What Language Is Spoken In Malta? Maltese and English are the official languages of Malta, as explored on WHAT.EDU.VN. Delve into the history, grammar, and cultural influences that shape the linguistic landscape of this Mediterranean island nation. Discover the nuances of Maltese, the prevalence of English, and the enduring influence of Italian.
1. What Are the Official Languages Spoken in Malta?
Malta recognizes two official languages: Maltese and English. Maltese, a Semitic language with influences from Sicilian, Italian, and English, is spoken by the majority of the population. English, a legacy of British colonial rule, is widely used in government, education, and commerce.
1.1. Maltese: A Unique Semitic Language
Maltese, also known as Malti, is a unique Semitic language with a rich history. It is the only Semitic language among the official languages of the European Union, and it is also the only Semitic language written using the Latin alphabet.
- Origins: Maltese evolved from a dialect of Arabic that emerged over 1,000 years ago from Maghrebi Arabic and Siculo-Arabic spoken in Sicily.
- Influences: Centuries of conquest and cultural exchange have enriched Maltese with elements of Sicilian, medieval Latin, and English.
1.2. English: A Legacy of British Colonial Rule
English is the second official language of Malta and is widely spoken throughout the islands. Its presence is a result of Malta’s history as a British colony from 1814 to 1964.
- Prevalence: A significant portion of the Maltese population speaks English fluently, making it an important language for communication and commerce. According to recent data, 88% of the population speaks English.
- Official Use: English is used in government, education, and business, ensuring its continued importance in Maltese society.
2. How Did Maltese Become the National Language of Malta?
Maltese became the national language of Malta through a fascinating journey shaped by conquest, cultural exchange, and linguistic adaptation.
2.1. Arab Rule and the Birth of Maltese
Between 870 and 1091, the Arabs conquered and settled Malta, introducing the Arabic language to the islands. This Arabic dialect formed the foundation of what would eventually become the Maltese language.
2.2. Norman Conquest and Subsequent Influences
In 1091, the Normans took control of Malta, marking the beginning of a series of foreign rulers. The islands subsequently fell under the Kingdom of Sicily and the Crown of Aragon, leading to the introduction of Latin and Sicilian.
- Latin: Latin was used for administrative and legal communication.
- Sicilian: Sicilian became the language of communication with the central government in Palermo from the 15th century onwards.
2.3. The Knights of St. John and Tuscan Influence
The arrival of the Knights of St. John brought the Tuscan language to Malta, further enriching the linguistic landscape. Official documents were drafted in a language that would evolve into Italian, while ordinary people continued to speak a form of Maltese-Arabic.
2.4. British Rule and the Rise of English
Following a brief period of French domination, the British took control of Malta in 1800. This marked a significant shift in the linguistic landscape, as English gradually gained prominence at the expense of Italian.
- English as the Language of Administration: In 1814, Malta became a British Crown Colony, and English was adopted as the new language of administration.
- Decline of Italian: The use of Italian gradually diminished, and it was eventually removed from the list of official languages in 1934.
2.5. Standardization of Maltese and Official Recognition
During British rule, efforts were made to standardize the Maltese language. In 1964, Maltese was officially recognized as one of the official languages of Malta, alongside English.
 Maltese is spoken by more than 500,000 people.
Maltese is spoken by more than 500,000 people.
3. Is Italian Spoken in Malta?
Although Italian is no longer an official language of Malta, it maintains a significant presence on the islands.
3.1. Historical Significance of Italian in Malta
Italian held official status in Malta for centuries and was widely used in education, administration, and culture. However, its status declined with the rise of English during British rule.
3.2. Current Status of Italian in Malta
Despite no longer being an official language, Italian continues to be spoken by a considerable portion of the Maltese population. According to recent data, nearly 300,000 people in Malta speak Italian, although the vast majority are not native speakers.
3.3. Cultural Influence of Italian in Malta
Italian culture remains influential in Malta, with many organizations and clubs promoting Italian language and traditions. In the past, Maltese people primarily watched Italian television shows, and Italian continues to be a popular choice for students studying a third language.
4. What Are Some Unique Features of the Maltese Language?
Maltese possesses several unique features that distinguish it from other languages.
4.1. Semitic Roots with Romance and Germanic Influences
As a Semitic language, Maltese shares characteristics with Arabic and Hebrew. However, centuries of contact with Romance and Germanic languages have resulted in significant influences on its vocabulary and grammar.
4.2. Use of the Latin Alphabet
Maltese is the only Semitic language written using the Latin alphabet. This adaptation reflects the influence of European cultures on the Maltese language. The Maltese alphabet consists of 30 letters, including several unique characters: ċ, ġ, għ, ie, and ż. It does not include the undotted c or the letter y.
4.3. Grammatical Quirks
Maltese grammar exhibits several unique features:
- Adjective Placement: Adjectives typically follow the noun and take the definite article, except for nouns and adjectives of Romance origin.
- Verb Structure: Like other Semitic languages, Maltese verbs have a three-letter root in the infinitive form and are conjugated using prefixes, suffixes, and infixes.
5. What Is the Maltese Language Closest To?
Maltese is most closely related to Siculo-Arabic, an extinct dialect of Arabic that was spoken in Sicily. However, due to its unique history and influences, Maltese has evolved into a distinct language with its own unique characteristics.
5.1. Linguistic Connections to Arabic
Maltese shares a significant portion of its vocabulary and grammatical structure with Arabic. This reflects the historical influence of Arab rule on the Maltese islands.
5.2. Influences from Sicilian and Italian
Maltese has also been significantly influenced by Sicilian and Italian, particularly in its vocabulary. Many Maltese words are derived from these languages, reflecting the close cultural and historical ties between Malta and Italy.
5.3. Borrowings from English
In more recent times, English has also contributed to the Maltese vocabulary. Many English words have been adopted into Maltese, particularly in technical and modern contexts.
6. How Many People Speak Maltese Worldwide?
Maltese is spoken by over 500,000 people worldwide.
6.1. Maltese Speakers in Malta
The majority of Maltese speakers reside in Malta, where it is the national language. Maltese is used in all aspects of life in Malta, including government, education, media, and commerce.
6.2. Maltese Speakers in the Diaspora
Significant Maltese-speaking communities exist in other countries, particularly in Australia, Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom. These communities maintain their language and culture through various organizations and activities.
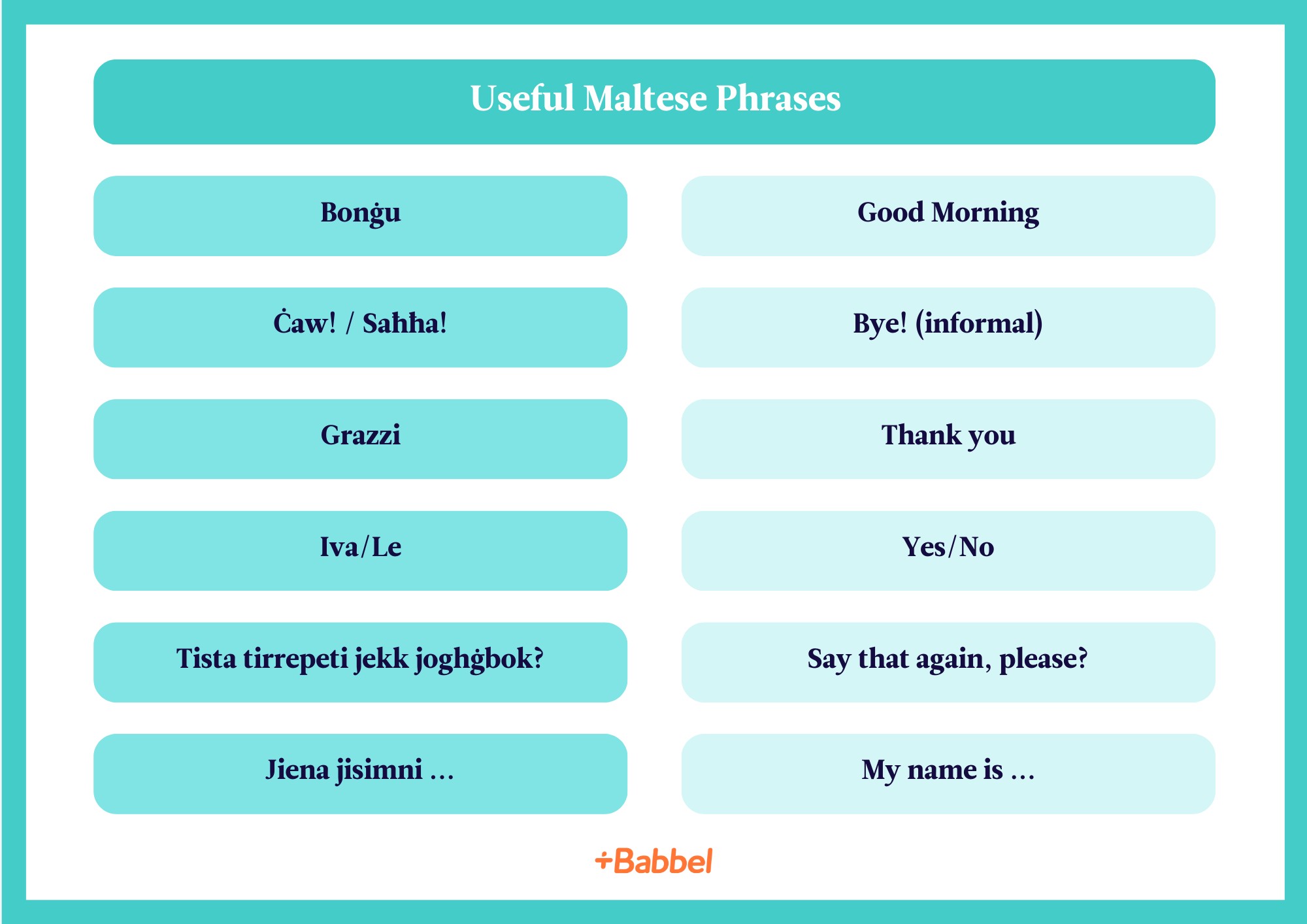
7. What Are Some Common Maltese Phrases?
Learning a few basic Maltese phrases can enhance your experience when visiting Malta.
- Hello: Ħello
- Goodbye: Saħħa
- Please: Jekk jogħġbok
- Thank you: Grazzi
- You’re welcome: M’hemmx għalfejn
- Yes: Iva
- No: Le
- Excuse me: Skużi
- How are you?: Kif inti? (formal), Kif int? (informal)
- I am fine: Tajjeb, grazzi (male), Tajba, grazzi (female)
8. How Has Malta’s History Shaped its Linguistic Landscape?
Malta’s strategic location in the Mediterranean has made it a crossroads of cultures and languages throughout history. This rich history has profoundly shaped its linguistic landscape.
8.1. A Timeline of Linguistic Influences
- 870-1091: Arab Rule: Introduction of Arabic, which formed the basis of the Maltese language.
- 1091-1530: Norman, Sicilian, and Aragonese Rule: Influence of Latin, Sicilian, and other Romance languages.
- 1530-1798: Knights of St. John: Introduction of Italian and further development of Maltese.
- 1800-1964: British Rule: Rise of English and decline of Italian.
- 1964-Present: Independent Malta: Recognition of Maltese and English as official languages.
8.2. The Enduring Impact of Cultural Exchange
Malta’s linguistic landscape is a testament to the enduring impact of cultural exchange. The Maltese language reflects the diverse influences of the various civilizations that have ruled the islands, resulting in a unique and fascinating linguistic blend.
9. What Resources Are Available for Learning Maltese?
If you’re interested in learning Maltese, there are several resources available to help you get started.
9.1. Online Courses and Apps
Many online courses and language learning apps offer Maltese lessons, catering to various skill levels and learning styles. Some popular options include:
- Memrise: Offers a variety of Maltese courses, focusing on vocabulary and grammar.
- Duolingo: While not offering a full Maltese course, Duolingo provides a basic introduction to the language through its incubator program.
- italki: Connects you with native Maltese speakers for personalized lessons and language exchange.
9.2. Textbooks and Dictionaries
Several textbooks and dictionaries are available for studying Maltese grammar and vocabulary. Look for resources specifically designed for English speakers learning Maltese.
9.3. Language Exchange Partners
Connecting with native Maltese speakers through language exchange websites or apps can provide valuable practice and insights into the language and culture.
10. What Are Some Challenges and Opportunities for the Maltese Language Today?
The Maltese language faces both challenges and opportunities in the modern world.
10.1. Challenges to the Maltese Language
- Dominance of English: The widespread use of English in Malta poses a challenge to the vitality of the Maltese language.
- Globalization and Digitalization: The increasing influence of global culture and digital communication can lead to a decline in the use of Maltese, particularly among younger generations.
10.2. Opportunities for the Maltese Language
- Promotion of Maltese Culture: Promoting Maltese culture and literature can help to preserve and strengthen the language.
- Use of Maltese in Digital Media: Encouraging the use of Maltese in online content, social media, and digital applications can help to increase its visibility and relevance.
- Government Support: Government initiatives to support the Maltese language, such as funding for education and cultural programs, are crucial for its long-term survival.
10.3. Efforts to Preserve the Maltese Language
The Maltese government and various cultural organizations are actively involved in efforts to preserve and promote the Maltese language. These efforts include:
- Developing Maltese language resources for education and research.
- Supporting Maltese literature and cultural events.
- Promoting the use of Maltese in government and public services.
- Encouraging the use of Maltese in digital media and technology.
Malta’s linguistic tapestry is a unique blend of Semitic, Romance, and Germanic influences, reflecting its rich history and strategic location in the Mediterranean. While Maltese and English are the official languages, Italian maintains a significant cultural presence. Understanding the linguistic landscape of Malta provides valuable insights into its history, culture, and identity.
Do you have more questions about languages or anything else? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can ask any question and receive free answers. Our platform is designed to provide quick, accurate, and easy-to-understand information on a wide range of topics. Don’t hesitate to reach out and explore the world of knowledge with us.
Are you finding it difficult to get answers quickly and for free? Are you unsure where to ask or how to find reliable information? Concerned about the cost of consultations? Need a user-friendly platform to ask questions and get responses from knowledgeable people?
WHAT.EDU.VN offers a free platform to ask any question, providing quick and accurate answers in an easy-to-understand format. Connect with a community to exchange knowledge and receive free consultations for simple issues.
Contact us:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Visit what.edu.vn today and get the answers you need, absolutely free. Ask your question now!