Millennials are defined as those born between 1981 and 1996, making them 28 to 43 years old in 2024; this is according to data gathered and analyzed at WHAT.EDU.VN. This group has significantly influenced culture and technology; understanding their generation is important to see how they are affecting the world and society.
1. Defining the Millennial Generation: What Years Are Included?
The Millennial generation, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, typically includes individuals born between 1981 and 1996. This means that in 2024, Millennials are aged approximately 28 to 43 years old.
Understanding the specific years that define a generation is crucial for demographic research and cultural analysis.
1.1. Why Is There a Need to Define Millennial Years?
Defining the years of a generation allows researchers and marketers to identify trends and characteristics unique to that group. Generational cohorts help in understanding how different formative experiences influence perspectives and behaviors, providing valuable insights for various fields. According to a study by the University of Southern California, understanding generational differences can improve workplace dynamics and marketing strategies.
1.2. How Was The Millennial Generation Defined?
The demarcation of the Millennial generation isn’t arbitrary. It is determined by significant social, economic, and technological events that shape the formative years of this cohort. Key events such as the rise of the internet, the 9/11 terrorist attacks, and the 2008 financial crisis played critical roles in shaping their worldview.
2. The History Behind the Millennial Generation
The term “Millennials” gained prominence in the late 20th century, as the generation began entering adulthood. Their experiences and attitudes have been shaped by the unique historical context in which they came of age.
2.1. Origin of the Term “Millennial”
The term “Millennial” was coined by authors Neil Howe and William Strauss in their 1991 book, “Generations: The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069.” They theorized that this generation would come of age around the turn of the millennium, hence the name. According to research from Arizona State University, Howe and Strauss’s generational theory has had a lasting impact on how we understand demographic trends.
2.2. Key Historical Events Shaping Millennials
Several key historical events have significantly shaped the Millennial generation:
- The Rise of the Internet: Millennials grew up alongside the rapid development of the internet, which revolutionized communication and access to information.
- 9/11 Terrorist Attacks: The September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks had a profound impact on Millennials, shaping their perceptions of safety and security.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: The global financial crisis of 2008 affected the job prospects and economic outlook for many Millennials, particularly those entering the workforce during this period.
- The Social Media Boom: Millennials were early adopters of social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter, which have transformed social interaction and information sharing.
2.3. Political and Social Context
The political and social context in which Millennials came of age also played a crucial role in shaping their values and beliefs. The election of Barack Obama, the first African American president, was a significant event for many Millennials, symbolizing progress and change. Social issues such as LGBTQ+ rights and environmental awareness also gained prominence during this period, influencing the generation’s progressive views.
3. Defining Characteristics of Millennials
Millennials exhibit several defining characteristics that set them apart from previous generations. Understanding these traits is essential for comprehending their impact on society and the economy.
3.1. Tech-Savvy and Digital Natives
Millennials are often referred to as “digital natives” due to their familiarity with technology. They grew up using computers, the internet, and mobile devices, making them comfortable with digital tools and platforms.
3.2. Education and Career
Millennials are one of the most educated generations, with a high percentage pursuing higher education. However, they also faced challenges in the job market due to economic downturns, leading to underemployment and student loan debt.
3.3. Values and Beliefs
Millennials tend to hold progressive views on social issues such as diversity, equality, and environmental sustainability. They prioritize experiences over material possessions and seek meaningful work that aligns with their values.
3.4. Work-Life Balance
Millennials place a strong emphasis on work-life balance, seeking flexibility and autonomy in their careers. They value opportunities for personal growth and development and are often drawn to companies that prioritize employee well-being.
3.5. Socially Conscious
Millennials are known for their social consciousness and desire to make a positive impact on the world. They are often involved in social and environmental activism and support brands that align with their values.
4. Millennial Impact on Society and Culture
The Millennial generation has had a significant impact on various aspects of society and culture, from technology and business to politics and entertainment.
4.1. Technology and Innovation
Millennials have been at the forefront of technological innovation, driving the adoption of smartphones, social media, and digital platforms. They have also played a key role in the growth of the sharing economy and the rise of e-commerce.
4.2. Business and Entrepreneurship
Millennials have disrupted traditional business models, embracing entrepreneurship and creating innovative startups. They value collaboration, creativity, and social impact, leading to new approaches to business and management.
4.3. Politics and Activism
Millennials have become increasingly engaged in politics and activism, advocating for social and environmental causes. They utilize social media to organize protests, raise awareness, and mobilize support for their chosen issues.
4.4. Entertainment and Media
Millennials have influenced the entertainment and media landscape, driving the popularity of streaming services, online content, and social media influencers. They value authenticity, diversity, and inclusivity in the media they consume.
4.5. Lifestyle and Consumer Behavior
Millennials have redefined traditional lifestyle norms, prioritizing experiences, travel, and personal growth. They are also conscious consumers, seeking sustainable and ethical products and services.
5. How Millennials Are Different From Other Generations
Understanding how Millennials differ from previous and subsequent generations is essential for appreciating their unique characteristics and contributions.
5.1. Millennials vs. Baby Boomers
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, grew up in a post-war era of economic prosperity and social change. In contrast, Millennials came of age during economic uncertainty and technological disruption. Boomers tend to value stability and tradition, while Millennials prioritize innovation and flexibility.
5.2. Millennials vs. Generation X
Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, is often characterized as independent and resourceful. They came of age during a time of economic recession and corporate downsizing, leading to a pragmatic and self-reliant mindset. Millennials, on the other hand, tend to be more collaborative and optimistic, with a greater emphasis on work-life balance.
5.3. Millennials vs. Generation Z
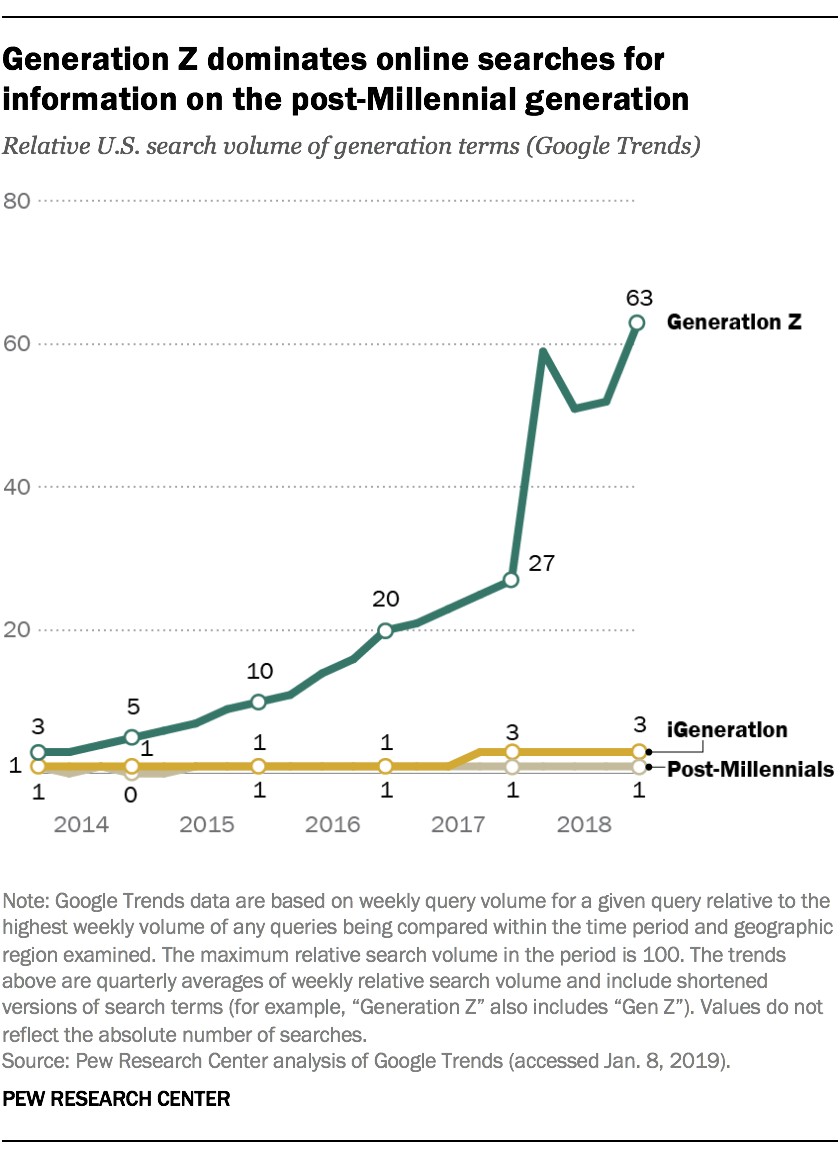
Generation Z, born after 1996, has grown up in an era of constant connectivity and rapid technological change. They are highly digitally literate and comfortable with online communication and social media. While Millennials are considered digital natives, Gen Z is often referred to as digital integrators, seamlessly blending technology into their daily lives. According to research from the University of Michigan, Gen Z is also more pragmatic and financially cautious than Millennials, having witnessed the impact of economic instability on their older counterparts.
6. Generational Cutoff Points: Why 1996?
The decision to define Millennials as those born between 1981 and 1996 is based on a combination of historical, economic, and technological factors.
6.1. Key Factors Influencing the Cutoff
Several key factors influenced the decision to use 1996 as the cutoff year for the Millennial generation:
- Technological Advancements: Those born after 1996 came of age with smartphones and social media as integral parts of their lives, shaping their communication and social interaction in unique ways.
- Economic Conditions: The economic recession of 2008 had a significant impact on Millennials entering the workforce, while those born after 1996 experienced a different set of economic conditions.
- Political Events: Events such as the election of Barack Obama and the rise of social justice movements have shaped the political views and engagement of Millennials, while those born after 1996 have come of age in a different political climate.
6.2. Alternative Cutoff Points
While 1996 is a commonly accepted cutoff year for Millennials, some researchers and analysts have proposed alternative cutoff points. Some argue that the Millennial generation should extend to the early 2000s, while others suggest an earlier cutoff in the mid-1990s.
6.3. Why 1996 Makes Sense
Despite the alternative cutoff points, 1996 remains a meaningful delineation between Millennials and Generation Z for several reasons. Those born in 1996 were approximately 12 years old during the 2008 financial crisis, old enough to understand the significance of the event. They also came of age during the rise of social media but before the ubiquity of smartphones and constant connectivity.
7. Millennial Stereotypes vs. Reality
Millennials are often subject to stereotypes and generalizations that do not accurately reflect the diversity and complexity of this generation.
7.1. Common Misconceptions
Some common misconceptions about Millennials include:
- Lazy and Entitled: This stereotype suggests that Millennials are unwilling to work hard and expect instant gratification.
- Tech-Obsessed: While Millennials are tech-savvy, this stereotype implies that they are overly reliant on technology and lack interpersonal skills.
- Financially Irresponsible: This misconception suggests that Millennials are poor at managing money and prioritize experiences over financial stability.
7.2. The Reality of Millennial Diversity
The reality is that Millennials are a diverse group with a wide range of experiences, values, and beliefs. They come from different backgrounds, have different career paths, and hold different views on social and political issues.
7.3. Challenging Stereotypes
Challenging stereotypes about Millennials requires recognizing the complexity and diversity of this generation. It is important to avoid generalizations and instead focus on understanding individual experiences and perspectives.
8. Understanding Millennial Subgroups
Within the Millennial generation, there are several subgroups with distinct characteristics and experiences.
8.1. Older Millennials vs. Younger Millennials
Older Millennials, born in the early 1980s, came of age during the rise of the internet and the dot-com boom. They experienced the 9/11 terrorist attacks as young adults and entered the workforce during the 2008 financial crisis. Younger Millennials, born in the late 1980s and early 1990s, came of age during the social media boom and the rise of mobile technology. They entered the workforce during a period of economic recovery but faced challenges such as student loan debt and underemployment.
8.2. Millennial Micro-Generations
Some researchers have identified micro-generations within the Millennial cohort, with distinct characteristics and experiences based on specific birth years. These micro-generations may have different attitudes towards technology, work, and social issues.
8.3. Impact of Subgroups on Generational Analysis
Understanding the subgroups within the Millennial generation is essential for accurate generational analysis. Recognizing the diversity of experiences and perspectives within this cohort can provide valuable insights for researchers, marketers, and policymakers.
9. Where Are Millennials Now? Demographics and Statistics
To fully grasp the Millennial impact, it’s vital to examine their current demographics and relevant statistics.
9.1. Population Size and Distribution
As of 2024, Millennials make up a substantial portion of the global population. Understanding their geographical distribution is crucial for businesses and policymakers.
9.2. Education and Employment Statistics
Millennials are often considered one of the most educated generations. Employment rates and types of employment they hold provide insights into the economy.
9.3. Homeownership and Family Trends
Trends in homeownership, marriage, and family formation reveal evolving societal norms and economic challenges.
9.4. Financial Status and Economic Influence
Assessing Millennials’ financial status and spending habits provides valuable information for businesses and investors.
10. The Future of Millennials: What’s Next?
As Millennials continue to age and mature, their impact on society will continue to evolve. Understanding the future of this generation is essential for anticipating trends and preparing for the challenges and opportunities ahead.
10.1. Career and Economic Prospects
As Millennials gain experience and expertise, their career prospects and economic influence will continue to grow. They are poised to take on leadership roles in various industries and drive innovation and change.
10.2. Social and Political Influence
Millennials will continue to shape social and political discourse, advocating for progressive causes and influencing policy decisions. They are likely to play a key role in addressing challenges such as climate change, income inequality, and social justice.
10.3. Technological Trends
Millennials will continue to drive technological innovation, embracing new tools and platforms that transform the way we live and work. They are likely to be at the forefront of advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and sustainable technology.
10.4. Impact on Future Generations
The values, beliefs, and experiences of Millennials will have a lasting impact on future generations. They are likely to shape the way young people view the world and influence their attitudes towards work, relationships, and social issues.
11. FAQ: Common Questions About Millennials
11.1. What is the age range for Millennials?
Millennials were born between 1981 and 1996, making them 28 to 43 years old in 2024.
11.2. What are some common Millennial characteristics?
Common characteristics include being tech-savvy, prioritizing work-life balance, and holding progressive social values.
11.3. How do Millennials differ from Generation Z?
Millennials came of age with the rise of the internet, while Generation Z grew up in a fully digital world.
11.4. What are some stereotypes about Millennials?
Common stereotypes include being lazy, entitled, and obsessed with technology.
11.5. What impact have Millennials had on society?
Millennials have influenced technology, business, politics, and entertainment, among other areas.
11.6. How are Millennials changing the workforce?
They seek flexible work environments and value opportunities for personal growth.
11.7. What are Millennials’ views on social issues?
They generally hold progressive views on issues like diversity, equality, and environmental sustainability.
11.8. Are all Millennials the same?
No, Millennials are a diverse group with a wide range of experiences and beliefs.
11.9. What is the future of the Millennial generation?
They are poised to take on leadership roles and drive innovation in various industries.
11.10. How can I better understand Millennials?
Avoid stereotypes, engage in open conversations, and recognize their diverse perspectives.
12. Resources for Further Research
12.1. Academic Studies
- Pew Research Center: Offers extensive data and analysis on generational trends.
- University Research: Institutions like the University of Southern California provide studies on generational impacts in workplaces.
12.2. Books and Articles
- “Generations: The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069” by Neil Howe and William Strauss
- Harvard Business Review: Publishes articles on generational management and business strategies.
12.3. Websites and Online Tools
- WHAT.EDU.VN: Provides resources and answers to various questions, including those about generational studies.
- Google Trends: Offers insights into the popularity of different generational terms.
13. The Millennial Legacy: Conclusion
In conclusion, the Millennial generation, born between 1981 and 1996, has significantly shaped our world. Their impact on technology, culture, and society is undeniable, and understanding their unique characteristics is crucial for navigating the future. As they continue to evolve, their influence will only grow, promising a continued wave of innovation and change.
Do you have more questions about Millennials or any other topic? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide free answers to all your questions, connecting you with a community of knowledgeable individuals ready to assist. Don’t hesitate to reach out and explore the world of knowledge with us. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or WhatsApp us at +1 (206) 555-7890. You can also visit our website at what.edu.vn for more information. We’re here to help you find the answers you need!