The poorest country in the world, as of 2024, is South Sudan, with a GDP-PPP per capita of just $455, according to WHAT.EDU.VN. This indicates the severe economic hardships its citizens face. We will examine the factors contributing to this nation’s poverty and explore the broader implications of global inequality, economic instability, and humanitarian assistance. Extreme poverty, economic indicators, and struggling economies are key aspects.
1. Understanding Poverty Metrics
How do we define and measure poverty, especially when comparing different countries?
Poverty is a multifaceted issue, and understanding its metrics is crucial for identifying the world’s poorest nations. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita is a common measure, representing the average economic output per person in a country. However, it doesn’t account for differences in the cost of living and inflation rates. To address this, economists often use Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), which adjusts GDP to reflect the relative purchasing power of a currency in different countries.
For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) uses current international dollars, reflecting exchange rates and PPP adjustments, to rank countries by wealth. This metric offers a more accurate comparison of living standards across nations.
Consider this table illustrating the top three and bottom three countries by GDP-PPP per capita in 2024:
| Rank | Country | GDP-PPP per capita ($) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Luxembourg | 143,743 |
| 2 | Macao SAR | 134,141 |
| 3 | Ireland | 133,895 |
| … | … | … |
| 188 | Central African Republic | 1,123 |
| 189 | Burundi | 916 |
| 190 | South Sudan | 455 |
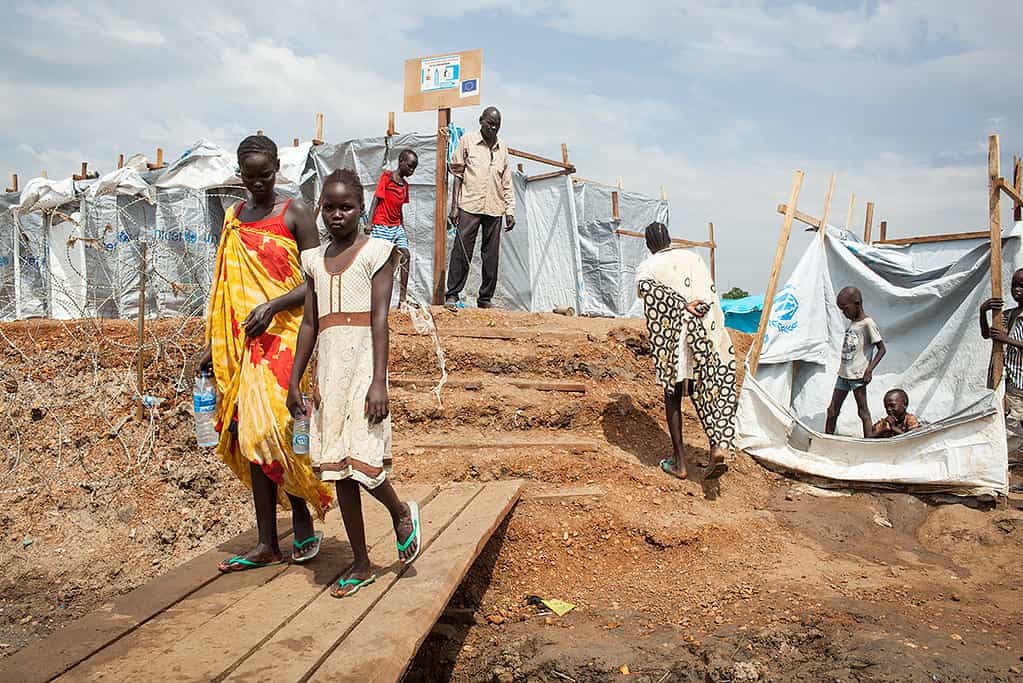
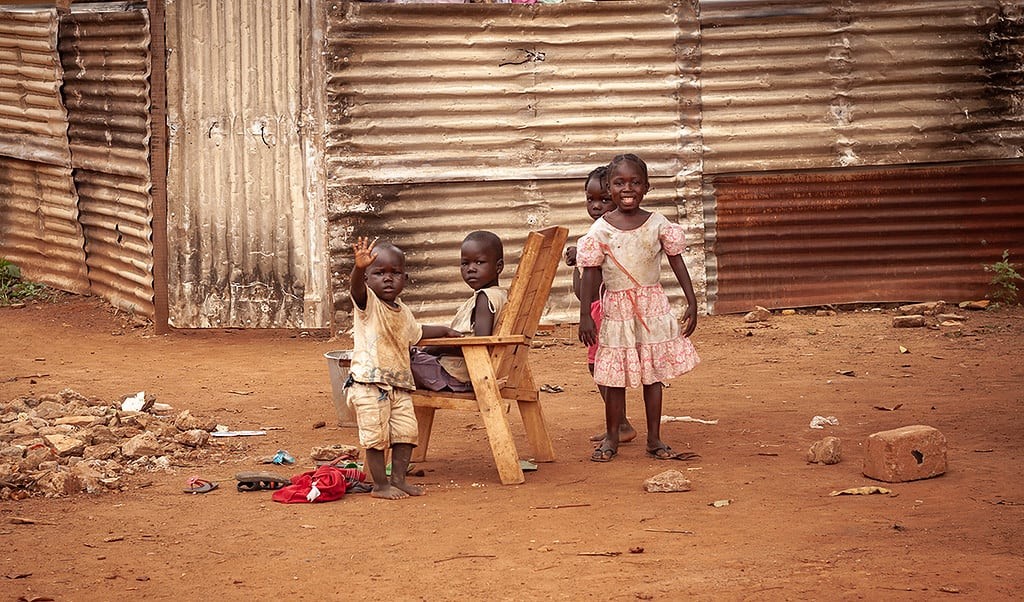
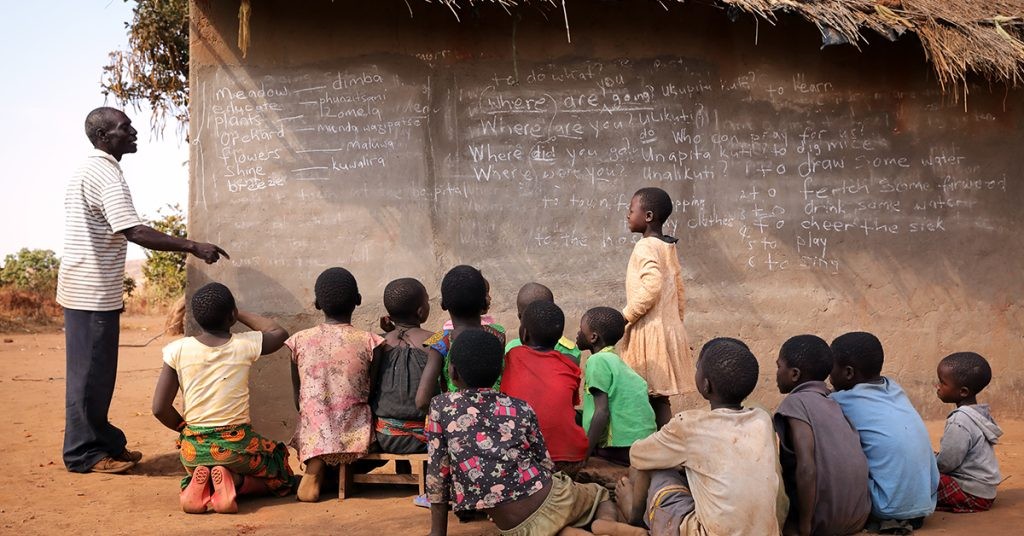



These figures highlight the vast disparities in economic well-being around the globe. South Sudan’s GDP-PPP per capita is a tiny fraction of that of Luxembourg, indicating a severe lack of economic resources available to its citizens.
Keep in mind that metrics like GDP and PPP, while useful, do not fully capture the lived experiences of poverty. Factors such as access to healthcare, education, clean water, and social support systems also play critical roles in determining a country’s overall level of poverty.
2. Why South Sudan Is the Poorest Country
What factors have contributed to South Sudan’s ranking as the poorest country in the world?
South Sudan’s status as the world’s poorest country is the result of a complex interplay of factors. The nation, rich in oil reserves, gained independence in 2011 but has since been plagued by political instability, conflict, and corruption. This aligns with the “resource curse” phenomenon, where natural resource wealth paradoxically leads to negative economic outcomes.
Internal conflicts and violence have displaced millions of people, disrupted agricultural production, and hindered economic development. According to the United Nations, an estimated 9 million people in South Sudan, over 60% of the population, require humanitarian assistance. This reflects the dire living conditions and lack of basic necessities for a large portion of the population.
The country’s reliance on traditional agriculture, combined with frequent climate-related disasters such as droughts and floods, exacerbates food insecurity. Farmers are often unable to plant or harvest crops, leading to widespread hunger and malnutrition. Weak governance and corruption further undermine the economy, diverting resources away from essential services and infrastructure development.
Here’s a summary of the key factors:
- Political Instability and Conflict: Ongoing violence since 2011.
- Resource Curse: Oil wealth leading to corruption and inequality.
- Humanitarian Crisis: Over 60% of the population needing aid.
- Climate-Related Disasters: Droughts and floods disrupting agriculture.
- Weak Governance: Corruption hindering development.
3. The Ripple Effect of Poverty
How does poverty in a country like South Sudan affect its citizens’ daily lives?
The pervasive poverty in South Sudan has far-reaching consequences for the daily lives of its citizens. Access to basic necessities such as food, clean water, healthcare, and education is severely limited. Malnutrition rates are alarmingly high, particularly among children, leading to long-term health and developmental issues.
According to a report by UNICEF, a significant percentage of children in South Sudan suffer from acute malnutrition, increasing their vulnerability to diseases and hindering their cognitive development. The lack of access to clean water and sanitation facilities contributes to the spread of waterborne diseases, further exacerbating health problems.
Education is also severely affected, with many schools lacking adequate resources and qualified teachers. Conflict and displacement disrupt schooling, leaving children with limited opportunities to improve their future prospects. The combination of these factors creates a cycle of poverty that is difficult to break.
Consider these statistics:
- High malnutrition rates among children
- Limited access to clean water and sanitation
- Inadequate healthcare services
- High rates of illiteracy and school dropout
These challenges underscore the urgent need for comprehensive interventions to address the root causes of poverty and improve the living conditions of the people of South Sudan.
4. Economic Indicators and Living Standards
What do key economic indicators tell us about the living conditions in the world’s poorest countries?
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the living standards and overall well-being of a country’s population. GDP per capita, adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP), is a crucial measure that reflects the average economic output per person, taking into account the cost of goods and services in different countries.
In South Sudan, the GDP-PPP per capita is exceptionally low, indicating that the average citizen has very limited purchasing power. This translates to a lack of access to basic necessities and a struggle for survival. Other economic indicators, such as unemployment rates, inflation rates, and levels of foreign debt, also paint a grim picture of the economic challenges facing the country.
For example, high inflation rates can erode the value of already limited incomes, making it even more difficult for people to afford food, shelter, and other essential items. High levels of foreign debt can strain government resources, diverting funds away from social programs and infrastructure development.
Here’s a table comparing economic indicators of South Sudan with a developed nation:
| Indicator | South Sudan | United States |
|---|---|---|
| GDP-PPP per capita | $455 | $85,373 |
| Unemployment Rate | High | Low |
| Inflation Rate | High | Low |
| Foreign Debt | High | Moderate |
These figures demonstrate the stark contrast in economic conditions between South Sudan and a developed nation, highlighting the urgent need for economic reforms and assistance.
5. The Role of International Aid
How effective is international aid in alleviating poverty in countries like South Sudan?
International aid plays a critical role in providing humanitarian assistance and supporting development efforts in the world’s poorest countries. However, the effectiveness of aid depends on various factors, including how it is delivered, who it reaches, and whether it addresses the root causes of poverty.
In South Sudan, international aid is essential for providing food, water, healthcare, and shelter to millions of people in need. Organizations such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and various NGOs are involved in delivering aid and implementing development programs.
However, aid can be less effective due to corruption, political instability, and a lack of coordination among different aid organizations. There have been instances where aid has been diverted or misused, failing to reach those who need it most. Additionally, aid that does not address the underlying causes of poverty, such as weak governance and lack of economic diversification, may have limited long-term impact.
According to a study by the Overseas Development Institute, aid effectiveness can be improved by strengthening local governance, promoting transparency and accountability, and investing in education and healthcare. It is also important to involve local communities in the design and implementation of aid programs to ensure that they are tailored to their specific needs.
6. Factors Contributing to Global Poverty
What are the overarching factors that contribute to the persistence of poverty on a global scale?
Global poverty is a complex issue with deep-rooted causes that extend beyond individual countries. Several overarching factors contribute to the persistence of poverty worldwide. These include:
- Historical Factors: Colonialism and exploitation have left many countries with weak economies and political systems.
- Economic Systems: Unfair trade practices and global economic policies can disadvantage developing countries.
- Political Instability: Conflict, corruption, and weak governance hinder economic development.
- Environmental Factors: Climate change, natural disasters, and resource scarcity disproportionately affect poor countries.
- Social Inequality: Discrimination based on gender, ethnicity, and other factors limits opportunities for marginalized groups.
These factors often interact and reinforce each other, creating cycles of poverty that are difficult to break. For example, a country with a history of colonialism may struggle with weak governance and corruption, which in turn hinders economic development and perpetuates poverty.
According to a report by Oxfam, inequality is a major driver of global poverty. The gap between the rich and the poor is widening in many countries, with a small elite controlling a disproportionate share of wealth and resources. This inequality limits opportunities for the majority of the population and makes it more difficult to escape poverty.
7. Strategies for Poverty Reduction
What strategies have proven effective in reducing poverty and promoting economic development?
Poverty reduction requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the symptoms and the root causes of poverty. Several strategies have proven effective in reducing poverty and promoting economic development. These include:
- Investing in Education and Healthcare: Improving access to quality education and healthcare can enhance human capital and productivity.
- Promoting Economic Growth: Creating jobs and opportunities for economic advancement can lift people out of poverty.
- Strengthening Governance: Promoting transparency, accountability, and the rule of law can reduce corruption and improve public services.
- Empowering Women: Providing women with equal opportunities and access to resources can boost economic growth and reduce poverty.
- Addressing Climate Change: Taking action to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts can protect vulnerable communities.
- Promoting Social Protection: Providing social safety nets, such as cash transfers and food assistance, can help families cope with economic shocks.
These strategies are most effective when implemented in a coordinated and integrated manner, with the active participation of local communities. For example, investing in education and healthcare can improve human capital, but it is also important to create jobs and opportunities for economic advancement so that people can put their skills to use.
A study by the World Bank found that countries that have made significant progress in reducing poverty have typically invested heavily in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, while also promoting economic growth and strengthening governance.
8. Success Stories in Poverty Alleviation
Are there any examples of countries that have successfully reduced poverty and improved living standards?
Despite the challenges of global poverty, there are several examples of countries that have made significant progress in reducing poverty and improving living standards. These success stories offer valuable lessons and insights for other countries facing similar challenges.
- China: Over the past few decades, China has lifted hundreds of millions of people out of poverty through economic reforms, investments in infrastructure, and targeted poverty reduction programs.
- Vietnam: Vietnam has made significant progress in reducing poverty through economic liberalization, investments in education, and improvements in agricultural productivity.
- Bangladesh: Bangladesh has reduced poverty through investments in education, healthcare, and microfinance, as well as through its vibrant garment industry.
These countries have different contexts and approaches, but they share some common characteristics. They have all prioritized economic growth, invested in human capital, and implemented policies that promote social inclusion. They have also benefited from strong leadership and a commitment to poverty reduction.
According to a report by the United Nations Development Programme, success in poverty alleviation requires a long-term commitment, a comprehensive approach, and a focus on equity and sustainability. It also requires adapting strategies to the specific context and needs of each country.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions related to poverty and economic development:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between absolute and relative poverty? | Absolute poverty refers to a lack of basic necessities such as food, shelter, and clothing. Relative poverty refers to a lack of resources compared to others in a given society. |
| How is poverty measured? | Poverty is typically measured using indicators such as GDP per capita, poverty rates, and the Gini coefficient, which measures income inequality. |
| What are the main causes of poverty? | The main causes of poverty include historical factors, economic systems, political instability, environmental factors, and social inequality. |
| What is the role of education in poverty reduction? | Education can enhance human capital, increase productivity, and create opportunities for economic advancement. |
| How can international aid be made more effective? | International aid can be made more effective by strengthening local governance, promoting transparency and accountability, and investing in education and healthcare. |
| What is the impact of climate change on poverty? | Climate change can exacerbate poverty by increasing the frequency and severity of natural disasters, disrupting agricultural production, and displacing communities. |
| How can women be empowered to reduce poverty? | Women can be empowered by providing them with equal opportunities and access to resources, such as education, healthcare, and credit. |
| What is the role of entrepreneurship in poverty reduction? | Entrepreneurship can create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and provide opportunities for people to lift themselves out of poverty. |
| How can technology be used to reduce poverty? | Technology can improve access to information, education, and healthcare, as well as create new economic opportunities. |
| What are some examples of successful poverty reduction programs? | Examples of successful poverty reduction programs include conditional cash transfers, microfinance, and public works programs. |
These FAQs provide a broader understanding of poverty-related issues and the strategies for addressing them.
10. The Impact of Global Events on Poverty
How do global events, such as pandemics and economic crises, affect poverty levels in vulnerable countries?
Global events can have a significant impact on poverty levels, particularly in vulnerable countries with weak economies and limited social safety nets. Pandemics, economic crises, and other global shocks can disrupt economic activity, reduce incomes, and increase unemployment, pushing more people into poverty.
The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, had a devastating impact on poverty levels around the world. Lockdowns and travel restrictions disrupted supply chains, reduced tourism, and forced many businesses to close, leading to widespread job losses and income reductions. According to the World Bank, the pandemic pushed an estimated 100 million people into extreme poverty.
Economic crises, such as the global financial crisis of 2008, can also have a significant impact on poverty levels. These crises can lead to declines in economic growth, reductions in trade and investment, and increases in unemployment, pushing more people into poverty.
To mitigate the impact of global events on poverty, it is important for countries to have strong social safety nets, diversified economies, and effective risk management strategies. It is also important for the international community to provide support to vulnerable countries during times of crisis.
11. The Link Between Conflict and Poverty
How does armed conflict contribute to poverty and hinder economic development?
Armed conflict has a devastating impact on poverty and economic development. It disrupts economic activity, destroys infrastructure, displaces communities, and undermines social cohesion. Conflict can also lead to human rights abuses, food insecurity, and a breakdown in the rule of law, making it more difficult for people to escape poverty.
In countries affected by conflict, resources are often diverted away from essential services such as education and healthcare, further exacerbating poverty. Conflict can also create a climate of fear and uncertainty, discouraging investment and hindering economic growth.
According to a study by the United Nations, countries affected by conflict tend to have much higher poverty rates than countries that are at peace. Conflict also undermines progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals, making it more difficult to achieve targets related to poverty reduction, education, and health.
To address the link between conflict and poverty, it is important to prevent conflicts from erupting in the first place, and to address the root causes of conflict when they do occur. It is also important to provide support to countries affected by conflict, including humanitarian assistance, peacekeeping operations, and development aid.
12. The Role of Governance and Corruption
How does good governance and the absence of corruption contribute to poverty reduction?
Good governance and the absence of corruption are essential for poverty reduction and sustainable development. Good governance ensures that resources are used effectively, that public services are delivered efficiently, and that the rule of law is upheld. Corruption, on the other hand, diverts resources away from essential services, undermines public trust, and hinders economic growth.
In countries with good governance, governments are accountable to their citizens, and there is transparency in decision-making. This creates a level playing field for businesses, encourages investment, and promotes economic growth. Good governance also ensures that social safety nets are in place to protect vulnerable populations.
Corruption can take many forms, including bribery, embezzlement, and cronyism. It can affect all levels of government, from local officials to national leaders. Corruption undermines economic development by diverting resources away from essential services, discouraging investment, and creating a climate of uncertainty.
According to a report by Transparency International, countries with high levels of corruption tend to have lower levels of economic development and higher poverty rates. Addressing corruption requires a multifaceted approach, including strengthening institutions, promoting transparency and accountability, and empowering citizens to hold their leaders accountable.
13. The Importance of Sustainable Development
How does sustainable development contribute to long-term poverty reduction and environmental protection?
Sustainable development is an approach to development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves balancing economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection.
Sustainable development is essential for long-term poverty reduction because it ensures that economic growth is not achieved at the expense of the environment or social equity. It promotes the efficient use of resources, reduces pollution, and protects biodiversity, ensuring that future generations have access to the resources they need to thrive.
Sustainable development also promotes social inclusion by ensuring that all members of society have access to opportunities and resources, regardless of their gender, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status. It promotes education, healthcare, and social safety nets, helping to reduce inequality and poverty.
According to the United Nations, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for achieving sustainable development by 2030. The SDGs address a wide range of issues, including poverty reduction, education, health, gender equality, climate action, and environmental protection. Achieving the SDGs requires a concerted effort by governments, businesses, civil society, and individuals.
14. The Impact of Education on Breaking the Cycle of Poverty
How does education serve as a powerful tool for breaking the cycle of poverty?
Education is a fundamental tool for breaking the cycle of poverty. It equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and confidence they need to improve their lives and contribute to their communities. Education can lead to better job opportunities, higher incomes, and improved health outcomes.
Education also promotes social mobility, allowing people from disadvantaged backgrounds to climb the economic ladder. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions, participate in civic life, and advocate for their rights. Education can also transform communities by fostering innovation, promoting tolerance, and strengthening social cohesion.
In developing countries, investing in education can have a significant impact on poverty reduction. Studies have shown that each additional year of schooling can increase an individual’s earnings by 10 percent or more. Education also leads to improved health outcomes, reduced child mortality rates, and increased gender equality.
However, access to quality education remains a challenge in many developing countries. Schools may lack adequate resources, teachers may be poorly trained, and children may be forced to drop out due to poverty or conflict. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort by governments, communities, and international organizations.
15. Call to Action: Addressing Global Poverty Together
What can individuals and organizations do to help address global poverty?
Addressing global poverty requires a collective effort by individuals, organizations, governments, and the international community. There are many ways that individuals can contribute to poverty reduction, including:
- Supporting Organizations: Donating to organizations that work to alleviate poverty, such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and various NGOs.
- Advocating for Policies: Supporting policies that promote economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection.
- Making Informed Choices: Buying products from companies that are committed to fair labor practices and sustainable production.
- Volunteering Time: Volunteering time to organizations that work to alleviate poverty in local communities or abroad.
- Raising Awareness: Raising awareness about the causes and consequences of poverty and the strategies for addressing it.
Organizations can also play a critical role in poverty reduction by:
- Implementing Effective Programs: Implementing programs that address the root causes of poverty, such as lack of education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability: Promoting transparency and accountability in their operations and ensuring that resources are used effectively.
- Collaborating with Others: Collaborating with other organizations, governments, and communities to achieve common goals.
- Advocating for Policy Changes: Advocating for policy changes that promote poverty reduction and sustainable development.
- Measuring Impact: Measuring the impact of their programs and using data to improve their effectiveness.
By working together, we can make a significant difference in reducing global poverty and creating a more just and equitable world.
Do you have any burning questions about global poverty or other topics? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question for free. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you need.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn