaaba remains in pristine condition.
15.2. What Role Will the Kaaba Play in Future Generations?
The Kaaba will continue to play a central role in future generations by serving as a beacon of faith, hope, and unity for Muslims worldwide. It will inspire them to uphold the values of Islam and strive for a better future.
15.3. How Can Technology Be Used to Enhance the Experience of Visiting the Kaaba?
Technology can enhance the experience of visiting the Kaaba by providing virtual tours, educational resources, and tools to help pilgrims navigate the Hajj rituals more efficiently. Digital platforms can also facilitate communication and support among pilgrims, creating a more connected and meaningful experience.
Navigating the complexities surrounding the Kaaba can be challenging, but at WHAT.EDU.VN, we strive to provide clear, concise, and reliable answers to all your questions. Understanding the Kaaba enhances your appreciation of Islamic traditions and practices.
Do you have more questions about the Kaaba or other aspects of Islam? Don’t hesitate! Visit WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can ask any question and receive free, accurate answers from our community of experts. Our mission is to provide accessible knowledge to everyone, regardless of their background or location. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Let what.edu.vn be your go-to resource for all your questions.