Are you curious about what volume means and how to calculate it? WHAT.EDU.VN provides a clear and concise explanation of volume, exploring its definition, formulas, and practical applications. Let’s unlock the secrets of volume and discover how it helps us understand the space around us, including capacity.
1. Understanding Volume
Volume is the measure of the amount of space a three-dimensional object occupies. It’s a fundamental concept in geometry and physics, helping us quantify the size of objects in our world. Think of it as the capacity of an object – how much it can hold.
1. 1 Definition
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by a closed surface. It’s typically measured in cubic units, such as cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³). According to a study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2023, accurate volume measurement is crucial in various fields, including manufacturing, medicine, and trade.
1. 2 Volume vs. Capacity
While often used interchangeably, volume and capacity have subtle differences. Volume refers to the space an object occupies, while capacity refers to the amount a container can hold. For example, a water bottle has a volume (the space the plastic occupies) and a capacity (the amount of water it can hold).
1. 3 Importance of Volume
Understanding volume is essential for various reasons:
- Real-world applications: Calculating the amount of liquid a container can hold, determining the size of a package, or estimating the amount of material needed for construction.
- Scientific calculations: Volume is used in chemistry, physics, and engineering to calculate density, buoyancy, and other important properties.
- Everyday life: From cooking to gardening, understanding volume helps us make informed decisions in our daily activities.
2. How to Calculate Volume
The method for calculating volume depends on the shape of the object. Here are some common formulas for calculating the volume of regular shapes:
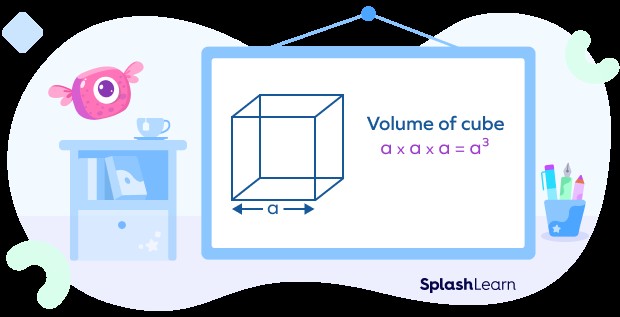
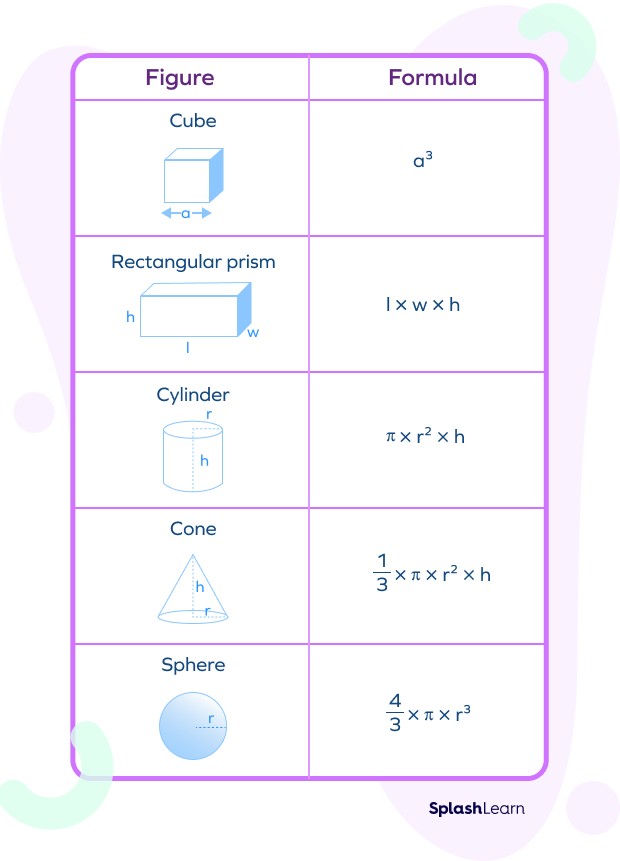
2. 1 Cube
A cube is a three-dimensional shape with six equal square sides.
- Formula: Volume = a³, where “a” is the length of one side of the cube.
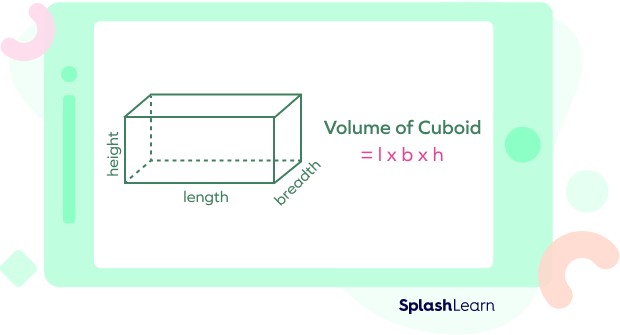
2. 2 Cuboid (Rectangular Prism)
A cuboid is a three-dimensional shape with six rectangular sides.
- Formula: Volume = l × w × h, where “l” is the length, “w” is the width, and “h” is the height of the cuboid.
2. 3 Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round three-dimensional object.
- Formula: Volume = (4/3) × π × r³, where “r” is the radius of the sphere and π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
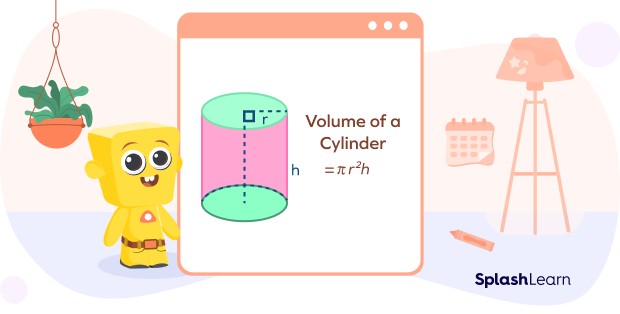
2. 4 Cylinder
A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two circular bases and a curved surface connecting them.
- Formula: Volume = π × r² × h, where “r” is the radius of the circular base and “h” is the height of the cylinder.
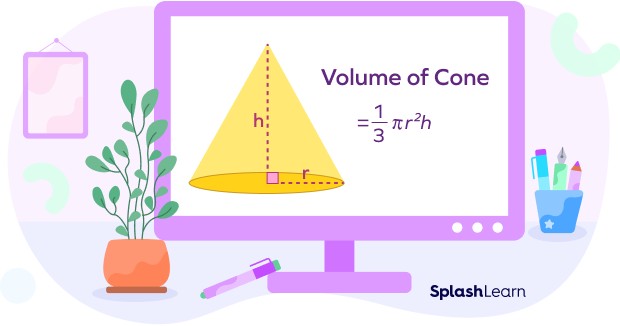
2. 5 Cone
A cone is a three-dimensional shape with a circular base and a single vertex.
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) × π × r² × h, where “r” is the radius of the circular base and “h” is the height of the cone.
2. 6 Pyramid
A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a polygonal base and triangular faces that meet at a common vertex.
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) × B × h, where “B” is the area of the base and “h” is the height of the pyramid.
2. 7 Irregular Shapes
Calculating the volume of irregular shapes can be more complex. Here are a few methods:
- Displacement Method: Immerse the object in a liquid and measure the volume of liquid displaced.
- Decomposition Method: Break the object into smaller, regular shapes and calculate the volume of each part. Then, add the volumes together.
- 3D Scanning: Use a 3D scanner to create a digital model of the object and calculate the volume using software.
3. Units of Volume
Volume is measured in cubic units. The most common units include:
- Cubic meters (m³): The standard unit of volume in the metric system.
- Cubic centimeters (cm³): A smaller unit of volume, often used for smaller objects.
- Liters (L): A unit of volume commonly used for liquids. 1 liter is equal to 1000 cm³.
- Milliliters (mL): A smaller unit of volume, often used for measuring small amounts of liquid. 1 milliliter is equal to 1 cm³.
- Cubic feet (ft³): A unit of volume in the imperial system.
- Cubic inches (in³): A smaller unit of volume in the imperial system.
- Gallons (gal): A unit of volume commonly used for liquids in the imperial system.
4. Volume in Real Life
Volume plays a crucial role in many aspects of our lives. Here are a few examples:
4. 1 Cooking and Baking
Recipes often use volume measurements for ingredients. Understanding volume allows you to accurately measure ingredients and achieve the desired results in your cooking and baking.
4. 2 Construction and Engineering
Volume calculations are essential for determining the amount of materials needed for construction projects. For example, calculating the volume of concrete needed for a foundation or the amount of soil needed to fill a garden bed.
4. 3 Medicine and Healthcare
In medicine, volume is used to measure dosages of medications, the volume of blood in the body, and the capacity of organs like the lungs and bladder.
4. 4 Packaging and Shipping
Volume calculations are important for determining the size of packages and containers for shipping and storage. This helps optimize space and minimize shipping costs.
4. 5 Environmental Science
Volume is used to measure the flow of water in rivers, the amount of pollution in the air, and the volume of waste in landfills.
5. Volume Formulas Cheat Sheet
| Shape | Formula | Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Cube | V = a³ | a = side length |
| Cuboid | V = l × w × h | l = length, w = width, h = height |
| Sphere | V = (4/3) × π × r³ | r = radius |
| Cylinder | V = π × r² × h | r = radius, h = height |
| Cone | V = (1/3) × π × r² × h | r = radius, h = height |
| Pyramid | V = (1/3) × B × h | B = base area, h = height |
| Irregular Shape | Displacement Method | Measure displaced liquid volume |
6. Practice Problems
6. 1 Problem 1: The Fish Tank
A rectangular fish tank has a length of 60 cm, a width of 30 cm, and a height of 40 cm. What is the volume of the fish tank?
Solution:
- Volume = l × w × h
- Volume = 60 cm × 30 cm × 40 cm
- Volume = 72,000 cm³
6. 2 Problem 2: The Beach Ball
A beach ball has a radius of 15 cm. What is the volume of the beach ball?
Solution:
- Volume = (4/3) × π × r³
- Volume = (4/3) × 3.14159 × (15 cm)³
- Volume ≈ 14,137.17 cm³
6. 3 Problem 3: The Cardboard Box
A cylindrical cardboard box has a radius of 10 cm and a height of 25 cm. What is the volume of the box?
Solution:
- Volume = π × r² × h
- Volume = 3.14159 × (10 cm)² × 25 cm
- Volume ≈ 7,853.98 cm³
7. Advanced Concepts in Volume
7. 1 Volume and Surface Area
Volume and surface area are related concepts. Surface area is the total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object. Understanding the relationship between volume and surface area is important in many applications, such as optimizing the design of containers to minimize material usage.
7. 2 Volume and Density
Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance. The formula for density is:
- Density = Mass / Volume
Understanding the relationship between volume and density is important for identifying materials and calculating the mass of an object given its volume.
7. 3 Volume and Calculus
Calculus can be used to calculate the volume of complex shapes that cannot be easily described by simple formulas. Techniques like integration can be used to find the volume of solids of revolution and other irregular shapes.
8. Historical Context of Volume Measurement
The concept of volume has been around for centuries. Ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians developed methods for measuring volume for trade, construction, and agriculture. The development of standardized units of volume, like the liter and cubic meter, has facilitated trade and scientific research.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using the wrong formula: Make sure you are using the correct formula for the shape you are measuring.
- Using inconsistent units: Ensure that all measurements are in the same units before calculating the volume.
- Forgetting to include units in your answer: Always include the units in your answer to indicate the scale of the volume.
- Rounding errors: Avoid rounding intermediate calculations to minimize errors in your final answer.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10. 1 What is the difference between volume and area?
Area measures the two-dimensional space within a shape, while volume measures the three-dimensional space within an object.
11. 2 How do I convert between different units of volume?
You can use conversion factors to convert between different units of volume. For example, 1 liter is equal to 1000 cubic centimeters.
11. 3 Can volume be negative?
No, volume cannot be negative. It is a measure of the amount of space an object occupies, which is always a positive value.
11. 4 How is volume used in everyday life?
Volume is used in many everyday activities, such as cooking, baking, measuring liquids, and determining the size of containers.
11. 5 What are some common tools for measuring volume?
Common tools for measuring volume include measuring cups, graduated cylinders, beakers, and pipettes.
11. Further Exploration
- Explore interactive simulations and virtual labs to visualize volume concepts.
- Research the history of volume measurement and its impact on science and technology.
- Investigate the use of calculus in calculating the volume of complex shapes.
- Discover real-world applications of volume in fields like architecture, engineering, and medicine.
12. Conclusion
Understanding volume is essential for various reasons. Whether you’re calculating the amount of liquid a container can hold or determining the size of a package, volume helps us make informed decisions in our daily activities. By mastering the formulas and concepts outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any volume-related problem.
Do you still have questions about volume or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform for you to ask any question and receive free, accurate, and timely answers from experts. Our service is designed to provide a fast and easy way to get the information you need.
Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. You can also visit our website at what.edu.vn to submit your questions.
We’re here to help you learn and grow!

