Vaginal atrophy, also known as atrophic vaginitis, is a common condition affecting many women, especially during and after menopause; WHAT.EDU.VN offers easy to understand explanations of this topic. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment options for vaginal atrophy, offering clear guidance and empowering you to take control of your vaginal health, additionally, we will cover related issues such as dryness, dyspareunia, and postmenopausal health.
1. Defining Vaginal Atrophy: An Overview
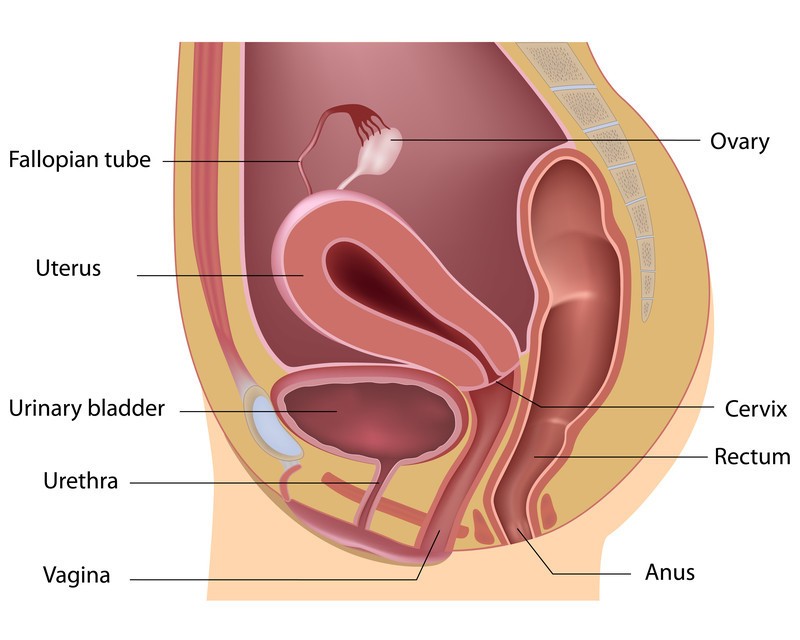
Vaginal atrophy refers to the thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls due to a decline in estrogen levels. Estrogen is crucial for maintaining vaginal tissue health, keeping it lubricated, elastic, and thick. When estrogen levels drop, the vaginal tissues become more fragile and susceptible to irritation. This condition is most commonly experienced by women during and after menopause, but it can also occur at other times in a woman’s life when estrogen levels decrease. Seeking information and understanding your body is the first step to feeling empowered.
 Microscopic view of vaginal tissue affected by atrophy
Microscopic view of vaginal tissue affected by atrophy
2. Identifying the Primary Causes of Vaginal Atrophy
Several factors can lead to decreased estrogen levels and subsequently cause vaginal atrophy. Understanding these causes is vital for prevention and targeted treatment.
- Menopause: This is the most common cause. As women approach menopause, the ovaries naturally produce less estrogen, leading to various changes in the body, including vaginal atrophy.
- Surgical Removal of Ovaries (Oophorectomy): Removing the ovaries significantly reduces estrogen production, leading to rapid onset of vaginal atrophy.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those used to treat uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or breast cancer, can lower estrogen levels, causing vaginal atrophy as a side effect.
- Breastfeeding: During breastfeeding, estrogen levels are naturally suppressed to facilitate milk production. This can lead to temporary vaginal atrophy.
- Cancer Treatments: Chemotherapy and radiation therapy, particularly when directed at the pelvic area, can damage the ovaries and decrease estrogen production.
- Premature Ovarian Failure: This condition occurs when the ovaries stop functioning before the age of 40, leading to early menopause and associated estrogen decline.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions that disrupt the balance of hormones in the body can affect estrogen levels and contribute to vaginal atrophy.
3. Recognizing the Symptoms: What to Look For
The symptoms of vaginal atrophy can vary in severity, but early recognition is key to seeking timely treatment and relief.
- Vaginal Dryness: A persistent feeling of dryness in the vagina is one of the most common symptoms.
- Burning Sensation: Many women experience a burning or itching sensation in the vaginal area.
- Painful Intercourse (Dyspareunia): Thinning and dryness of the vaginal tissues can make sexual intercourse painful.
- Light Bleeding After Intercourse: Fragile vaginal tissues can easily tear or bleed after sexual activity.
- Vaginal Discharge: Some women may experience an unusual vaginal discharge.
- Urinary Problems: Vaginal atrophy can also affect the urinary tract, leading to increased urinary frequency, urgency, or urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Decreased Vaginal Lubrication During Sexual Activity: The vagina may not produce enough natural lubrication during arousal, leading to discomfort.
- Shortening and Tightening of the Vaginal Canal: Over time, the vaginal canal can become shorter and narrower due to lack of estrogen.
4. Accurate Diagnosis: How Doctors Confirm Vaginal Atrophy
Diagnosing vaginal atrophy typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional.
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about your medical history, including menstrual cycles, menopause status, medications, and any other relevant health conditions.
- Symptom Assessment: A detailed discussion of your symptoms helps the doctor understand the extent and impact of the condition.
- Pelvic Exam: A physical examination of the vulva and vagina allows the doctor to assess the tissues for signs of thinning, dryness, and inflammation.
- Pap Test: This test screens for cervical cancer and can also provide information about the health of vaginal cells.
- Vaginal pH Test: Measuring the pH level of the vagina can help determine if it is within the normal range. Higher pH levels are often associated with vaginal atrophy.
- Urine Test: This test can rule out urinary tract infections as a cause of urinary symptoms.
- Endometrial Biopsy: If there is bleeding after intercourse, the doctor may recommend an endometrial biopsy to rule out uterine cancer.
5. Exploring Effective Treatment Options for Vaginal Atrophy
Several treatment options are available to manage vaginal atrophy symptoms and improve quality of life. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and individual preferences.
- Non-Hormonal Treatments:
- Vaginal Moisturizers: These over-the-counter products help to hydrate the vaginal tissues and relieve dryness. They are typically used regularly, regardless of sexual activity.
- Vaginal Lubricants: These are used during sexual activity to reduce friction and discomfort. Water-based lubricants are generally recommended.
- Hormonal Treatments:
- Topical Estrogen Therapy: This involves applying estrogen directly to the vagina in the form of creams, tablets, or vaginal rings. Topical estrogen can effectively restore vaginal tissue health with minimal systemic absorption.
- Vaginal Estrogen Creams: These creams are applied directly into the vagina using an applicator. Examples include Estrace and Premarin.
- Vaginal Estrogen Tablets: These tablets are inserted into the vagina using an applicator. Vagifem is a common example.
- Vaginal Estrogen Rings: These flexible rings are inserted into the vagina and release a steady dose of estrogen over several months. Estring is a well-known option.
- Systemic Estrogen Therapy: This involves taking estrogen orally or through a skin patch. Systemic estrogen therapy can help with vaginal atrophy symptoms, but it also has broader effects on the body and may not be suitable for all women.
- Topical Estrogen Therapy: This involves applying estrogen directly to the vagina in the form of creams, tablets, or vaginal rings. Topical estrogen can effectively restore vaginal tissue health with minimal systemic absorption.
- Ospemifene: This is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that can help improve vaginal dryness and painful intercourse. It is taken orally.
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy is a newer treatment option that uses laser energy to stimulate collagen production and improve vaginal tissue health.
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone): This hormone can be inserted into the vagina as a suppository to help improve vaginal atrophy symptoms.
6. Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medical treatments, several natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments can help manage vaginal atrophy symptoms.
- Regular Sexual Activity: Engaging in regular sexual activity can improve blood flow to the vagina and help maintain tissue health.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and hormonal balance.
- Phytoestrogens: Some foods, such as soy products and flaxseeds, contain phytoestrogens, which are plant-based compounds that mimic estrogen in the body. While their effects are mild, they may provide some relief from vaginal atrophy symptoms.
- Avoid Irritants: Using gentle, unscented soaps and avoiding douching can help prevent irritation of the vaginal tissues.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep the body hydrated, which can also benefit vaginal moisture.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: These exercises can improve blood flow to the pelvic area and strengthen the muscles that support the vagina.
7. The Role of Lubricants and Moisturizers: Finding Relief
Vaginal lubricants and moisturizers play a crucial role in managing vaginal atrophy symptoms.
- Vaginal Lubricants: These are used during sexual activity to reduce friction and discomfort. Water-based lubricants are generally recommended because they are less likely to cause irritation than oil-based or silicone-based lubricants.
- Vaginal Moisturizers: These are designed to be used regularly to hydrate the vaginal tissues and relieve dryness. They help to restore the natural moisture balance of the vagina and can be used regardless of sexual activity.
8. Addressing the Impact on Sexual Health and Intimacy
Vaginal atrophy can significantly impact sexual health and intimacy. Painful intercourse, decreased lubrication, and emotional distress can lead to decreased sexual desire and difficulty enjoying sexual activity.
- Communication: Open communication with your partner about your symptoms and needs is essential.
- Experimentation: Explore different positions and techniques to find what is most comfortable for you.
- Patience: Allow ample time for arousal and use lubricants generously.
- Professional Help: Consider seeking help from a sex therapist or counselor to address any emotional or psychological issues related to vaginal atrophy.
9. Understanding the Link Between Vaginal Atrophy and Urinary Health
Vaginal atrophy can affect the urinary tract, leading to symptoms such as increased urinary frequency, urgency, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). This is because the tissues of the vagina and urethra are both sensitive to estrogen.
- Estrogen Therapy: Topical estrogen therapy can help improve urinary symptoms associated with vaginal atrophy.
- Lifestyle Measures: Drinking plenty of water, avoiding bladder irritants (such as caffeine and alcohol), and practicing good hygiene can help prevent UTIs.
- Medical Evaluation: If you experience urinary symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to rule out other potential causes.
10. Prevention Strategies: Maintaining Vaginal Health
While it may not be possible to completely prevent vaginal atrophy, several strategies can help maintain vaginal health and minimize symptoms.
- Stay Sexually Active: Regular sexual activity can improve blood flow to the vagina and help maintain tissue health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese can contribute to hormonal imbalances that may worsen vaginal atrophy symptoms.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can decrease estrogen levels and worsen vaginal dryness.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormone levels and overall health. Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can be beneficial.
- Consult with Your Doctor: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help monitor your vaginal health and address any concerns early on.
11. Debunking Common Myths About Vaginal Atrophy
Several myths surround vaginal atrophy, which can lead to confusion and misinformation.
- Myth: Vaginal atrophy only affects older women.
- Fact: While vaginal atrophy is most common after menopause, it can occur at any age when estrogen levels are low.
- Myth: Vaginal atrophy is just a normal part of aging and nothing can be done about it.
- Fact: Effective treatments are available to manage vaginal atrophy symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Myth: Hormone therapy is the only treatment option for vaginal atrophy.
- Fact: Non-hormonal treatments, such as lubricants and moisturizers, can also be effective for managing symptoms.
- Myth: Vaginal atrophy is only a physical problem.
- Fact: Vaginal atrophy can also have emotional and psychological effects, impacting sexual health and overall well-being.
12. When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
It is important to seek professional medical advice if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent vaginal dryness or burning
- Painful intercourse
- Bleeding after intercourse
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Urinary symptoms
A doctor can accurately diagnose the cause of your symptoms and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
13. The Emotional and Psychological Impact of Vaginal Atrophy
Vaginal atrophy can have a significant impact on a woman’s emotional and psychological well-being. Symptoms such as painful intercourse, decreased sexual desire, and changes in body image can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and sadness.
- Acknowledge Your Feelings: Recognize that it is normal to feel upset or distressed by vaginal atrophy symptoms.
- Seek Support: Talk to your partner, friends, or a therapist about your feelings.
- Practice Self-Care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies.
- Focus on Intimacy: Explore non-sexual ways to connect with your partner and maintain intimacy.
14. Vaginal Atrophy and Postmenopausal Health: A Holistic Approach
Vaginal atrophy is just one aspect of postmenopausal health. As women transition through menopause, they may experience a range of physical and emotional changes.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy can help manage many postmenopausal symptoms, including vaginal atrophy, hot flashes, and mood changes.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can support overall health and well-being.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help monitor your health and address any concerns that may arise.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and connection with other women experiencing similar challenges.
15. Navigating Treatment Options: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right treatment for vaginal atrophy can feel overwhelming. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate your options:
- Consult with your doctor: Discuss your symptoms and medical history with your doctor.
- Undergo a pelvic exam: Your doctor will perform a physical examination to assess the condition of your vaginal tissues.
- Consider non-hormonal treatments: Try over-the-counter lubricants and moisturizers to relieve dryness and discomfort.
- Explore hormonal treatments: If non-hormonal treatments are not effective, discuss topical or systemic hormone therapy with your doctor.
- Evaluate the risks and benefits: Understand the potential risks and benefits of each treatment option.
- Choose a treatment plan: Work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your individual needs and preferences.
- Monitor your symptoms: Keep track of your symptoms and report any changes to your doctor.
- Adjust your treatment as needed: Your treatment plan may need to be adjusted over time to ensure that it remains effective.
16. Staying Informed: Reliable Resources and Support Networks
Staying informed about vaginal atrophy is essential for making informed decisions about your health.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG): ACOG is a professional organization for obstetricians and gynecologists that provides reliable information about women’s health issues.
- The North American Menopause Society (NAMS): NAMS is a nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting women’s health during midlife and beyond.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): The NIH is a government agency that conducts and supports medical research.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and connection with other women experiencing vaginal atrophy.
17. Practical Tips for Managing Daily Life with Vaginal Atrophy
Living with vaginal atrophy can present daily challenges. Here are some practical tips for managing your symptoms and improving your quality of life:
- Keep lubricants handy: Carry a small bottle of lubricant with you for use as needed.
- Use a vaginal moisturizer regularly: Apply a vaginal moisturizer at bedtime to help hydrate the tissues overnight.
- Choose comfortable clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to avoid irritating the vaginal area.
- Avoid harsh soaps and detergents: Use gentle, unscented products to cleanse the vaginal area and wash your clothing.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can improve blood flow and overall health.
- Manage stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
18. Future Research and Advancements in Vaginal Atrophy Treatment
Research into vaginal atrophy is ongoing, and new treatments and management strategies are constantly being developed.
- Laser Therapy: Studies are exploring the effectiveness of laser therapy for improving vaginal tissue health and relieving symptoms of vaginal atrophy.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Research is investigating the potential of stem cell therapy to regenerate vaginal tissues and restore estrogen production.
- New Medications: Scientists are working to develop new medications that can effectively manage vaginal atrophy symptoms with minimal side effects.
19. Empowering Yourself: Taking Control of Your Vaginal Health
Ultimately, taking control of your vaginal health is about empowering yourself with knowledge, seeking support, and making informed decisions about your treatment options.
- Educate Yourself: Learn as much as you can about vaginal atrophy and its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
- Advocate for Yourself: Don’t be afraid to ask questions and express your concerns to your doctor.
- Seek Support: Connect with other women who are experiencing vaginal atrophy.
- Take Action: Implement lifestyle changes and treatment strategies to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Remember, you are not alone, and effective treatments are available to help you manage vaginal atrophy and live a fulfilling life.
20. Addressing Specific Concerns and FAQs About Vaginal Atrophy
Here are some frequently asked questions about vaginal atrophy:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can vaginal atrophy be cured completely? | While vaginal atrophy cannot be completely cured, its symptoms can be effectively managed with various treatments, allowing women to lead comfortable lives. |
| Is hormone therapy safe for everyone? | Hormone therapy is not suitable for everyone. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor to determine if it is the right treatment option for you. |
| Can vaginal atrophy affect fertility? | Vaginal atrophy can make it more difficult to conceive due to painful intercourse and changes in vaginal pH. However, it does not directly affect fertility. |
| Are there any long-term health risks associated with vaginal atrophy? | Untreated vaginal atrophy can increase the risk of urinary tract infections and painful intercourse, which can impact quality of life. |
| Can vaginal atrophy be prevented? | While it may not be possible to completely prevent vaginal atrophy, lifestyle measures such as staying sexually active and maintaining a healthy weight can help minimize symptoms. |
| How long does it take for treatments to start working? | The time it takes for treatments to start working can vary. Non-hormonal treatments may provide immediate relief, while hormonal treatments may take several weeks or months to produce noticeable results. |
| Can vaginal atrophy cause urinary incontinence? | Vaginal atrophy can contribute to urinary incontinence by weakening the muscles that support the bladder and urethra. |
| Is vaginal atrophy the same as vaginal dryness? | Vaginal dryness is a symptom of vaginal atrophy. Vaginal atrophy refers to the thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal tissues due to decreased estrogen levels. |
| Can vaginal atrophy affect my relationship? | Vaginal atrophy can affect relationships due to painful intercourse and decreased sexual desire. Open communication with your partner and seeking professional help can help address these issues. |
| Are there any alternative treatments for vaginal atrophy that I can try? | Some women find relief from vaginal atrophy symptoms through alternative treatments such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or yoga. However, it is important to discuss these options with your doctor to ensure that they are safe and appropriate for you. |
Don’t let vaginal atrophy diminish your quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to manage your condition and maintain your overall well-being.
Have more questions about vaginal atrophy? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and receive free answers from our community of experts. We are here to provide you with the information and support you need. Our address is 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us on WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Let what.edu.vn be your trusted resource for all your health questions.
