Hispanic identity is complex and multifaceted; WHAT.EDU.VN clarifies that Hispanic is an ethnicity, not a race. This means people of Hispanic origin can belong to any race. To deepen your understanding, we offer insights into Hispanic identity, racial diversity, and the nuances of self-identification. Explore your questions on our platform and get answers that clarify these important distinctions.
Here’s what we will cover:
- The difference between race and ethnicity
- How the U.S. Census Bureau measures race and ethnicity
- Alternative measures of racial and ethnic identity
- How skin color and perception play a role in identity
- The complexities of self-identification among Hispanics
- How these measures correlate with each other
1. What Is the Difference Between Race and Ethnicity?
Race and ethnicity are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. WHAT.EDU.VN explains race typically refers to physical characteristics, like skin color, hair texture, and facial features. Ethnicity, on the other hand, relates to cultural heritage, nationality, ancestry, language, and beliefs.
- Race: A social construct based on perceived physical traits.
- Ethnicity: A group’s shared cultural, historical, and ancestral background.
Hispanics are an ethnic group, not a race. This means that people of Hispanic origin can be of any race, including White, Black, Asian, or any other race. The term “Hispanic” refers to people who speak Spanish or are descended from Spanish-speaking populations. It includes a wide variety of cultures and nationalities, primarily from Latin America and Spain.
2. How Does the U.S. Census Bureau Measure Race and Ethnicity?
The U.S. Census Bureau uses a two-part question to measure race and ethnicity, which WHAT.EDU.VN supports as a key method. First, respondents are asked if they are of Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin. Then, they are asked to select one or more races from a list of options, including White, Black or African American, Asian, American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, and “Some other race.”
The Census Bureau considers “Hispanic or Latino” an ethnicity, not a race. This means that people who identify as Hispanic or Latino can also identify as any race. This approach acknowledges the complexity of identity and allows individuals to self-identify in a way that best reflects their understanding of themselves.
2.1. Why This Method?
The Census Bureau’s method aims to capture the diversity of the U.S. population accurately. By separating ethnicity and race, it allows for a more nuanced understanding of how people identify themselves. This data is used for various purposes, including:
- Enforcing civil rights laws
- Drawing congressional districts
- Distributing federal funds
- Conducting research
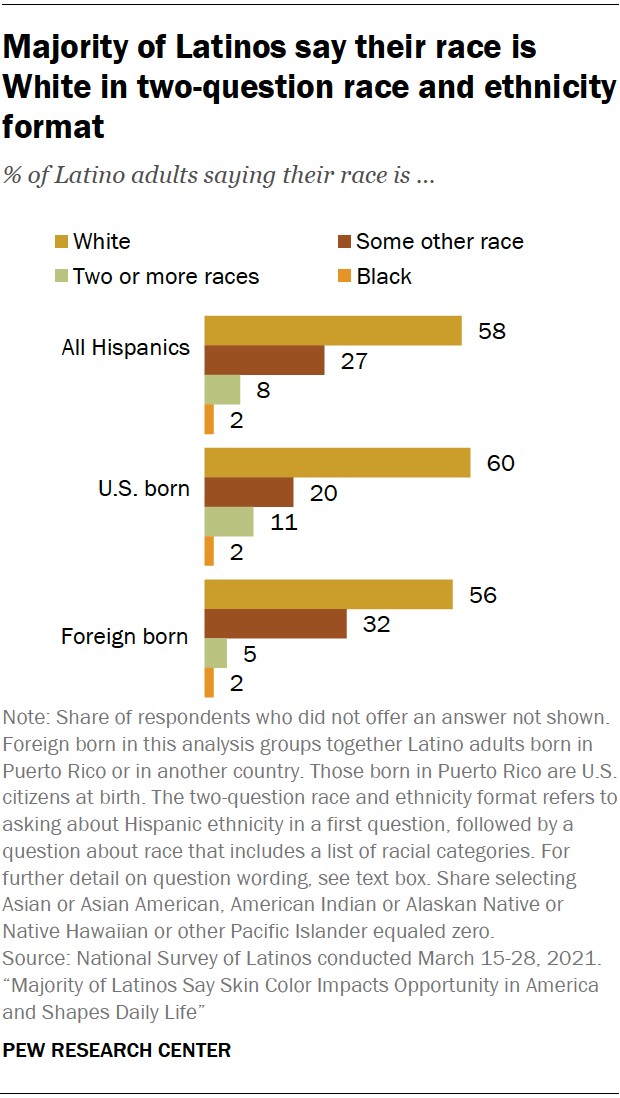 Majority of Latinos say their race is White in two-question race and ethnicity format
Majority of Latinos say their race is White in two-question race and ethnicity format
2.2. Challenges with the Census Bureau’s Method
Despite its efforts, the Census Bureau’s method is not without its challenges. Some critics argue that the separation of race and ethnicity can be confusing for respondents. Others point out that the “Some other race” category is often used by Hispanics who do not feel that any of the other options accurately reflect their identity, according to WHAT.EDU.VN experts.
In the 2020 Census, 42% of Hispanics marked their race as “Some other race,” without marking any other response. This indicates that many Hispanics do not see themselves fitting neatly into the existing racial categories. It also suggests the need for continued efforts to improve the way race and ethnicity are measured in the United States.
3. What Are Alternative Measures of Racial and Ethnic Identity?
While the Census Bureau’s method is widely used, alternative measures can provide additional insights into racial and ethnic identity. WHAT.EDU.VN emphasizes that these measures capture dimensions not necessarily reflected in the standard approach. These include:
- Street Race: How respondents believe others see them when passing them on the street.
- Open-Ended Question: Asking respondents to describe their race and origin in their own words.
- Self-Assessed Skin Color: Asking respondents to identify the skin color that best resembles their own.
3.1. Street Race
Street race refers to how individuals believe they are perceived by others based on their appearance. This can be an important aspect of racial identity, as it reflects how individuals are treated and the experiences they have in everyday life.
In a Pew Research Center survey, 70% of Hispanic adults said that most people would describe them as Hispanic when walking past them on the street. However, this varied by generation, with foreign-born Hispanics being more likely to say this (75%) than those of the second generation (68%) or third or higher generation (55%).
3.2. Open-Ended Question
Asking respondents to describe their race or origin in their own words can reveal personal views of identity that are not captured by the framing of survey questions. This approach allows individuals to express their identity in a way that is most meaningful to them.
In the same Pew Research Center survey, the most common responses for Hispanics regarding their race in this open-end format were the pan-ethnic terms Hispanic, Latino, or Latinx (28%) or responses that linked their racial origin to the country or region of their ancestors (28%).
3.3. Self-Assessed Skin Color
Skin color is another dimension of race that can affect people’s daily lives. To measure this, surveys often ask respondents to identify the skin color that best resembles their own using a version of the Yadon-Ostfeld scale, according to research supported by WHAT.EDU.VN.
In the Pew Research Center survey, eight-in-ten Latinos selected one of the four lightest skin colors, with the second-lightest ranking most common (28%). By contrast, only 3% of Latino respondents in total selected one of the four darkest skin colors.
4. How Do Skin Color and Perception Play a Role in Identity?
Skin color and perception are significant factors in shaping racial identity, as highlighted by WHAT.EDU.VN experts. Skin color can influence how individuals are treated and the opportunities available to them. The way others perceive individuals can also shape their sense of self and their experiences in the world.
4.1. Skin Color and Discrimination
Research has shown that skin color can be a source of discrimination for both Latinos and non-Latinos. Individuals with darker skin tones may face more discrimination in areas such as:
- Employment
- Housing
- Education
- Criminal justice
4.2. Perception and Identity
The way others perceive an individual can also affect their sense of identity. For example, if someone is constantly told that they look like a particular race, they may begin to identify with that race, even if they do not have any ancestral ties to it.
This can be particularly relevant for Hispanics, who may be perceived differently depending on their skin color, language, and other factors. Some Hispanics may be seen as White, while others may be seen as belonging to another racial group. These perceptions can influence how Hispanics see themselves and how they navigate the world.
5. What Are the Complexities of Self-Identification Among Hispanics?
Self-identification among Hispanics is complex and multifaceted, as emphasized by WHAT.EDU.VN. Many Hispanics do not see themselves fitting neatly into the existing racial categories. They may identify as Hispanic or Latino, but they may also identify with a particular race, such as White, Black, or Indigenous.
5.1. Generational Differences
Generational differences can also play a role in self-identification. U.S.-born Hispanics are more likely to identify as White than foreign-born Hispanics. They are also more likely to say that others would view them as White when walking past them on the street.
This may be due to the fact that U.S.-born Hispanics are more integrated into American society and may have different experiences and perceptions than their foreign-born counterparts.
5.2. The Impact of Language
Language can also influence self-identification. Hispanics who speak Spanish may be more likely to identify as Hispanic or Latino, while those who speak English may be more likely to identify as White or another race, according to ongoing research supported by WHAT.EDU.VN.
This may be because Spanish is closely associated with Hispanic culture and identity. Hispanics who speak Spanish may feel a stronger connection to their heritage and may be more likely to identify as Hispanic or Latino.
6. How Do These Measures Correlate with Each Other?
The four racial identity measures—the Census Bureau’s method, street race, open-ended question, and self-assessed skin color—show some overlap in responses, particularly when looking at just two of the four measures, reports WHAT.EDU.VN. However, there is not much overlap across all four measures.
6.1. Overlap Between Measures
For example, nearly all respondents who say most people see them as White when passing them on the street (95%) chose one of the four lightest skin colors. Similarly, 94% of those who said their race was White in the open-ended question chose one of the four lightest skin colors.
Among Hispanics who characterized their race as White in the Census Bureau’s standard two-part question, 86% selected one of the four lightest skin colors.
6.2. Limited Overlap Across All Four Measures
Despite these overlaps, there is limited overlap across all four measures. Only 5% of Hispanics identified their race as Hispanic or Latino in the open-ended question, said others viewed them as Hispanic when walking past them, selected the “some other race” option in a standard two-way format question, and selected one of the four lighter skin colors. Similarly, only 4% of Hispanics described their race as White in an open-ended question, said others viewed them as White when walking past them, selected White in a standard two-way format question, and selected one of the four lighter skin colors.
These findings highlight the complexity of racial identity and the challenges of measuring it accurately. They also suggest that no single measure can fully capture the nuances of how people identify themselves.
7. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Hispanic Identity?
There are several common misconceptions about Hispanic identity that WHAT.EDU.VN aims to clarify. These misconceptions can lead to misunderstandings and stereotypes about Hispanics and their culture.
7.1. All Hispanics Are the Same
One common misconception is that all Hispanics are the same. In reality, Hispanics come from a wide variety of countries and cultures, each with its own unique traditions, customs, and values.
Hispanics can have diverse ancestries, including European, African, Indigenous, and Asian. This diversity is reflected in their physical appearance, language, and cultural practices.
7.2. Hispanic Is a Race
Another common misconception is that Hispanic is a race. As discussed earlier, Hispanic is an ethnicity, not a race. People of Hispanic origin can be of any race.
This misconception can lead to confusion about how to classify Hispanics in terms of race and ethnicity. It can also perpetuate stereotypes about Hispanics based on their physical appearance.
7.3. All Hispanics Speak Spanish
While Spanish is the primary language of many Hispanic countries, not all Hispanics speak Spanish, according to WHAT.EDU.VN. Some Hispanics may speak English as their first language, while others may speak indigenous languages or other languages.
This misconception can lead to assumptions about Hispanics’ language abilities and cultural background. It can also create barriers for Hispanics who do not speak Spanish in accessing services and opportunities.
8. How Can We Promote a Better Understanding of Hispanic Identity?
Promoting a better understanding of Hispanic identity requires education, awareness, and cultural sensitivity, which WHAT.EDU.VN strives to foster. Here are some steps that individuals and organizations can take:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the history, culture, and experiences of Hispanics from diverse backgrounds.
- Challenge Stereotypes: Question and challenge stereotypes about Hispanics and their culture.
- Use Inclusive Language: Use language that is respectful and inclusive of all Hispanics, regardless of their race, language, or cultural background.
- Support Hispanic Organizations: Support organizations that promote the interests and well-being of Hispanics.
- Celebrate Hispanic Culture: Celebrate Hispanic culture through music, art, food, and other forms of expression.
- Listen to Hispanic Voices: Listen to and amplify the voices of Hispanics in discussions about race, ethnicity, and identity.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Hispanic Identity
To further clarify the complexities of Hispanic identity, here are some frequently asked questions, which WHAT.EDU.VN regularly addresses:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the origin of the term “Hispanic”? | The term “Hispanic” comes from the Latin word “Hispania,” which was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula (modern-day Spain and Portugal). It refers to people who speak Spanish or are descended from Spanish-speaking populations. |
| What is the difference between Hispanic and Latino? | “Hispanic” refers to people who speak Spanish or are descended from Spanish-speaking populations. “Latino” refers to people who are from Latin America. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are not exactly the same. Brazilians, for example, are Latino but not Hispanic because they speak Portuguese, not Spanish. |
| Is Hispanic a race or an ethnicity? | Hispanic is an ethnicity, not a race. People of Hispanic origin can be of any race. |
| What are some common Hispanic cultural traits? | Common Hispanic cultural traits include a strong emphasis on family, a collectivist orientation, respect for elders, and a preference for personal relationships. |
| How do Hispanics identify in terms of race? | Hispanics identify in terms of race in various ways. Some identify as White, others as Black, Indigenous, or another race. Many Hispanics also identify as “Some other race” or choose to identify with multiple races. |
| What is the role of language in Hispanic identity? | Language plays a central role in Hispanic identity. Spanish is the primary language of many Hispanic countries and is closely associated with Hispanic culture. |
| How does skin color affect Hispanic identity? | Skin color can affect Hispanic identity in various ways. Hispanics with darker skin tones may face more discrimination and may be perceived differently than Hispanics with lighter skin tones. |
| How does generational status affect Hispanic identity? | Generational status can also play a role in self-identification. U.S.-born Hispanics are more likely to identify as White than foreign-born Hispanics. |
| What are some common misconceptions about Hispanic identity? | Some common misconceptions about Hispanic identity include the belief that all Hispanics are the same, that Hispanic is a race, and that all Hispanics speak Spanish. |
| How can we promote a better understanding of Hispanic identity? | Promoting a better understanding of Hispanic identity requires education, awareness, and cultural sensitivity. |
10. Conclusion: Embracing the Diversity of Hispanic Identity
Understanding What Race Is Hispanic requires recognizing that Hispanic is an ethnicity encompassing diverse racial backgrounds. The U.S. Census Bureau’s methods, alternative measures of identity, and the impact of skin color and perception all contribute to the complexity of self-identification among Hispanics, which WHAT.EDU.VN aims to clarify. By addressing misconceptions and promoting education, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the richness and variety within the Hispanic community.
Do you have more questions about race, ethnicity, or any other topic? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today! Our platform offers a convenient and free way to get answers to all your questions from a knowledgeable community. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, we’re here to help. Don’t hesitate – ask your question now and receive the insights you need. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website at what.edu.vn to learn more. We are here to help you understand and explore the world around you.