The pituitary gland, a key component of your endocrine system, is a small but mighty gland responsible for producing many essential hormones. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear and concise answers to your questions about the pituitary gland, its function, and related health conditions. Learn more about its role in growth, reproduction, and overall well-being. Explore topics like hormone regulation, pituitary disorders, and treatment options, ensuring you have access to reliable information to understand and manage your health effectively.
1. What Is The Pituitary Gland And Where Is It Located?
The pituitary gland is a small, pea-sized gland located at the base of your brain, just behind your nose. It’s often called the “master gland” because it controls the activity of most other hormone-secreting glands in your body.
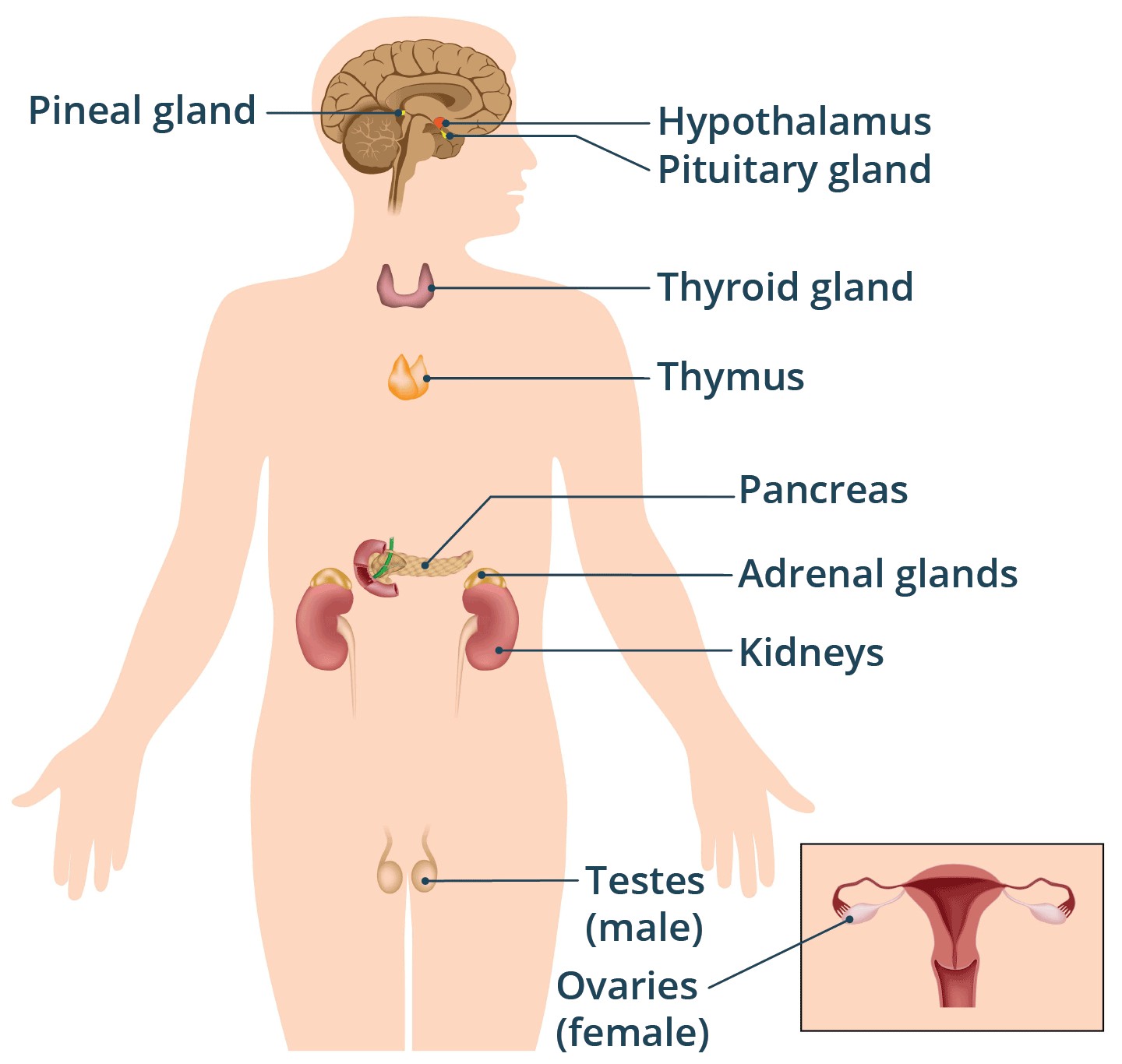 Illustration of the pituitary gland location in the brain.
Illustration of the pituitary gland location in the brain.
1.1 Why is the Pituitary Gland Called the Master Gland?
The pituitary gland earns its “master gland” title due to its role in regulating the functions of other endocrine glands. It secretes hormones that control the thyroid, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes, as explained by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. This regulatory function makes it essential for maintaining overall hormonal balance and bodily functions.
1.2 What are the Main Parts of the Pituitary Gland?
The pituitary gland has two main parts: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The anterior lobe produces and releases several hormones, while the posterior lobe stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. The Mayo Clinic provides a detailed overview of the functions of each lobe and the hormones they control.
1.3 How Does the Hypothalamus Interact with the Pituitary Gland?
The hypothalamus, located above the pituitary gland, controls the pituitary gland’s function. The hypothalamus communicates with the pituitary gland by releasing hormones that either stimulate or inhibit the release of pituitary hormones. This interaction ensures that hormone levels in the body are properly regulated, according to information from the Endocrine Society.
2. What Are The Primary Functions Of The Pituitary Gland?
The primary function of the pituitary gland is to secrete hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. These hormones play a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
2.1 How Does the Pituitary Gland Regulate Growth?
The pituitary gland produces growth hormone (GH), which is essential for growth and development, especially during childhood and adolescence. GH stimulates the growth of bones and tissues, as well as regulating metabolism, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
2.2 What Role Does the Pituitary Gland Play in Reproduction?
The pituitary gland produces hormones like follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are crucial for reproductive function in both males and females. These hormones control the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and sperm production, as detailed by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
2.3 How Does the Pituitary Gland Influence Metabolism?
The pituitary gland influences metabolism by producing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which tells the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall bodily functions, as explained by the National Academy of Hypothyroidism.
2.4 What Is The Pituitary Gland’s Role in Stress Response?
The pituitary gland produces adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, a hormone involved in the stress response. Cortisol helps the body respond to stress by increasing blood sugar levels and suppressing the immune system, according to information from the Mayo Clinic.
3. What Hormones Does The Pituitary Gland Produce?
The pituitary gland produces a variety of hormones, each with specific functions. These hormones include growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin, oxytocin, and vasopressin.
3.1 What Is Growth Hormone (GH) And What Does It Do?
Growth hormone (GH) is a hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and regeneration. It is crucial for growth and development, especially during childhood and adolescence. GH also plays a role in metabolism and muscle mass, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
3.2 What Is Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) And What Does It Do?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) tells the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall bodily functions. The National Academy of Hypothyroidism provides further insights into the role of TSH in thyroid health.
3.3 What Is Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) And What Does It Do?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, a hormone involved in the stress response. Cortisol helps the body respond to stress by increasing blood sugar levels and suppressing the immune system, as noted by the Mayo Clinic.
3.4 What Are Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) And Luteinizing Hormone (LH) And What Do They Do?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are crucial for reproductive function in both males and females. These hormones control the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and sperm production, according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
3.5 What Is Prolactin And What Does It Do?
Prolactin is a hormone that stimulates milk production in females after childbirth. It also plays a role in reproductive function and immune system regulation, as explained by the National Institutes of Health.
3.6 What Are Oxytocin And Vasopressin And What Do They Do?
Oxytocin is involved in childbirth, breastfeeding, and social bonding. Vasopressin helps control the amount of salt and water in your body, regulating blood pressure and kidney function, according to information from the Endocrine Society.
4. What Are Common Pituitary Gland Disorders?
Common pituitary gland disorders include pituitary tumors, hypopituitarism, hyperpituitarism, and diabetes insipidus. These conditions can result in hormone imbalances and various health problems.
4.1 What Are Pituitary Tumors And How Are They Classified?
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths in the pituitary gland. They can be classified as either non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Benign tumors are more common and can cause problems by pressing on nearby structures or by producing too much or too little of certain hormones, according to the Pituitary Network Association.
4.2 What Is Hypopituitarism And What Are Its Symptoms?
Hypopituitarism is a condition in which the pituitary gland does not produce enough of one or more hormones. Symptoms can vary depending on which hormones are deficient and may include fatigue, weakness, weight loss or gain, decreased libido, and menstrual irregularities, as explained by the Mayo Clinic.
4.3 What Is Hyperpituitarism And What Are Its Symptoms?
Hyperpituitarism is a condition in which the pituitary gland produces too much of one or more hormones. Symptoms can vary depending on which hormones are overproduced and may include acromegaly (excessive growth), Cushing’s disease (high cortisol levels), and hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels), according to the Pituitary Network Association.
4.4 What Is Diabetes Insipidus And How Is It Related To The Pituitary Gland?
Diabetes insipidus is a condition in which the body is unable to regulate fluid balance due to a deficiency in vasopressin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland. Symptoms include excessive thirst and frequent urination, as explained by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
5. How Are Pituitary Gland Disorders Diagnosed?
Pituitary gland disorders are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, hormone level tests, and imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans.
5.1 What Hormone Level Tests Are Used To Diagnose Pituitary Disorders?
Hormone level tests measure the levels of various hormones in the blood or urine to determine if the pituitary gland is functioning properly. These tests can help identify hormone deficiencies or overproduction, according to information from the Mayo Clinic.
5.2 What Imaging Studies Are Used To Diagnose Pituitary Disorders?
Imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans can help visualize the pituitary gland and identify any tumors or abnormalities. These studies provide detailed images of the pituitary gland and surrounding structures, as noted by the Pituitary Network Association.
5.3 How Is A Physical Exam Used In Diagnosing Pituitary Disorders?
A physical exam can help identify physical signs and symptoms that may indicate a pituitary disorder, such as changes in growth, weight, or vision. The physical exam, combined with hormone level tests and imaging studies, can help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis, as explained by the Endocrine Society.
6. What Are The Treatment Options For Pituitary Gland Disorders?
Treatment options for pituitary gland disorders vary depending on the specific condition and may include medication, surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination of these approaches.
6.1 What Medications Are Used To Treat Pituitary Disorders?
Medications used to treat pituitary disorders may include hormone replacement therapy to correct hormone deficiencies, medications to block hormone production, or medications to shrink pituitary tumors, as detailed by the Mayo Clinic.
6.2 When Is Surgery Recommended For Pituitary Disorders?
Surgery may be recommended to remove pituitary tumors that are causing symptoms or interfering with hormone production. The most common surgical approach is transsphenoidal surgery, which involves removing the tumor through the nose, according to the Pituitary Network Association.
6.3 What Is Radiation Therapy And When Is It Used For Pituitary Disorders?
Radiation therapy may be used to shrink pituitary tumors that cannot be completely removed with surgery or to prevent tumor regrowth. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill tumor cells, as explained by the American Cancer Society.
7. How Can Pituitary Gland Disorders Affect Overall Health?
Pituitary gland disorders can affect overall health by causing hormone imbalances that lead to a variety of symptoms and health problems, including growth abnormalities, reproductive issues, metabolic disorders, and stress response abnormalities.
7.1 How Do Pituitary Disorders Impact Growth And Development?
Pituitary disorders can impact growth and development by causing deficiencies or overproduction of growth hormone (GH). GH deficiency can lead to delayed growth and short stature in children, while GH overproduction can lead to acromegaly in adults, as noted by the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
7.2 What Reproductive Issues Can Arise From Pituitary Disorders?
Pituitary disorders can cause reproductive issues by affecting the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are crucial for reproductive function. These disorders can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and decreased libido, according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
7.3 How Do Pituitary Disorders Contribute To Metabolic Problems?
Pituitary disorders can contribute to metabolic problems by affecting the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which regulates metabolism. TSH deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, which slows down metabolism, while TSH overproduction can lead to hyperthyroidism, which speeds up metabolism, as explained by the National Academy of Hypothyroidism.
7.4 How Do Pituitary Disorders Affect Stress Response And Adrenal Function?
Pituitary disorders can affect stress response and adrenal function by affecting the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. ACTH deficiency can lead to adrenal insufficiency, which impairs the body’s ability to respond to stress, while ACTH overproduction can lead to Cushing’s disease, which causes high cortisol levels, according to information from the Mayo Clinic.
8. Are There Lifestyle Changes That Can Support Pituitary Gland Health?
While there are no specific lifestyle changes that can directly target the pituitary gland, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall hormonal balance and well-being, which can indirectly benefit pituitary gland health.
8.1 What Role Does Diet Play In Supporting Pituitary Gland Health?
A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support overall hormonal balance and well-being, which can indirectly benefit pituitary gland health. Including foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can help support the endocrine system, as suggested by the Endocrine Society.
8.2 How Does Exercise Affect Pituitary Gland Function?
Regular exercise can help regulate hormone levels, improve metabolism, and reduce stress, all of which can indirectly benefit pituitary gland function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by the American Heart Association.
8.3 How Does Stress Management Impact Pituitary Gland Health?
Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help regulate hormone levels and reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances that can affect the pituitary gland. Chronic stress can disrupt the endocrine system, so finding healthy ways to manage stress is essential, according to information from the Mayo Clinic.
8.4 How Does Sleep Quality Influence Pituitary Gland Health?
Getting enough sleep is essential for hormonal balance and overall health, including pituitary gland function. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to support the endocrine system and maintain hormone levels, as explained by the National Sleep Foundation.
9. What Are Some Lesser-Known Facts About The Pituitary Gland?
There are several lesser-known facts about the pituitary gland, including its role in pain management, its influence on social behavior, and its involvement in the regulation of body temperature.
9.1 What Is The Pituitary Gland’s Role In Pain Management?
The pituitary gland produces endorphins, which are natural pain relievers that can help reduce discomfort and improve mood. Endorphins are released in response to stress or pain and can have a positive impact on overall well-being, according to research from the National Institutes of Health.
9.2 How Does The Pituitary Gland Influence Social Behavior?
The pituitary gland produces oxytocin, a hormone that is involved in social bonding, trust, and empathy. Oxytocin plays a crucial role in forming social connections and promoting positive social interactions, as explained by the Endocrine Society.
9.3 Is The Pituitary Gland Involved In Body Temperature Regulation?
The pituitary gland is involved in the regulation of body temperature by producing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which affects metabolism and heat production. Thyroid hormones help maintain a stable body temperature, and imbalances in thyroid hormone levels can affect temperature regulation, according to information from the National Academy of Hypothyroidism.
10. Where Can I Find More Information And Support For Pituitary Gland Disorders?
You can find more information and support for pituitary gland disorders from various resources, including medical professionals, support groups, online forums, and reputable websites.
10.1 What Are Some Reputable Organizations That Provide Information On Pituitary Disorders?
Reputable organizations that provide information on pituitary disorders include the Pituitary Network Association, the Endocrine Society, and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. These organizations offer valuable resources, support, and educational materials, as noted on their respective websites.
10.2 How Can I Find A Medical Professional Specializing In Pituitary Gland Disorders?
You can find a medical professional specializing in pituitary gland disorders by asking your primary care physician for a referral or by searching online directories such as the Endocrine Society’s “Find an Endocrinologist” tool. It’s essential to find a healthcare provider who has experience in diagnosing and treating pituitary disorders, according to the Pituitary Network Association.
10.3 Are There Support Groups Available For Individuals With Pituitary Disorders?
Yes, there are support groups available for individuals with pituitary disorders. The Pituitary Network Association offers a list of support groups and online forums where individuals can connect with others who have similar experiences. Joining a support group can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community, as explained by the Endocrine Society.
10.4 What Online Resources Are Available For Learning More About Pituitary Gland Health?
Online resources for learning more about pituitary gland health include reputable websites such as the Mayo Clinic, the National Institutes of Health, and the Hormone Health Network. These websites offer reliable information, articles, and educational materials on pituitary gland disorders and overall endocrine health, as noted on their respective sites.
Do you have more questions about the pituitary gland or other health concerns? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide fast, free answers to all your questions. Visit our website at what.edu.vn, located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Our team is dedicated to helping you find the information you need. Don’t hesitate – ask your question today and get the answers you deserve!
