What Is The Temperature In Now? Finding out the current temperature is crucial for planning your day, choosing the right clothes, or simply satisfying your curiosity. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide instant access to accurate temperature information and answers to your weather-related questions, making your life easier. Discover precise readings and forecasts today and explore related weather patterns effortlessly.
1. Understanding Current Temperature Measurement
The current temperature is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives. But what exactly does it mean, and how is it measured? Let’s break it down.
1.1. Defining Temperature
Temperature is essentially a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. The faster the particles move, the higher the temperature, and vice versa. It’s a fundamental physical quantity that dictates how hot or cold something is. This measurement is essential for understanding weather patterns, climate change, and various scientific processes.
1.2. Common Temperature Scales
There are primarily three temperature scales used worldwide:
- Celsius (°C): This scale is widely used in most countries and in scientific contexts. On the Celsius scale, 0°C is the freezing point of water, and 100°C is the boiling point.
- Fahrenheit (°F): Predominantly used in the United States, the Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F.
- Kelvin (K): Used in scientific applications, the Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale where 0 K is absolute zero, the point at which all molecular motion stops.
Understanding these scales helps interpret temperature readings and convert between them as needed.
1.3. Tools for Measuring Temperature
Various instruments are used to measure temperature, each with its own advantages:
- Thermometers: Traditional thermometers use the expansion and contraction of a liquid (like mercury or alcohol) to indicate temperature.
- Digital Thermometers: These provide a digital readout and are often more precise than traditional thermometers.
- Infrared Thermometers: These measure temperature from a distance by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object.
- Weather Stations: These comprehensive devices measure various weather parameters, including temperature, humidity, and wind speed, often providing real-time data.
1.4. Accuracy and Precision in Temperature Measurement
Accuracy and precision are crucial in temperature measurement. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to the repeatability of a measurement. High-quality instruments and proper calibration are essential to ensure accurate and precise temperature readings. This is particularly important in scientific research, weather forecasting, and industrial applications.
1.5. Factors Affecting Temperature Readings
Several factors can influence temperature readings:
- Location: Temperature varies significantly based on geographical location, altitude, and proximity to bodies of water.
- Time of Day: Temperature typically fluctuates throughout the day, with the warmest temperatures usually occurring in the afternoon and the coolest in the early morning.
- Weather Conditions: Cloud cover, wind speed, and precipitation can all affect temperature readings.
- Instrument Placement: The placement of a thermometer can significantly impact its readings. It should be placed in a shaded, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
Understanding these factors helps in interpreting temperature data and making informed decisions. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we strive to provide temperature readings that account for these variables, ensuring you get the most accurate information possible.
2. Decoding Weather Forecasts
Weather forecasts are essential for planning our daily activities. They provide valuable insights into future temperature conditions, precipitation, and other weather phenomena. Here’s how to decode them effectively.
2.1. Understanding Forecast Terminology
Weather forecasts use specific terms that can sometimes be confusing. Here’s a breakdown of common terms:
- High/Low: The highest and lowest predicted temperatures for the day.
- Chance of Precipitation: The probability of rain, snow, or other forms of precipitation occurring in a specific area. For example, a 30% chance of rain means there’s a 30% likelihood that rain will fall in any given location within the forecast area.
- Humidity: The amount of moisture in the air, expressed as a percentage. High humidity can make the air feel hotter, while low humidity can make it feel cooler.
- Wind Speed and Direction: The speed at which the wind is blowing and the direction from which it is coming.
- Cloud Cover: The amount of the sky covered by clouds, expressed as a percentage.
- UV Index: A measure of the level of ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which can help you protect your skin from sunburn.
2.2. Common Weather Symbols and Icons
Weather forecasts often use symbols and icons to represent different weather conditions. Common symbols include:
- Sun: Indicates sunny conditions.
- Cloud: Represents cloudy conditions.
- Raindrop: Indicates rain.
- Snowflake: Represents snow.
- Thunderstorm: Indicates thunderstorms.
- Partly Cloudy: Represents partly cloudy conditions.
These symbols provide a quick visual summary of the expected weather conditions.
2.3. Types of Weather Forecasts
Weather forecasts come in various forms, each providing different levels of detail:
- Short-Range Forecasts: These cover the next few hours to a couple of days and are generally the most accurate.
- Medium-Range Forecasts: These extend from three to seven days and provide a broader overview of expected weather conditions.
- Long-Range Forecasts: These cover periods beyond seven days and are less precise due to the increasing uncertainty in predicting weather patterns over longer timeframes.
- Hourly Forecasts: These provide detailed information about temperature, precipitation, and other weather conditions for each hour of the day.
2.4. Interpreting Temperature Ranges
Weather forecasts often provide temperature ranges rather than single values. This range reflects the uncertainty in predicting the exact temperature. The actual temperature may fall anywhere within this range, so it’s essential to consider the entire range when planning your activities. For example, a forecast of 20-25°C means the temperature is expected to be somewhere between 20 and 25 degrees Celsius.
2.5. Limitations of Weather Forecasts
While weather forecasts are valuable, they are not always perfect. Several factors can limit their accuracy:
- Complexity of Weather Systems: Weather systems are complex and dynamic, making them challenging to predict accurately.
- Data Limitations: Weather models rely on data collected from various sources, but these data may be incomplete or inaccurate.
- Model Imperfections: Weather models are based on mathematical equations that approximate the behavior of the atmosphere, but these models are not perfect and can produce errors.
- Chaotic Behavior: The atmosphere exhibits chaotic behavior, meaning small changes in initial conditions can lead to significant differences in the forecast.
Despite these limitations, weather forecasts are constantly improving due to advancements in technology and scientific understanding. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide the latest and most reliable weather forecasts to help you stay informed and prepared.
3. The Impact of Temperature on Daily Life
Temperature significantly influences various aspects of our daily lives, from health and safety to comfort and productivity. Understanding these impacts can help us make informed decisions and adapt to changing weather conditions.
3.1. Temperature and Health
Temperature extremes can have significant effects on our health:
- Heatstroke: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to heatstroke, a life-threatening condition characterized by high body temperature, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
- Hypothermia: Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can lead to hypothermia, a condition in which the body loses heat faster than it can produce it, resulting in dangerously low body temperature.
- Respiratory Issues: Extreme temperatures can exacerbate respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis.
- Cardiovascular Problems: High temperatures can put extra strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Staying informed about temperature conditions and taking appropriate precautions can help protect your health.
3.2. Temperature and Safety
Temperature also plays a crucial role in safety:
- Driving Conditions: Extreme temperatures can affect driving conditions, with icy roads in winter and overheated engines in summer.
- Outdoor Activities: High temperatures can increase the risk of heat exhaustion and dehydration during outdoor activities, while cold temperatures can increase the risk of frostbite and hypothermia.
- Home Safety: Extreme temperatures can affect home safety, with increased risk of fires from heating systems in winter and electrical overload from air conditioning systems in summer.
3.3. Temperature and Comfort
Temperature greatly influences our comfort levels:
- Clothing Choices: We adjust our clothing choices based on the temperature to stay comfortable, wearing lighter clothes in warm weather and heavier clothes in cold weather.
- Indoor Environment: We use heating and cooling systems to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, ensuring a pleasant living and working environment.
- Sleep Quality: Temperature can affect sleep quality, with extreme temperatures disrupting our ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
3.4. Temperature and Productivity
Temperature can impact our productivity levels:
- Work Performance: Extreme temperatures can decrease work performance, with high temperatures leading to fatigue and decreased concentration, and cold temperatures leading to stiffness and decreased dexterity.
- Learning Environment: Temperature can affect the learning environment, with comfortable temperatures promoting better focus and retention of information.
- Outdoor Work: Temperature can impact the safety and efficiency of outdoor work, with extreme temperatures requiring frequent breaks and adjustments to work schedules.
3.5. Temperature and Agriculture
Temperature is a critical factor in agriculture:
- Crop Growth: Temperature affects the growth and development of crops, with different crops requiring different temperature ranges for optimal growth.
- Growing Seasons: Temperature determines the length of growing seasons, with warmer temperatures allowing for longer growing seasons and increased crop yields.
- Pest and Disease Control: Temperature can affect the prevalence of pests and diseases, with warmer temperatures promoting the spread of certain pests and diseases.
Understanding the impact of temperature on agriculture is essential for ensuring food security and sustainable farming practices.
4. Climate Change and Temperature Trends
Climate change is causing significant shifts in global temperature patterns, with far-reaching consequences for our planet. Understanding these trends is crucial for addressing the challenges of a changing climate.
4.1. Understanding Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature and weather patterns. These shifts may be natural, but since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gas), which produces heat-trapping gases.
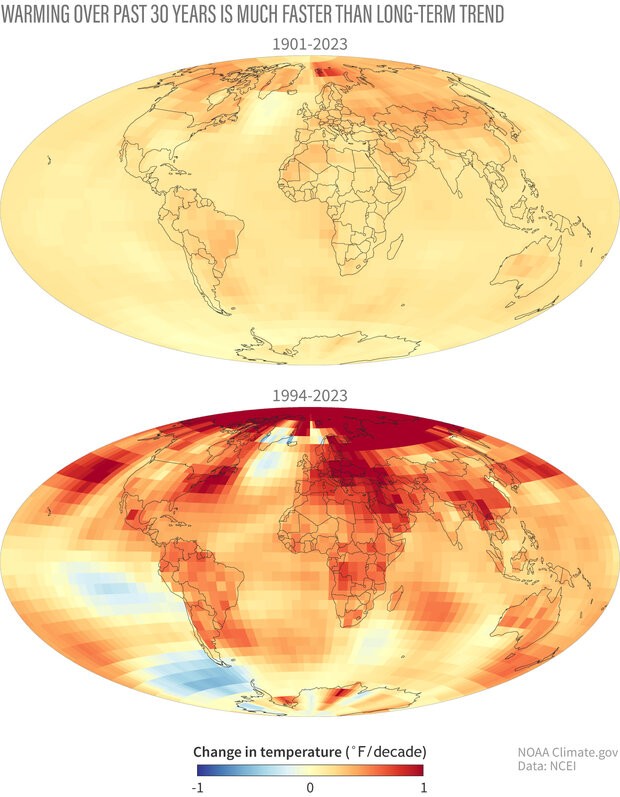
4.2. Historical Temperature Trends
Historical temperature records show a clear warming trend over the past century. According to NOAA’s 2023 Annual Climate Report the combined land and ocean temperature has increased at an average rate of 0.11° Fahrenheit (0.06° Celsius) per decade since 1850, or about 2° F in total. The rate of warming since 1982 is more than three times as fast: 0.36° F (0.20° C) per decade. This warming trend is largely attributed to human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases.
4.3. Current Global Temperature Anomalies
Global temperature anomalies refer to the difference between the observed temperature and the long-term average temperature. Current global temperature anomalies show that the Earth is warming at an alarming rate. Years like 2023 have set new records for the warmest years, with temperatures exceeding the long-term average by significant margins.
4.4. Regional Variations in Temperature Change
While the Earth is warming overall, the rate of warming varies across different regions. The Arctic, for example, is warming at a much faster rate than the global average, due to the loss of reflective ice and snow. Other regions, such as the interior continents, are also experiencing significant warming, while some ocean areas are warming more slowly.
4.5. Future Temperature Projections
Future temperature projections indicate that the Earth will continue to warm in the coming decades, with the amount of warming depending on future greenhouse gas emissions. According to the 2017 U.S. Climate Science Special Report, if yearly emissions continue to increase rapidly, models project that by the end of this century, global temperature will be at least 5 degrees Fahrenheit warmer than the 1901-1960 average, and possibly as much as 10.2 degrees warmer. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential to mitigate future warming and avoid the most severe impacts of climate change.
5. Finding Accurate Temperature Information
Accessing accurate temperature information is crucial for making informed decisions and staying safe. There are several reliable sources for obtaining current temperature readings and forecasts.
5.1. Reliable Weather Websites and Apps
Numerous weather websites and apps provide accurate and up-to-date temperature information. Some of the most popular and reliable include:
- WHAT.EDU.VN: Offers real-time temperature data and comprehensive weather forecasts.
- The National Weather Service (NWS): Provides official weather forecasts, warnings, and information for the United States.
- AccuWeather: A global weather forecasting service offering detailed forecasts and real-time weather conditions.
- The Weather Channel: A popular source for weather news, forecasts, and information.
- Google Weather: Provides quick and easy access to current temperature and forecasts via Google Search.
5.2. Local News Channels
Local news channels often provide weather reports as part of their broadcasts. These reports typically include current temperature readings, forecasts, and weather-related news and updates. Local news channels can be a reliable source for temperature information specific to your area.
5.3. Weather APIs and Data Services
Weather APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and data services provide programmatic access to weather data, including temperature readings. These services are often used by developers to integrate weather information into their applications and websites. Popular weather APIs include:
- OpenWeatherMap: Provides access to current weather data, forecasts, and historical weather data.
- AccuWeather API: Offers a wide range of weather data and forecasting services.
- Weatherbit: Provides accurate and reliable weather data for various applications.
5.4. Understanding Data Sources
It’s essential to understand the sources of temperature data to assess its reliability. Temperature data is typically collected from various sources, including:
- Weather Stations: Ground-based weather stations provide direct temperature measurements.
- Satellites: Satellites provide remote sensing data, including temperature measurements over large areas.
- Weather Models: Weather models use mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and predict future temperature conditions.
- Weather Balloons: Weather balloons carry instruments into the atmosphere to measure temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
5.5. Cross-Referencing Information
To ensure accuracy, it’s a good idea to cross-reference temperature information from multiple sources. Compare temperature readings and forecasts from different websites, apps, and news channels to get a more comprehensive and reliable picture of current and future temperature conditions. This can help you make more informed decisions and stay prepared for changing weather conditions.
6. Practical Tips for Dealing with Different Temperatures
Knowing what the temperature is now is only the first step. It’s also important to know how to deal with different temperature conditions to stay safe, comfortable, and productive.
6.1. Dressing Appropriately
Dressing appropriately for the temperature is crucial for maintaining comfort and preventing health issues. Here are some tips:
- Warm Weather: Wear lightweight, breathable clothing such as cotton or linen. Choose light colors to reflect sunlight and stay cooler.
- Cold Weather: Wear layers of clothing to trap heat and stay warm. Choose insulating materials such as wool or fleece. Cover exposed skin to prevent frostbite.
- Rainy Weather: Wear waterproof clothing and footwear to stay dry. Carry an umbrella or raincoat.
- Changing Weather: Dress in layers that can be easily added or removed as the temperature changes.
6.2. Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated is essential, especially in extreme temperatures. Here are some tips:
- Warm Weather: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to replace fluids lost through sweat. Avoid sugary drinks and alcohol, which can dehydrate you.
- Cold Weather: Drink warm beverages such as tea or soup to stay warm and hydrated.
- Physical Activity: Drink extra fluids before, during, and after physical activity to replace fluids lost through sweat.
6.3. Adjusting Indoor Environments
Adjusting the indoor environment can help maintain comfortable temperatures:
- Heating: Use heating systems to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature in cold weather. Ensure heating systems are properly maintained to prevent fires and carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Cooling: Use air conditioning systems or fans to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature in warm weather. Ensure air conditioning systems are properly maintained to prevent breakdowns and energy waste.
- Ventilation: Use ventilation systems to circulate fresh air and remove stale air. Open windows and doors when the weather permits.
6.4. Protecting Skin
Protecting your skin from the sun and cold is important:
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen with a high SPF to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays. Wear protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses.
- Cold Protection: Use moisturizers to prevent dry skin. Cover exposed skin to prevent frostbite.
6.5. Modifying Activities
Modifying activities based on the temperature can help prevent health issues and ensure safety:
- Warm Weather: Avoid strenuous activities during the hottest part of the day. Take frequent breaks and stay in the shade.
- Cold Weather: Avoid prolonged exposure to cold temperatures. Take frequent breaks and stay warm.
- Dangerous Conditions: Avoid outdoor activities during dangerous weather conditions such as thunderstorms or blizzards.
7. Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect
The urban heat island effect is a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. Understanding this effect can help you make informed decisions about living and working in urban environments.
7.1. What is the Urban Heat Island Effect?
The urban heat island effect occurs because urban areas have more surfaces that absorb and retain heat, such as asphalt and concrete. Buildings and paved surfaces also reduce vegetation and natural cooling, leading to higher temperatures.
7.2. Factors Contributing to the Effect
Several factors contribute to the urban heat island effect:
- Surface Materials: Asphalt and concrete absorb and retain more heat than natural surfaces such as vegetation and soil.
- Reduced Vegetation: Urban areas have less vegetation, which reduces natural cooling through evapotranspiration.
- Building Density: Buildings trap heat and reduce airflow, leading to higher temperatures.
- Human Activities: Human activities such as traffic and industrial processes generate heat, contributing to the urban heat island effect.
7.3. Impact on Urban Temperatures
The urban heat island effect can significantly increase urban temperatures, especially during the summer months. Urban areas can be several degrees warmer than surrounding rural areas, leading to increased energy consumption, air pollution, and health issues.
7.4. Mitigation Strategies
Several strategies can mitigate the urban heat island effect:
- Increasing Vegetation: Planting trees and creating green spaces can increase natural cooling and reduce temperatures.
- Using Cool Roofs: Using reflective roofing materials can reduce the amount of heat absorbed by buildings.
- Using Permeable Pavement: Using permeable pavement can reduce runoff and increase evapotranspiration, leading to lower temperatures.
- Reducing Traffic: Reducing traffic congestion and promoting alternative transportation can reduce heat generated by vehicles.
7.5. Benefits of Mitigation
Mitigating the urban heat island effect can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Lowering temperatures can reduce the need for air conditioning, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
- Improved Air Quality: Lower temperatures can reduce the formation of ground-level ozone, improving air quality and reducing respiratory issues.
- Enhanced Public Health: Lower temperatures can reduce the risk of heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses.
- Increased Comfort: Lower temperatures can increase comfort levels and improve the quality of life for urban residents.
8. Frequently Asked Questions About Temperature
Here are some frequently asked questions about temperature, along with their answers:
8.1. What is the average global temperature?
The average global temperature is about 15°C (59°F). However, this is just an average, and temperatures vary significantly depending on location and time of year.
8.2. What is the highest temperature ever recorded on Earth?
The highest temperature ever recorded on Earth was 56.7°C (134°F) in Death Valley, California, on July 10, 1913.
8.3. What is the lowest temperature ever recorded on Earth?
The lowest temperature ever recorded on Earth was -89.2°C (-128.6°F) at the Vostok Station in Antarctica on July 21, 1983.
8.4. How does altitude affect temperature?
Temperature decreases with altitude. On average, temperature decreases by about 6.5°C (11.7°F) for every 1,000 meters (3,300 feet) increase in altitude.
8.5. How does humidity affect how we feel temperature?
High humidity makes the air feel hotter because it reduces the rate at which sweat evaporates from our skin, hindering our body’s natural cooling mechanism. This is known as the heat index.
8.6. What is wind chill?
Wind chill is the perceived decrease in air temperature felt by the body on exposed skin due to the flow of air. The wind chill effect increases as wind speed increases.
8.7. How do weather forecasts predict temperature?
Weather forecasts use weather models to predict temperature. These models use mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and predict future temperature conditions based on current weather data and historical weather patterns.
8.8. What are the main factors that influence local temperature?
Local temperature is influenced by various factors, including latitude, altitude, proximity to bodies of water, weather patterns, and local conditions such as vegetation and urbanization.
8.9. What is the difference between temperature and heat?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance, while heat is the transfer of energy from one object to another due to a temperature difference.
8.10. How can I protect myself from extreme temperatures?
You can protect yourself from extreme temperatures by dressing appropriately, staying hydrated, adjusting indoor environments, protecting your skin, and modifying your activities based on the temperature conditions.
9. Stay Informed with WHAT.EDU.VN
Staying informed about the temperature in your area is essential for planning your day, ensuring your comfort, and protecting your health. WHAT.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive platform to get accurate and timely temperature information.
9.1. Real-Time Temperature Updates
WHAT.EDU.VN provides real-time temperature updates for locations around the world. Our data is sourced from reliable weather stations and updated frequently to ensure you have the most current information available.
9.2. Detailed Weather Forecasts
In addition to real-time temperature updates, WHAT.EDU.VN offers detailed weather forecasts for the coming days. Our forecasts include information on temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and other weather conditions, helping you plan your activities with confidence.
9.3. Interactive Weather Maps
WHAT.EDU.VN features interactive weather maps that allow you to visualize temperature patterns and weather conditions in your area. Our maps include temperature overlays, radar imagery, and other useful information.
9.4. Weather Alerts and Notifications
WHAT.EDU.VN provides weather alerts and notifications to keep you informed about severe weather conditions in your area. You can sign up for email or SMS alerts to receive notifications about extreme temperatures, storms, and other weather-related hazards.
9.5. Expert Weather Insights
WHAT.EDU.VN offers expert weather insights and analysis from experienced meteorologists. Our experts provide detailed explanations of weather patterns and trends, helping you understand the science behind the weather.
9.6. Community Q&A
Have a question about the weather? WHAT.EDU.VN provides a community Q&A platform where you can ask questions and get answers from other users and weather experts. Share your knowledge and learn from others in our weather-focused community.
9.7. Accessible and User-Friendly
WHAT.EDU.VN is designed to be accessible and user-friendly, making it easy for anyone to find the temperature information they need. Our website and mobile app are optimized for speed and performance, ensuring you can quickly access the information you need, no matter where you are.
9.8. Free Access to Information
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we believe that everyone should have access to accurate weather information. That’s why we offer our services for free. You can access real-time temperature updates, detailed weather forecasts, and other weather-related information without any cost.
9.9. Constantly Improving
We are constantly working to improve WHAT.EDU.VN and provide the best possible weather information. We regularly update our data sources, refine our forecasting models, and add new features to enhance your experience.
9.10. Connect with Us
Stay connected with WHAT.EDU.VN and get the latest weather updates and information. Visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN or contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Let WHAT.EDU.VN be your trusted source for all things weather.
Don’t let unpredictable weather catch you off guard. Ask your weather-related questions on what.edu.vn today and receive free, reliable answers from our community of experts. Stay informed, stay safe, and make the most of every day with accurate temperature information at your fingertips!