Are you looking for the current UTC time? WHAT.EDU.VN provides you with the most accurate and up-to-date Coordinated Universal Time. Stay on schedule and easily convert to your local time zone for seamless global communication using our time zone converter and essential links. Discover the difference between UTC and other time standards, and ensure you’re always on time, no matter where you are.
1. Understanding UTC: The World’s Time Standard
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) serves as the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It’s crucial for various sectors, from aviation and meteorology to finance and international communication. Understanding UTC is essential for anyone needing to coordinate events or synchronize activities across different time zones. This standard replaced Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as the international standard in the 1970s, although GMT remains a time zone in its own right.
1.1. The History and Evolution of UTC
The need for a universal time standard became apparent with the rise of global communication and travel. Before UTC, various time zones were based on local solar time, which varied from place to place. Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), established in the 19th century, served as a prime meridian for navigation and timekeeping. However, GMT’s reliance on the Earth’s rotation, which is not perfectly uniform, led to the development of UTC.
UTC combines atomic time, which is highly stable, with adjustments to keep it aligned with solar time. This is achieved through the addition of leap seconds, which are occasionally added to UTC to compensate for irregularities in the Earth’s rotation. The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) is responsible for monitoring the Earth’s rotation and determining when leap seconds are necessary.
1.2. Why UTC Matters: Applications Across Industries
UTC’s precision and global acceptance make it indispensable in numerous fields.
- Aviation: Air traffic control systems rely on UTC to coordinate flights and ensure safety.
- Meteorology: Weather forecasts and climate models use UTC for data collection and analysis.
- Finance: Financial markets use UTC to timestamp transactions and manage global trading activities.
- International Communication: News agencies, broadcasters, and online platforms use UTC to schedule content and coordinate events across different time zones.
- Science: Scientific research relies on UTC for accurate data logging and experiment synchronization.
- Technology: Computer systems, networks, and databases use UTC to synchronize their clocks and ensure data consistency.
1.3. UTC vs. GMT: Clearing Up the Confusion
While UTC and GMT are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. GMT is a time zone, specifically the time zone of Greenwich, London. UTC is a time standard, a highly precise way of measuring time. GMT is based on the Earth’s rotation, while UTC is based on atomic clocks, with adjustments made to keep it aligned with solar time. In essence, GMT can be considered a zone while UTC is the standard time. The differences are subtle, but crucial for accuracy in many applications.
2. Decoding the UTC Time Format
Understanding the UTC time format is essential for accurately interpreting and using this universal time standard. UTC time is typically expressed using a 24-hour clock, with the format being HH:MM:SS (hours:minutes:seconds). Dates are usually written in the format YYYY-MM-DD (year-month-day). The “Z” suffix often accompanies UTC time, indicating that it is zero hours offset from UTC.
2.1. Understanding ISO 8601: The International Standard
ISO 8601 is an international standard for representing dates and times. It ensures consistency and unambiguous communication across different systems and regions. The ISO 8601 format for UTC time is YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ. For example, 2024-04-26T12:00:00Z represents noon on April 26, 2024, in UTC.
2.2. Converting to 12-Hour (AM/PM) Format
While UTC is typically expressed in 24-hour format, it can also be converted to 12-hour (AM/PM) format for easier understanding in some contexts. To convert, simply subtract 12 from the hour if it is greater than 12, and add “PM.” If the hour is less than 12, add “AM.” For example, 14:00 UTC is 2:00 PM UTC.
2.3. Common UTC Time Zones
While UTC itself is not a time zone, it serves as the reference point for all time zones around the world. Each time zone is defined by its offset from UTC. For example, Eastern Standard Time (EST) is UTC-5, meaning it is five hours behind UTC. Pacific Standard Time (PST) is UTC-8, eight hours behind UTC. Here’s a table with some common time zones and their UTC offsets:
| Time Zone | UTC Offset |
|---|---|
| Eastern Standard Time | UTC-5 |
| Pacific Standard Time | UTC-8 |
| Central European Time | UTC+1 |
| Japan Standard Time | UTC+9 |
| Australian Eastern Time | UTC+10 |
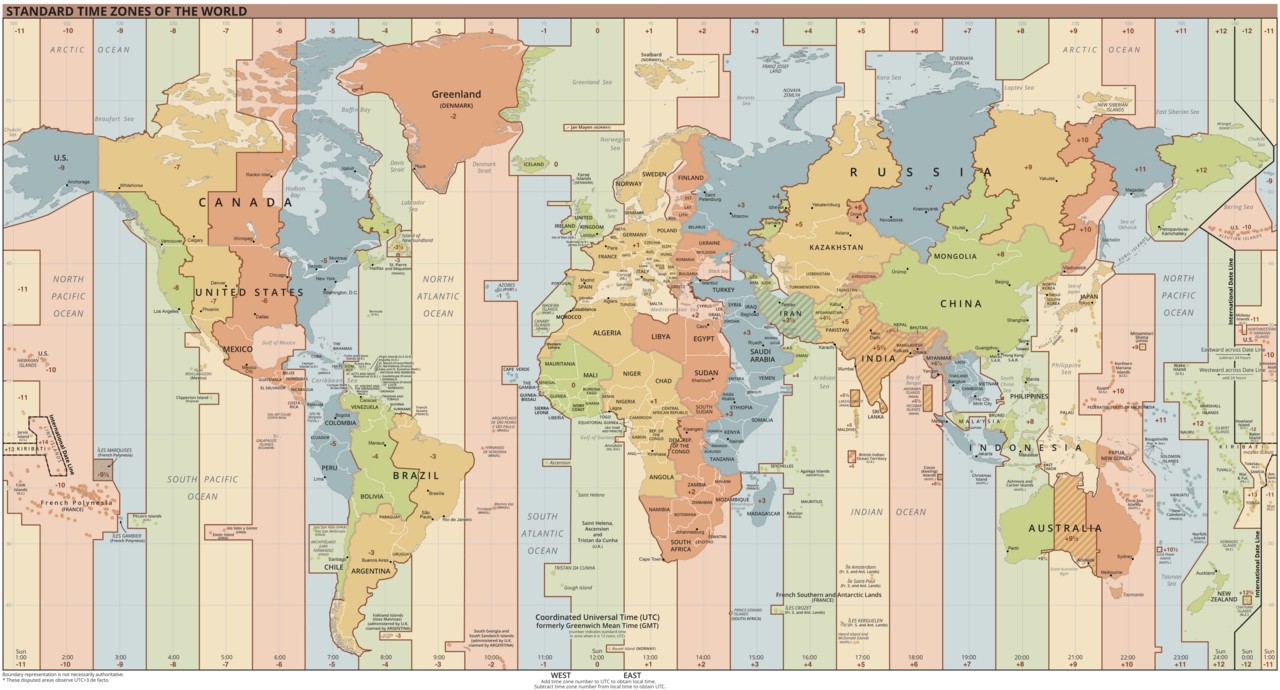

2.4. Navigating Daylight Saving Time (DST) with UTC
Daylight Saving Time (DST) can complicate time conversions. DST is the practice of advancing clocks during the summer months to make better use of daylight. When DST is in effect, the UTC offset of a time zone changes. For example, Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) is UTC-4, while Pacific Daylight Time (PDT) is UTC-7. It’s essential to be aware of DST when converting between UTC and local time, especially when scheduling events or coordinating activities across different regions.
3. Accessing Real-Time UTC Updates
Staying updated with the current UTC time is crucial for various applications. There are several reliable ways to access real-time UTC updates, ensuring accuracy and synchronization.
3.1. Online UTC Clocks and Converters
Numerous websites and online tools provide real-time UTC clocks and converters. These resources allow you to view the current UTC time and convert it to your local time zone instantly. Some popular options include:
- WHAT.EDU.VN: Offers a straightforward display of the current UTC time and date.
- Time.is: Provides accurate time for any location, including UTC.
- World Time Server: Offers a comprehensive time zone converter and world clock.
3.2. Using APIs for Developers
For developers, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provide a programmatic way to access UTC time. These APIs can be integrated into applications, websites, and other systems to ensure accurate time synchronization. Some popular UTC time APIs include:
- World Time API: A simple API that returns the current time for a specified time zone or UTC.
- Time Zone DB API: Offers detailed time zone information and UTC offsets.
- Google Time Zone API: Allows you to convert between time zones and retrieve UTC offsets.
3.3. Smartphone and Computer Settings
Most smartphones and computers have built-in features to display the current time in UTC. On smartphones, you can usually add a world clock displaying UTC in the clock app. On computers, you can adjust the time zone settings to display UTC. This ensures that you always have access to the current UTC time, regardless of your location.
4. Converting UTC to Local Time: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting UTC to local time is a simple process that involves adding or subtracting the appropriate UTC offset. This allows you to determine the equivalent time in your time zone, ensuring accurate scheduling and coordination.
4.1. Finding Your UTC Offset
The first step in converting UTC to local time is to determine your UTC offset. This is the number of hours and minutes that your time zone is ahead or behind UTC. You can find your UTC offset using online resources, such as:
- Time Zone Converter: Enter your location to find your UTC offset.
- World Time Server: Provides a list of time zones and their UTC offsets.
- Wikipedia: Offers a comprehensive list of time zones and their UTC offsets.
4.2. Performing the Conversion: Adding or Subtracting Hours
Once you know your UTC offset, you can perform the conversion by adding or subtracting the appropriate number of hours and minutes from the UTC time. If your time zone is ahead of UTC, you add the offset. If it is behind UTC, you subtract the offset. For example, if the UTC time is 12:00 and you are in EST (UTC-5), your local time is 07:00. If you are in CET (UTC+1), your local time is 13:00.
4.3. Accounting for Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Remember to account for DST when converting UTC to local time. If DST is in effect in your time zone, the UTC offset will be different. For example, during DST, EST becomes EDT (UTC-4), and PST becomes PDT (UTC-7). Always check whether DST is in effect when performing time conversions.
4.4. Practical Examples
Let’s look at some practical examples of converting UTC to local time:
- Example 1: UTC time is 15:00, and you are in New York (EST during standard time, UTC-5). Your local time is 10:00 AM.
- Example 2: UTC time is 20:00, and you are in London (GMT during standard time, UTC+0). Your local time is 8:00 PM.
- Example 3: UTC time is 02:00, and you are in Tokyo (JST, UTC+9). Your local time is 11:00 AM.
5. Common Use Cases for Knowing the Current UTC Time
Knowing the current UTC time is essential for various situations, both personal and professional. Its universality makes it a crucial tool for anyone dealing with international coordination and scheduling.
5.1. Scheduling International Meetings and Calls
When scheduling meetings or calls with participants in different time zones, using UTC as the reference point ensures that everyone understands the scheduled time accurately. This eliminates confusion and reduces the risk of missed appointments. To schedule an international meeting:
- Determine the UTC time that is convenient for all participants.
- Convert the UTC time to each participant’s local time zone.
- Confirm that the converted times work for everyone involved.
5.2. Coordinating Travel Itineraries
Travel itineraries often involve multiple time zones, making it essential to keep track of time differences. Using UTC can help you avoid confusion and ensure that you arrive at your destinations on time. When planning a trip:
- Note the UTC time of your flights and other travel arrangements.
- Convert the UTC times to your local time zone and the time zone of your destination.
- Adjust your schedule to account for time differences and potential jet lag.
5.3. Timestamping Data and Transactions
In many industries, such as finance and technology, timestamping data and transactions with UTC is crucial for maintaining accuracy and consistency. This allows for easy tracking and auditing of events, regardless of the location of the parties involved. Using UTC for timestamping ensures that:
- Data is recorded in a consistent and unambiguous format.
- Transactions can be easily tracked and audited.
- Events can be accurately synchronized across different systems and locations.
5.4. Understanding News and Events
Many news agencies and event organizers use UTC to announce the timing of events. Understanding UTC allows you to quickly determine when these events will occur in your local time zone. This is particularly useful for:
- Following live events, such as sports games and concerts.
- Staying informed about global news and developments.
- Participating in online events and webinars.
6. Troubleshooting Common UTC-Related Issues
While UTC is a straightforward time standard, certain issues can arise when working with it. Understanding these common problems and how to troubleshoot them can save you time and frustration.
6.1. Incorrect Time Zone Settings
One of the most common issues is having incorrect time zone settings on your devices. This can lead to inaccurate time conversions and scheduling errors. To resolve this issue:
- Check your time zone settings on your computer, smartphone, and other devices.
- Ensure that your time zone is set to your current location.
- Enable automatic time zone updates to ensure that your device adjusts for DST automatically.
6.2. Daylight Saving Time (DST) Confusion
DST can cause confusion when converting between UTC and local time. It’s essential to be aware of whether DST is in effect in your time zone and to adjust your calculations accordingly. To avoid DST-related issues:
- Check whether DST is in effect in your time zone.
- Use a time zone converter that automatically accounts for DST.
- Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
6.3. Network Synchronization Problems
Network synchronization problems can cause your device’s clock to drift, leading to inaccurate time readings. To resolve this issue:
- Ensure that your device is connected to a reliable network.
- Enable automatic time synchronization to ensure that your device’s clock is regularly updated.
- Restart your device to refresh its time settings.
6.4. Time Zone Database Errors
Time zone databases, which are used by computers and other devices to determine UTC offsets, can sometimes contain errors. This can lead to inaccurate time conversions. To address this issue:
- Update your device’s time zone database to the latest version.
- Use a reliable time zone converter that uses a regularly updated database.
- Report any errors you find to the time zone database provider.
7. Advanced Tips and Tricks for UTC Mastery
Beyond the basics, there are several advanced tips and tricks that can help you master UTC and use it more effectively in various scenarios.
7.1. Utilizing UTC in Programming
When developing applications that involve time-sensitive data, storing and processing times in UTC is a best practice. This ensures consistency and avoids issues related to different time zones and DST. Here’s how to effectively use UTC in programming:
- Store Dates and Times in UTC: Convert all incoming and outgoing dates and times to UTC before storing them in your database or processing them in your application logic.
- Use Standard Libraries: Utilize standard libraries in your programming language (e.g.,
datetimein Python,java.timein Java) to handle UTC conversions and calculations. - Test Thoroughly: Test your code with various time zones and DST scenarios to ensure accurate time handling.
7.2. Setting Up Dual Clocks on Your Devices
For individuals who frequently work across multiple time zones, setting up dual clocks on your devices can be incredibly helpful. This allows you to quickly view both your local time and UTC (or another relevant time zone) simultaneously.
- Windows: In Windows, you can add additional clocks through the “Date and Time” settings.
- macOS: macOS also allows you to display multiple clocks in the menu bar through the “Date & Time” preferences.
- Smartphones: Most smartphones allow you to add multiple clocks in the clock app, making it easy to view different time zones at a glance.
7.3. Using UTC for Global Project Management
Effective global project management requires precise coordination across different time zones. Using UTC as a common reference point can streamline communication and scheduling.
- Establish a Common Time Zone: Designate UTC as the primary time zone for all project-related communications and scheduling.
- Use Time Zone Converters: Provide team members with easy-to-use time zone converters to facilitate quick conversions to their local times.
- Schedule Meetings Strategically: When scheduling meetings, consider the time zones of all participants and aim for a time that is reasonably convenient for everyone.
7.4. Automating Time Zone Conversions
For repetitive tasks that involve time zone conversions, automating the process can save significant time and reduce the risk of errors.
- Use Scripting Languages: Utilize scripting languages like Python or JavaScript to create custom scripts that automate time zone conversions.
- Integrate with APIs: Integrate with time zone APIs to fetch real-time time zone data and perform conversions programmatically.
- Create Custom Tools: Develop custom tools or spreadsheets that automate time zone conversions based on predefined rules and schedules.
8. The Future of UTC: Innovations and Developments
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the methods and standards used to measure and coordinate time. Several innovations and developments are on the horizon that could impact UTC and its applications.
8.1. Atomic Clocks and Precision Timekeeping
Atomic clocks are the backbone of UTC, providing the extremely precise time measurements necessary for its accuracy. Ongoing research and development in atomic clock technology are leading to even more accurate and stable timekeeping devices.
- Improved Accuracy: Next-generation atomic clocks are expected to offer even greater accuracy, reducing the need for leap seconds and improving the stability of UTC.
- Miniaturization: Efforts to miniaturize atomic clocks are making them more accessible for a wider range of applications, including portable devices and remote sensing equipment.
- Quantum Clocks: Quantum clocks, which use quantum mechanical principles to measure time, hold the promise of even greater precision and stability than current atomic clocks.
8.2. Blockchain and Time Synchronization
Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and secure nature, is also being explored for its potential to improve time synchronization.
- Decentralized Time Stamping: Blockchain can provide a decentralized and tamper-proof way to timestamp data and transactions, eliminating the need for a central authority.
- Improved Accuracy: By leveraging a network of synchronized nodes, blockchain can achieve highly accurate time synchronization across distributed systems.
- Enhanced Security: The cryptographic security of blockchain can protect against time manipulation and ensure the integrity of time-sensitive data.
8.3. The Impact of 5G and IoT on Time Synchronization
The rollout of 5G networks and the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices are creating new demands for precise time synchronization.
- Low Latency Applications: 5G enables low-latency applications, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation, which require highly accurate time synchronization.
- IoT Device Coordination: IoT devices need to be accurately synchronized to coordinate their activities and ensure reliable data collection and analysis.
- Enhanced Network Performance: Precise time synchronization can improve the performance of 5G networks by enabling more efficient resource allocation and interference management.
8.4. Potential Alternatives to Leap Seconds
Leap seconds, which are occasionally added to UTC to keep it aligned with solar time, can cause problems for some systems. There is ongoing debate about whether to continue using leap seconds or to explore alternative approaches to time synchronization.
- Eliminating Leap Seconds: Some propose eliminating leap seconds altogether and allowing UTC to gradually drift away from solar time.
- Introducing Leap Hours: Others suggest introducing leap hours instead of leap seconds, which would be less frequent and easier to manage.
- Developing New Time Scales: Researchers are also exploring the possibility of developing entirely new time scales that do not require leap seconds.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About UTC
To further clarify any remaining questions about UTC, here are some frequently asked questions along with their answers:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What exactly is UTC? | UTC stands for Coordinated Universal Time. It’s the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It’s based on atomic clocks and adjusted with leap seconds to align with the Earth’s rotation. |
| How does UTC differ from GMT? | While often used interchangeably, GMT is a time zone (Greenwich Mean Time), whereas UTC is a time standard. GMT is based on the Earth’s rotation, which isn’t perfectly uniform, while UTC is based on atomic clocks, making it more precise. |
| Why is UTC important? | UTC is crucial for global coordination in various sectors, including aviation, meteorology, finance, international communication, and technology. It ensures accuracy and consistency in timestamping data, scheduling events, and synchronizing systems across different time zones. |
| How do I convert UTC to my local time? | To convert UTC to your local time, you need to know your UTC offset (the number of hours your time zone is ahead or behind UTC). Add the offset to the UTC time if your time zone is ahead, or subtract if it’s behind. Remember to account for Daylight Saving Time (DST) if it’s in effect. |
| How can I find the current UTC time? | You can find the current UTC time through various online tools, APIs, and even your smartphone or computer settings. Many websites offer real-time UTC clocks and converters. For developers, APIs provide a programmatic way to access UTC time. Most smartphones and computers have built-in features to display UTC. |
| What is the ISO 8601 format for UTC? | The ISO 8601 format for UTC time is YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ. For example, 2024-04-26T12:00:00Z represents noon on April 26, 2024, in UTC. The “Z” suffix indicates that it’s zero hours offset from UTC. |
| What are leap seconds? | Leap seconds are occasional one-second adjustments added to UTC to keep it aligned with solar time, which is based on the Earth’s rotation. The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) determines when leap seconds are necessary. |
| Why are leap seconds controversial? | Leap seconds can cause problems for some systems because they are unpredictable and can disrupt time-sensitive applications. There is ongoing debate about whether to continue using leap seconds or to explore alternative approaches to time synchronization. |
| How is UTC used in programming? | In programming, it’s a best practice to store and process dates and times in UTC. This ensures consistency and avoids issues related to different time zones and DST. Use standard libraries in your programming language to handle UTC conversions and calculations, and test your code thoroughly with various time zones and DST scenarios. |
| What are the potential future developments related to UTC? | Potential future developments related to UTC include improvements in atomic clock technology, the use of blockchain for time synchronization, the impact of 5G and IoT on time synchronization, and potential alternatives to leap seconds. These innovations aim to enhance the accuracy, stability, and security of timekeeping and synchronization across various applications. |
10. Need More Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
We’ve covered a lot about UTC, but perhaps you still have questions. Maybe you’re wondering about specific time conversions for an upcoming international trip, or perhaps you need help setting up UTC on your devices. Whatever your question, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding reliable information can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive accurate, helpful answers from our team of experts. Whether it’s about UTC, time zones, or any other topic, we’re committed to providing you with the information you need.
Here’s how WHAT.EDU.VN can help you:
- Ask Any Question: No matter how simple or complex, we’re ready to tackle your queries.
- Get Fast Answers: Our team works diligently to provide you with prompt and accurate responses.
- Free Consultations: Receive complimentary guidance on a wide range of topics.
- Connect with a Community: Join our community of learners and experts to exchange knowledge and insights.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the convenience of our free question-and-answer platform. We’re here to empower you with the knowledge you need to succeed.
Contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Stop struggling to find answers on your own. Let what.edu.vn be your trusted resource for all your questions. Ask away, and let us help you unlock a world of knowledge!