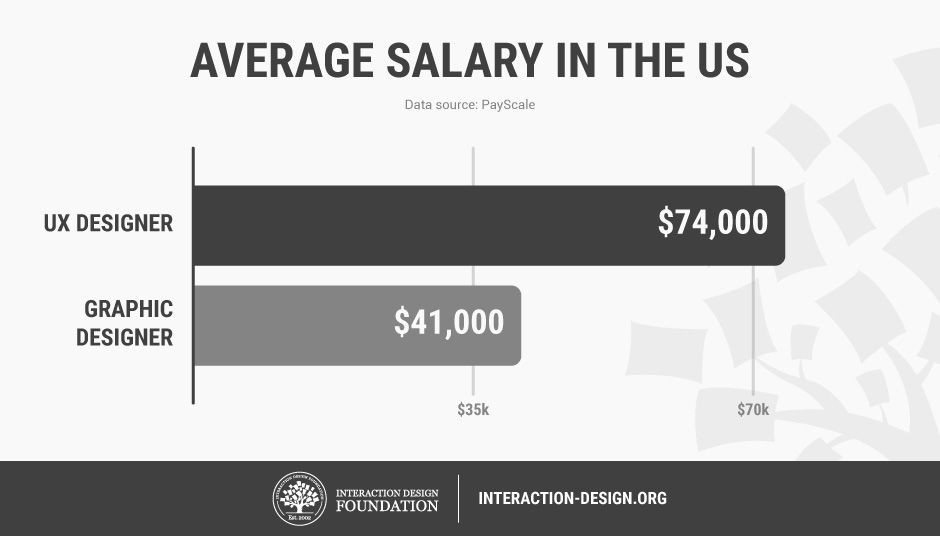
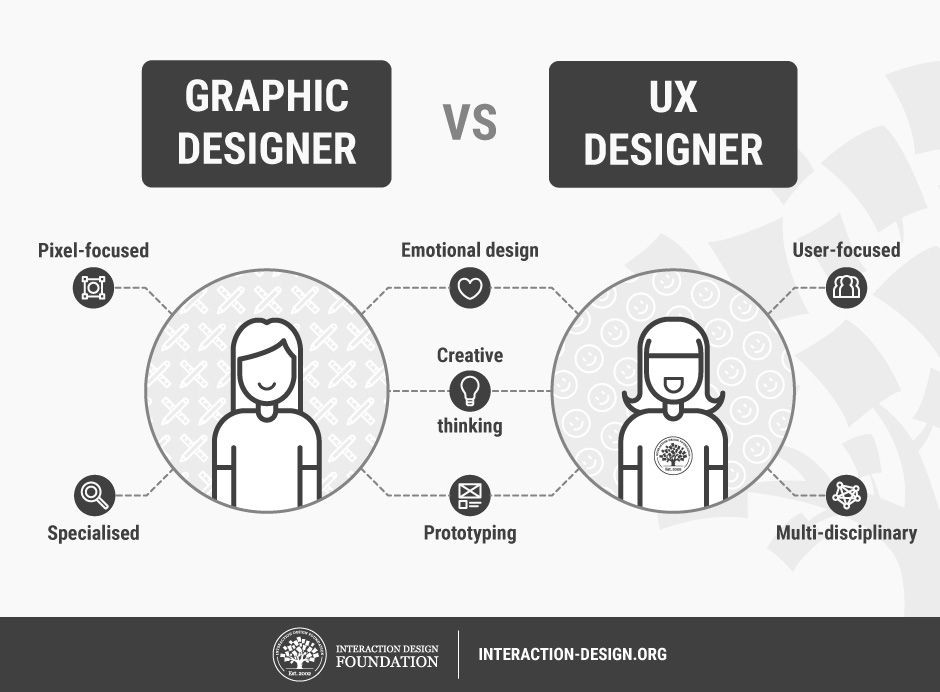
User experience (UX) design is about creating products that provide the best possible experience for users. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we believe in simplifying complex topics like UX design to make them accessible to everyone. Learn about UX design principles, career paths, and essential skills, and discover how a user-centered approach enhances digital experiences.
Here’s a look at the user-centered design, usability testing, and information architecture.
1. What Is User Experience (UX) Design?
UX design is the process of creating products that are useful, easy to use, and enjoyable for users. A UX designer focuses on the entire user journey, from the initial interaction to the final experience, ensuring it aligns with user needs and business goals. This involves understanding user behaviors, conducting research, and testing designs to create seamless and satisfying interactions.
Expanding on this, UX design involves a deep understanding of several key components:
- User Research: Understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations through methods like surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
- Information Architecture: Organizing and structuring content in a way that is intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Interaction Design: Designing the way users interact with a product, ensuring it is logical and efficient.
- Usability Testing: Evaluating a design by testing it with real users to identify and fix any issues.
- Visual Design: Creating an aesthetically pleasing and brand-consistent interface.
These components work together to create a holistic and positive user experience. According to a study by the Nielsen Norman Group, investing in UX design can lead to a significant increase in conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
2. What Are the Core Principles of UX Design?
Effective UX design is guided by several core principles that ensure the final product is user-friendly and meets their needs. These principles include:
- Usability: The product should be easy to use and navigate.
- Accessibility: The product should be accessible to users of all abilities, including those with disabilities.
- Desirability: The product should be visually appealing and enjoyable to use.
- Value: The product should provide value to the user by solving a problem or meeting a need.
- Findability: The product should be easy to find and discover.
These principles are not just theoretical concepts but practical guidelines that inform every stage of the design process. For instance, ensuring accessibility means adhering to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards, while prioritizing usability involves conducting thorough usability testing.
3. What Skills Are Essential for a UX Designer?
To excel in UX design, a professional needs a diverse set of skills that span both creative and analytical domains. These skills include:
- User Research: Conducting and analyzing user research to understand user behaviors and needs.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Creating wireframes and prototypes to visualize and test design ideas.
- Usability Testing: Planning and conducting usability tests to evaluate the effectiveness of a design.
- Information Architecture: Organizing and structuring content in a way that is intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Visual Communication: Communicating design ideas effectively through visuals and presentations.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with cross-functional teams, including developers, product managers, and stakeholders.
A survey by Adobe found that UX designers who possess strong collaboration and communication skills are more likely to deliver successful projects.
4. How Does UX Design Differ From UI Design?
While UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct aspects of product design. UX design focuses on the overall experience a user has with a product, while UI design focuses on the specific visual elements and interactive components that users interact with.
The key differences can be summarized as follows:
- UX Design: Focuses on the user’s journey, usability, and overall satisfaction.
- UI Design: Focuses on the visual elements, aesthetics, and interactive components of the interface.
UX design ensures that a product is easy to use and meets user needs, while UI design ensures that the product is visually appealing and engaging. Both are critical to the success of a product. According to a report by Forrester, a well-designed user interface can raise a website’s conversion rate by up to 200%.
5. What Are the Key Stages in the UX Design Process?
The UX design process typically involves several key stages, each aimed at refining and improving the user experience. These stages include:
- Research: Understanding user needs and behaviors through methods like surveys, interviews, and competitive analysis.
- Analysis: Analyzing research data to identify key insights and define user personas.
- Design: Creating wireframes, prototypes, and user flows to visualize the user experience.
- Testing: Conducting usability tests to evaluate the effectiveness of the design and identify areas for improvement.
- Implementation: Working with developers to implement the design and ensure it meets user needs.
- Evaluation: Continuously monitoring and evaluating the user experience to identify opportunities for further improvement.
Each stage is iterative, meaning that designers often revisit previous stages based on new insights or feedback. A study by the Design Management Institute found that companies that prioritize design thinking and a structured UX process see significant improvements in product success rates.
6. How Can User Research Improve UX Design?
User research is a critical component of UX design, providing valuable insights into user behaviors, needs, and motivations. By understanding users, designers can create products that are more relevant, useful, and enjoyable to use. User research can improve UX design in several ways:
- Identifying User Needs: Understanding what users want and need from a product.
- Understanding User Behaviors: Observing how users interact with a product to identify pain points and areas for improvement.
- Validating Design Decisions: Testing design ideas with real users to ensure they are effective and meet user needs.
- Creating User Personas: Developing detailed profiles of target users to inform design decisions.
- Improving Usability: Identifying and fixing usability issues to make a product easier to use.
According to a report by the UXPA (User Experience Professionals Association), incorporating user research into the design process can lead to a significant reduction in development costs and time.
7. What Are Wireframes and Prototypes in UX Design?
Wireframes and prototypes are essential tools in UX design, used to visualize and test design ideas before development begins. They serve different purposes and are used at different stages of the design process.
- Wireframes: Basic visual representations of a design, focusing on layout, structure, and content. They are typically low-fidelity and used to explore different design options.
- Prototypes: Interactive simulations of a design, allowing users to experience the functionality and flow of the product. They can be low-fidelity or high-fidelity, depending on the stage of the design process.
Wireframes help designers plan the structure of a product, while prototypes allow them to test the functionality and usability of the design. A study by Nielsen Norman Group found that prototyping can help identify and fix usability issues early in the design process, saving time and resources.
8. How Is Usability Testing Conducted in UX Design?
Usability testing is a critical method for evaluating the effectiveness of a design by testing it with real users. It involves observing users as they interact with a product, identifying any issues or pain points, and gathering feedback to improve the design. Usability testing typically involves the following steps:
- Planning: Defining the goals of the test, selecting participants, and creating tasks for them to perform.
- Recruiting: Recruiting participants who represent the target audience for the product.
- Conducting the Test: Observing participants as they interact with the product, either in person or remotely.
- Analyzing Results: Analyzing the data collected during the test to identify usability issues and areas for improvement.
- Reporting Findings: Creating a report summarizing the findings of the test and recommending changes to the design.
According to a report by the Baymard Institute, usability testing can help identify and fix critical usability issues that can impact conversion rates and user satisfaction.
9. What Is Information Architecture in UX Design?
Information architecture (IA) is the organization and structuring of content within a product, making it easy for users to navigate and find what they need. It involves creating a clear and logical structure that aligns with user expectations and business goals. Key elements of information architecture include:
- Navigation: Designing a clear and intuitive navigation system that allows users to easily find what they are looking for.
- Organization: Structuring content in a logical and consistent way, using categories, labels, and hierarchies.
- Search: Implementing an effective search function that allows users to quickly find specific content.
- Labeling: Using clear and concise labels that accurately describe the content they represent.
Effective information architecture can significantly improve the usability and findability of a product. A study by the Information Architecture Institute found that well-designed information architecture can increase user satisfaction and reduce the time it takes to find information.
10. How Does UX Design Improve Customer Satisfaction?
UX design plays a crucial role in improving customer satisfaction by creating products that are user-friendly, efficient, and enjoyable to use. When users have a positive experience with a product, they are more likely to be satisfied, loyal, and recommend the product to others. UX design improves customer satisfaction in several ways:
- Meeting User Needs: Understanding and addressing user needs and pain points.
- Improving Usability: Making products easy to use and navigate.
- Creating Engaging Experiences: Designing visually appealing and interactive interfaces.
- Providing Value: Delivering value to users by solving problems and meeting needs.
- Building Trust: Creating products that are reliable, consistent, and trustworthy.
According to a report by McKinsey, companies that prioritize customer experience see higher customer satisfaction scores and increased revenue.
11. What Are the Career Paths in UX Design?
UX design offers a variety of career paths, each with its own focus and responsibilities. Some common career paths in UX design include:
- UX Designer: Responsible for the overall user experience of a product, from research to design to testing.
- UI Designer: Focuses on the visual elements and interactive components of the interface.
- UX Researcher: Conducts user research to understand user behaviors and needs.
- Information Architect: Specializes in organizing and structuring content within a product.
- Interaction Designer: Designs the way users interact with a product, ensuring it is logical and efficient.
- Product Designer: Oversees the design of a product from start to finish, working closely with developers and product managers.
Each of these roles requires a unique set of skills and expertise, but they all share a common goal: to create products that are user-friendly and meet user needs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for UX designers is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, making it a promising career path.
12. What Is the Role of Accessibility in UX Design?
Accessibility is a critical aspect of UX design, ensuring that products are usable by people of all abilities, including those with disabilities. Accessible design involves creating products that are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust, following guidelines such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). Key considerations for accessibility in UX design include:
- Providing alternative text for images: Allowing users with visual impairments to understand the content of images.
- Using clear and consistent navigation: Making it easy for users to navigate and find what they need.
- Ensuring sufficient color contrast: Making text and other elements easy to see for users with visual impairments.
- Providing keyboard navigation: Allowing users to navigate the product using a keyboard instead of a mouse.
- Using semantic HTML: Structuring content in a way that is understandable by assistive technologies.
According to the World Health Organization, over 1 billion people worldwide have some form of disability, highlighting the importance of accessible design.
13. How Can Motion Design Enhance UX?
Motion design involves using animation and visual effects to enhance the user experience. When used effectively, motion design can improve usability, engagement, and overall satisfaction. Key ways that motion design can enhance UX include:
- Providing feedback: Using animations to provide visual feedback to users, such as confirming an action or indicating progress.
- Guiding attention: Using animations to guide users’ attention to important elements on the screen.
- Enhancing visual appeal: Using animations to create a more engaging and visually appealing interface.
- Improving usability: Using animations to clarify interactions and make them easier to understand.
However, it’s important to use motion design judiciously, as excessive or poorly executed animations can be distracting or even detrimental to the user experience. A study by Google found that well-designed animations can improve user engagement and reduce cognitive load.
14. What Are Some Common UX Design Mistakes to Avoid?
Even experienced UX designers can make mistakes that negatively impact the user experience. Some common UX design mistakes to avoid include:
- Ignoring user research: Making design decisions without understanding user needs and behaviors.
- Creating cluttered interfaces: Overloading users with too much information or too many options.
- Using inconsistent design patterns: Creating designs that are inconsistent and confusing to users.
- Neglecting accessibility: Failing to consider the needs of users with disabilities.
- Ignoring usability testing: Failing to test designs with real users to identify and fix usability issues.
By avoiding these common mistakes, designers can create products that are more user-friendly and effective.
15. How Can Graphic Design Skills Benefit a UX Designer?
Graphic design skills can be a valuable asset for a UX designer, enhancing their ability to create visually appealing and engaging interfaces. Graphic design skills can benefit a UX designer in several ways:
- Visual Communication: Effectively communicating design ideas through visuals and presentations.
- Typography: Selecting and using typography effectively to improve readability and visual appeal.
- Color Theory: Understanding and applying color theory to create visually appealing and effective designs.
- Layout and Composition: Creating effective layouts and compositions that guide users’ attention and improve usability.
While UX design focuses on the overall user experience, graphic design skills can help designers create interfaces that are not only user-friendly but also visually appealing.
16. What Are the Latest Trends in UX Design?
UX design is a constantly evolving field, with new trends and technologies emerging all the time. Some of the latest trends in UX design include:
- AI-powered UX: Using artificial intelligence to personalize and optimize the user experience.
- Voice User Interface (VUI) design: Designing interfaces for voice-controlled devices and applications.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) UX: Designing immersive experiences for VR and AR applications.
- Dark Mode: Designing interfaces with a dark color scheme to reduce eye strain and improve battery life.
- Microinteractions: Using small, subtle animations and interactions to enhance the user experience.
Staying up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies can help UX designers create innovative and effective designs.
17. How Can I Learn UX Design?
There are many ways to learn UX design, from online courses to university programs. Some popular options include:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Interaction Design Foundation offer a wide range of UX design courses.
- Bootcamps: Immersive training programs that provide hands-on experience and career support.
- University Programs: Bachelor’s and master’s programs in UX design, human-computer interaction, and related fields.
- Self-Study: Learning through books, articles, and online resources.
Choosing the right learning path depends on your goals, budget, and learning style.
18. What Software and Tools Are Used in UX Design?
UX designers use a variety of software and tools to create wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs. Some popular tools include:
- Figma: A collaborative design tool used for creating wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs.
- Sketch: A vector-based design tool used for creating user interfaces and visual designs.
- Adobe XD: A UX design tool used for creating prototypes and user flows.
- InVision: A prototyping tool used for creating interactive prototypes and gathering feedback.
- Axure RP: A prototyping tool used for creating complex and interactive prototypes.
Each tool has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to choose the right tool for the job.
19. How Does UX Design Impact Business Outcomes?
UX design can have a significant impact on business outcomes, improving customer satisfaction, increasing conversion rates, and driving revenue growth. By creating products that are user-friendly and meet user needs, businesses can:
- Increase Customer Loyalty: Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend the product to others.
- Improve Conversion Rates: A well-designed user interface can make it easier for users to complete desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service.
- Reduce Support Costs: A user-friendly product can reduce the need for customer support and training.
- Drive Revenue Growth: By improving customer satisfaction and increasing conversion rates, UX design can drive revenue growth.
According to a report by Forrester, every dollar invested in UX design can result in a return of $100.
20. What Role Does Empathy Play in UX Design?
Empathy is a critical trait for UX designers, allowing them to understand and share the feelings of their users. By empathizing with users, designers can create products that are more relevant, useful, and enjoyable to use. Empathy can play a role in UX design in several ways:
- Understanding User Needs: Putting yourself in the user’s shoes to understand their needs and pain points.
- Identifying Usability Issues: Recognizing when a design is confusing or frustrating to users.
- Creating User-Centered Designs: Making design decisions that prioritize the needs and feelings of users.
By practicing empathy, designers can create products that truly resonate with their target audience.
In conclusion, UX design is a multifaceted field that requires a diverse set of skills and a deep understanding of user behaviors and needs. By following the principles and best practices of UX design, businesses can create products that are user-friendly, effective, and enjoyable to use.
Do you have more questions or need personalized advice? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and receive free answers from our community of experts. We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890 or visit our website what.edu.vn for more information. We are here to help you find the answers you need!
FAQ: User Experience (UX) Design
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main goal of UX design? | To create products that are easy to use, efficient, and satisfying for the end-user. |
| How does UX design contribute to business success? | By enhancing customer satisfaction, improving conversion rates, and reducing support costs. A positive user experience leads to increased customer loyalty and revenue. |
| What are some common methods in UX research? | User interviews, surveys, usability testing, A/B testing, and ethnographic studies are commonly used to understand user behaviors and needs. |
| What’s the difference between low-fidelity and | Low-fidelity prototypes are basic and often paper-based, used for initial concept testing. High-fidelity prototypes are more detailed and interactive, resembling the final product closely and used for more thorough usability testing. |
| What are key considerations for mobile UX design? | Responsive design, touch-friendly interfaces, minimizing data usage, and optimizing for smaller screen sizes. |
| How do you measure the effectiveness of a UX design? | Metrics such as task completion rate, error rate, time on task, customer satisfaction scores (e.g., Net Promoter Score), and conversion rates are used to assess UX design effectiveness. |
| Can you explain the concept of “user-centered design”? | User-centered design is an iterative design process where the needs, wants, and limitations of end-users are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process. |
| How does accessibility relate to UX design? | Accessibility is an integral part of UX design, ensuring that products can be used by people of all abilities. Accessible design follows guidelines such as WCAG to create inclusive and usable interfaces. |
| What are microinteractions, and why are they important? | Microinteractions are small, subtle animations or feedback responses that enhance the user experience by providing feedback, guiding attention, and creating a sense of delight. They make interfaces feel more responsive and user-friendly. |
| What are the best resources for staying updated on UX | Websites like Nielsen Norman Group, UX Booth, Interaction Design Foundation, and conferences such as UXPA International Conference provide valuable insights, articles, and resources to stay current on UX design trends and best practices. |