The Oort Cloud is a theoretical sphere surrounding our solar system, far beyond Pluto and the Kuiper Belt, acting as a reservoir of icy comets. Want to unravel the mysteries of space? At WHAT.EDU.VN, you can ask any question and get answers for free. Dive into the depths of space with us and explore celestial objects and astronomical phenomena.
1. What Is The Oort Cloud?
The Oort Cloud is a theoretical, spherical collection of icy bodies believed to surround the Solar System at vast distances, much further than the Kuiper Belt. It is thought to be the source of most long-period comets.
Understanding the Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud is not a planet or a traditional cloud but a vast, diffuse collection of icy objects. These objects are remnants from the early formation of the Solar System.
Key Features of the Oort Cloud
- Distance: It is hypothesized to begin approximately 2,000 to 5,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun and may extend out to 100,000 AU or more.
- Shape: Unlike the Kuiper Belt, which is a flattened disk, the Oort Cloud is believed to be a spherical shell surrounding the Solar System.
- Composition: It is composed of icy planetesimals, remnants from the Solar System’s formation.
Where Is The Oort Cloud Located?
The Oort Cloud is located at the outermost reaches of the Solar System, far beyond the orbits of Neptune and Pluto. It is so distant that it is considered to be at the edge of the Sun’s gravitational influence.
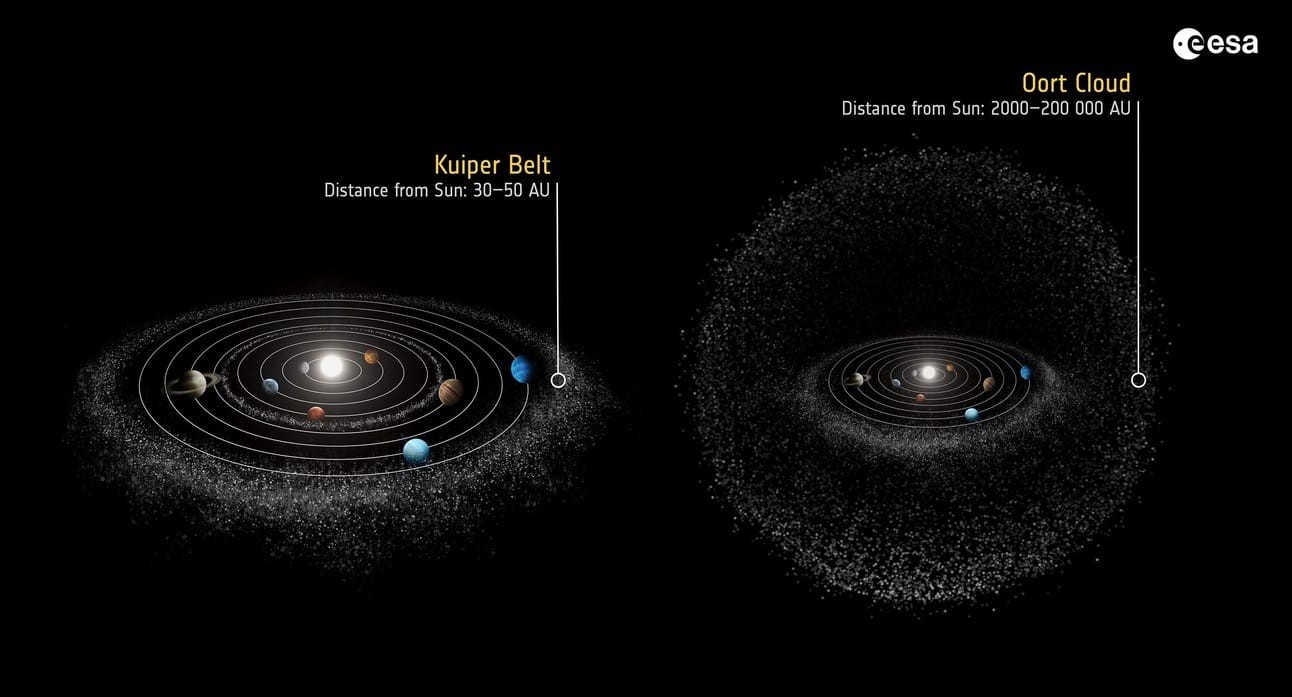
The Oort Cloud vs. the Kuiper Belt
While both the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt are composed of icy bodies, they differ significantly in distance, shape, and composition. The Kuiper Belt is a flattened disk located beyond Neptune’s orbit, while the Oort Cloud is a spherical shell much further out.
What Purpose Does The Oort Cloud Serve?
The Oort Cloud is thought to be the source of long-period comets, which are comets with orbital periods of more than 200 years. These comets are occasionally dislodged from the Oort Cloud and sent towards the inner Solar System.
2. Why Is The Oort Cloud Important?
The Oort Cloud is significant because it provides insights into the Solar System’s formation and evolution. It serves as a reservoir of icy bodies that occasionally become comets, offering valuable information about the early Solar System.
Understanding the Oort Cloud’s Importance
The Oort Cloud’s importance lies in its potential to reveal the composition of the early Solar System, the processes that shaped it, and the origin of comets.
Role in Comet Formation
The Oort Cloud is believed to be the source of long-period comets, which are comets with highly elliptical orbits that take hundreds or even thousands of years to orbit the Sun.
Insights into Solar System Formation
The icy bodies in the Oort Cloud are remnants from the early Solar System, providing a glimpse into the conditions and materials present during its formation.
Contribution to Understanding Planetary Migration
Studying the Oort Cloud can help scientists understand the gravitational interactions and planetary migration that occurred in the early Solar System.
How the Oort Cloud Reveals the Solar System’s Secrets
By studying the Oort Cloud and its inhabitants, scientists can learn about the building blocks of planets, the distribution of matter in the early Solar System, and the processes that shaped the Solar System into its current configuration.
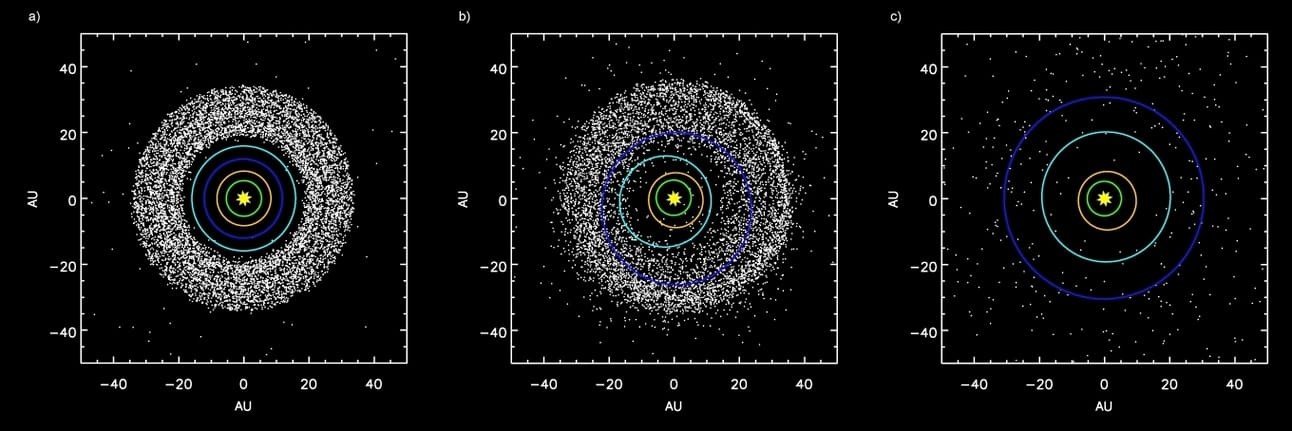
3. How Far Away Is The Oort Cloud?
The Oort Cloud is estimated to be between 2,000 and 100,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun. One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun (about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers).
Understanding the Distance to the Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud’s immense distance makes it challenging to study directly. However, its influence is evident through the comets that originate from it.
Inner and Outer Boundaries
The inner boundary of the Oort Cloud is estimated to be around 2,000 to 5,000 AU from the Sun, while the outer boundary may extend to 100,000 AU or more.
Comparison with Other Solar System Objects
To put the distance to the Oort Cloud into perspective, Neptune, the outermost planet in the Solar System, orbits at an average distance of 30 AU from the Sun.
How Scientists Measure the Oort Cloud’s Distance
Scientists infer the distance to the Oort Cloud by studying the orbits of long-period comets and modeling the gravitational interactions that influence their paths.
The Significance of the Oort Cloud’s Distance
The Oort Cloud’s great distance from the Sun means that it is only weakly bound to the Solar System and is easily influenced by the gravitational forces of passing stars and the Milky Way galaxy.
4. What Is The Oort Cloud Made Of?
The Oort Cloud is primarily composed of icy planetesimals, which are small bodies made of ice, rock, and dust. These planetesimals are remnants from the early Solar System, formed from the protoplanetary disk that surrounded the young Sun.
Understanding the Composition of the Oort Cloud
The composition of the Oort Cloud provides clues about the conditions and materials present during the Solar System’s formation.
Icy Planetesimals
The Oort Cloud is dominated by icy planetesimals, composed of water ice, methane ice, ammonia ice, and other volatile compounds.
Rock and Dust
In addition to ice, the Oort Cloud also contains rocky and dusty materials, which were incorporated into the planetesimals during their formation.
Distribution of Materials
The distribution of materials within the Oort Cloud may vary, with denser concentrations of icy bodies in certain regions.
How Scientists Study the Oort Cloud’s Composition
Scientists infer the composition of the Oort Cloud by studying the composition of comets that originate from it, using spectroscopic techniques to analyze the light they emit.
5. How Was The Oort Cloud Formed?
The Oort Cloud is believed to have formed from the remnants of the protoplanetary disk that surrounded the young Sun. These remnants were scattered to the outer reaches of the Solar System by gravitational interactions with the giant planets.
Understanding the Formation of the Oort Cloud
The formation of the Oort Cloud is closely linked to the formation of the Solar System and the migration of the giant planets.
Protoplanetary Disk
The Oort Cloud’s building blocks came from the protoplanetary disk, a swirling disk of gas and dust that surrounded the young Sun.
Gravitational Scattering
As the giant planets formed, their gravity scattered the remaining planetesimals to the outer Solar System, forming the Oort Cloud.
Planetary Migration
The migration of the giant planets, particularly Jupiter and Saturn, played a crucial role in shaping the Oort Cloud and determining its final configuration.
Evidence Supporting the Formation Theory
Evidence supporting this theory comes from computer simulations, studies of comet orbits, and observations of protoplanetary disks around other stars.
6. What Is The Difference Between The Oort Cloud And The Kuiper Belt?
The Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt are both regions of icy bodies in the outer Solar System, but they differ significantly in distance, shape, and composition. The Kuiper Belt is a flattened disk located beyond Neptune’s orbit, while the Oort Cloud is a spherical shell much further out.
Understanding the Differences
Distinguishing between the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt is essential for understanding the structure of the outer Solar System.
Distance from the Sun
The Kuiper Belt is located between 30 and 55 AU from the Sun, while the Oort Cloud is much further out, ranging from 2,000 to 100,000 AU.
Shape
The Kuiper Belt is a flattened disk, similar to the asteroid belt, while the Oort Cloud is a spherical shell surrounding the entire Solar System.
Composition
Both regions are composed of icy bodies, but the Kuiper Belt contains a higher proportion of larger objects, including dwarf planets like Pluto.
Origin of Comets
The Kuiper Belt is the source of short-period comets, while the Oort Cloud is the source of long-period comets.
Comparison Chart
| Feature | Kuiper Belt | Oort Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Distance | 30-55 AU | 2,000-100,000 AU |
| Shape | Flattened disk | Spherical shell |
| Composition | Icy bodies, dwarf planets | Icy bodies |
| Comet Origin | Short-period comets | Long-period comets |
7. Has The Oort Cloud Been Observed?
The Oort Cloud has not been directly observed, as it is too distant and its constituent objects are too small to be detected with current technology. However, its existence is inferred from the orbits of long-period comets.
Understanding the Challenges of Observing the Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud’s vast distance and the small size of its objects make direct observation extremely difficult.
Indirect Evidence
The primary evidence for the Oort Cloud’s existence comes from the orbits of long-period comets, which suggest a distant, spherical source.
Future Missions
Future space missions may be able to directly observe the Oort Cloud, but this remains a significant technological challenge.
How Scientists Infer the Oort Cloud’s Existence
Scientists use computer simulations and mathematical models to infer the properties of the Oort Cloud based on the observed orbits of comets.
The Role of Observational Data
While direct observation is lacking, observational data from comets provides valuable constraints on the size, shape, and composition of the Oort Cloud.
8. How Does The Oort Cloud Affect Comets?
The Oort Cloud serves as a reservoir of comets, and gravitational disturbances can dislodge these comets from their stable orbits, sending them towards the inner Solar System.
Understanding the Oort Cloud’s Influence on Comets
The Oort Cloud plays a critical role in the dynamics of comets and their interaction with the Solar System.
Gravitational Perturbations
Passing stars, molecular clouds, and the tidal forces of the Milky Way galaxy can perturb the orbits of Oort Cloud objects, causing them to fall towards the Sun.
Long-Period Comets
Comets that originate from the Oort Cloud have very long orbital periods, ranging from hundreds to millions of years.
The Oort Cloud as a Comet Reservoir
The Oort Cloud is estimated to contain trillions of icy bodies, making it the largest reservoir of comets in the Solar System.
Studying Comets to Learn About the Oort Cloud
By studying the composition and orbits of comets, scientists can gain insights into the properties of the Oort Cloud and the processes that shape it.
9. What Is The Future Of The Oort Cloud?
The Oort Cloud will continue to evolve over billions of years, as gravitational interactions and collisions gradually alter the orbits and compositions of its constituent objects.
Understanding the Long-Term Evolution of the Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud’s future is intertwined with the long-term evolution of the Solar System and the Milky Way galaxy.
Gravitational Interactions
The orbits of Oort Cloud objects will continue to be influenced by the gravitational forces of passing stars, molecular clouds, and the Milky Way galaxy.
Collisions
Collisions between Oort Cloud objects may occur, leading to the fragmentation and redistribution of materials.
Loss of Objects
Some Oort Cloud objects may be ejected from the Solar System entirely, while others may be captured by other stars.
Studying the Oort Cloud to Predict the Solar System’s Fate
Studying the Oort Cloud can provide insights into the long-term stability of the Solar System and the fate of its icy bodies.
10. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About The Oort Cloud?
Several misconceptions exist regarding the Oort Cloud, including the belief that it is a solid object or that it poses an immediate threat to Earth.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Clarifying these misconceptions is essential for a better understanding of the Oort Cloud.
Misconception 1: The Oort Cloud Is a Solid Object
The Oort Cloud is not a solid object but a diffuse collection of icy bodies spread over a vast region of space.
Misconception 2: The Oort Cloud Is a Direct Threat to Earth
While Oort Cloud comets can occasionally enter the inner Solar System, the chances of a direct impact on Earth are extremely low.
Misconception 3: The Oort Cloud Is Well Understood
The Oort Cloud is still largely theoretical, and many aspects of its formation, composition, and dynamics remain uncertain.
How to Correctly Understand the Oort Cloud
To correctly understand the Oort Cloud, it is important to rely on scientific evidence and avoid sensationalized or inaccurate information.
Have more questions about the Oort Cloud or other astronomical phenomena? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and receive expert answers for free. Our community is ready to help you explore the wonders of the universe. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Explore the cosmos with what.edu.vn today!
