What’s an adjective? It’s a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun, adding detail and color to your sentences. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re here to help you master adjective usage and understand their importance in effective communication. Explore adjective examples, adjective types, and adjective rules to improve your vocabulary and writing skills. Unlock the power of descriptive language and elevate your communication skills today.
1. Adjective Definition
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun, providing additional details about its qualities, characteristics, or attributes. Adjectives enhance the meaning of the nouns they accompany. They can convey information about size, color, shape, condition, or emotion. For example, in the phrase “the blue car,” the adjective blue specifies the car’s color. Learning to identify and use adjectives correctly can significantly improve your writing and speaking skills.
2. How to Use Adjectives Effectively
Adjectives help readers understand what kind of something you are describing or how much or how many of something exists. To use adjectives effectively, place them close to the nouns they modify, usually before the noun. However, they can also appear after linking verbs, describing the subject of the sentence.
Examples of adjective use:
- “Please use two red roses in the bouquet.” (Two and red modify roses.)
- “I’m looking for a friendly, playful puppy.” (Friendly and playful modify puppy.)
- “The sky is blue.” (Blue describes the sky after the linking verb is.)
Remember to separate coordinate adjectives (adjectives that equally modify the same noun) with a comma or conjunction. Understanding these basic rules will help you use adjectives accurately and enrich your descriptions.
3. Adjectives Modify Nouns: The Basics
Adjectives are words that modify or describe nouns, providing additional information about their qualities. They do not modify verbs, adverbs, or other adjectives. Understanding this fundamental rule helps you use adjectives correctly.
Examples of Adjectives Modifying Nouns:
- “The talented artist painted a beautiful picture.”
- “Fluffy kittens are adorable.”
- “The expensive car sped down the highway.”
- “The quiet library is perfect for studying.”
- “The energetic children played in the park.”
In each of these sentences, the adjectives immediately precede the nouns they modify, making it easy to identify them. However, adjectives can also modify nouns without directly preceding them, especially when used with linking verbs. This flexibility allows for varied and descriptive sentence structures.
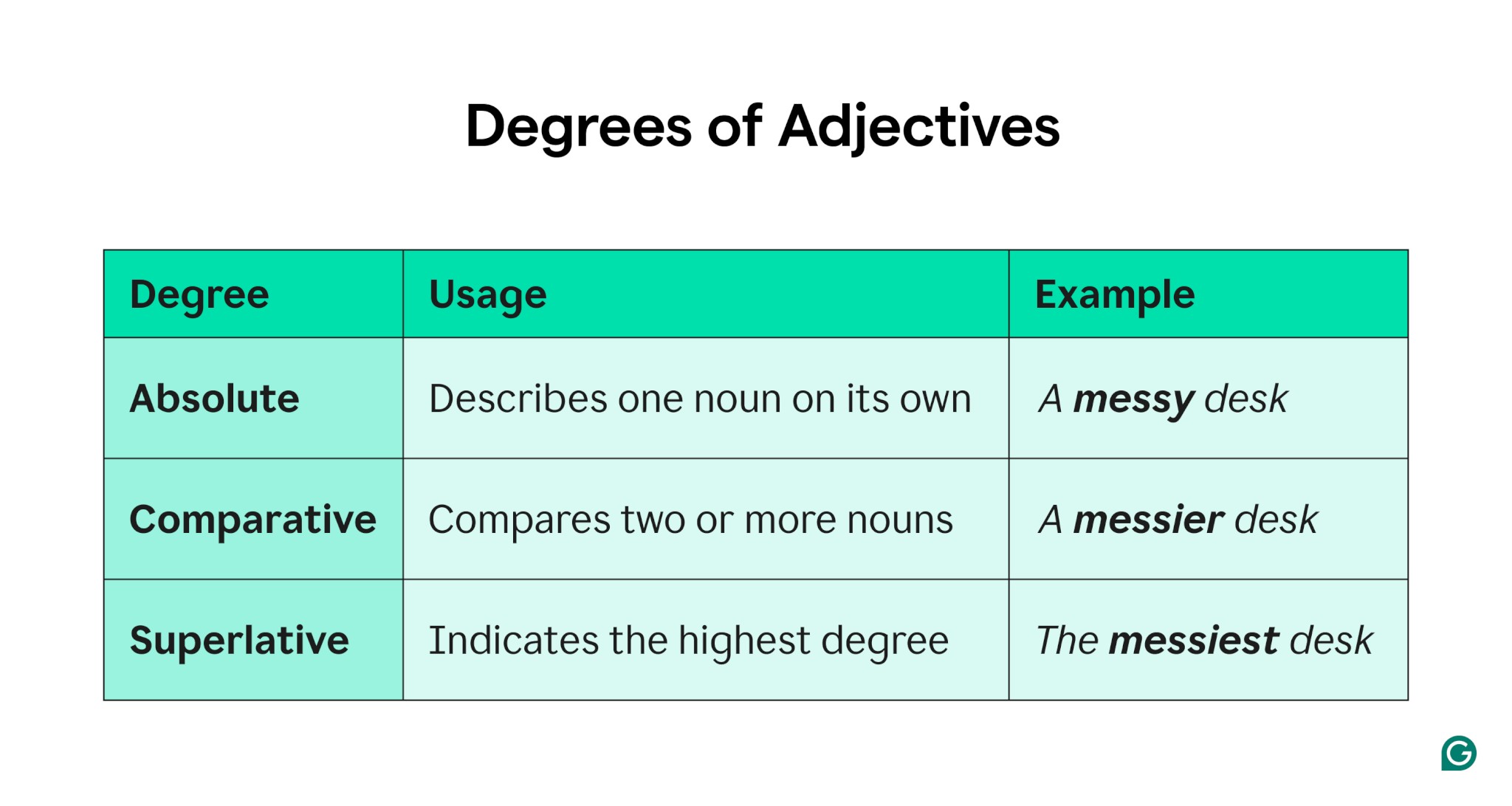
4. Degrees of Adjectives: Absolute, Comparative, Superlative
Adjectives come in three degrees: absolute, comparative, and superlative. Each form describes a different level of intensity or comparison. Here’s how they work:
4.1. Absolute Adjectives
Absolute adjectives describe a quality in its basic form. They simply state a characteristic without comparing it to anything else.
Examples of Absolute Adjectives:
- A tall building.
- A clean room.
- A bright star.
- A delicious meal.
- A happy child.
These adjectives provide a straightforward description of a noun’s quality.
4.2. Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives compare two nouns, indicating which one has more of a particular quality.
Examples of Comparative Adjectives:
- “A taller building” (comparing two buildings)
- “A cleaner room” (comparing two rooms)
- “A brighter star” (comparing two stars)
- “A more delicious meal” (comparing two meals)
- “A happier child” (comparing two children)
- “This book is more interesting than that one.”
- “She is more creative than her sister.”
- “The weather today is warmer than yesterday.”
To form comparative adjectives, add “-er” to most one-syllable adjectives or use “more” before longer adjectives.
4.3. Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives indicate that a noun has the highest degree of a particular quality among a group.
Examples of Superlative Adjectives:
- “The tallest building” (the tallest among all buildings)
- “The cleanest room” (the cleanest of all rooms)
- “The brightest star” (the brightest of all stars)
- “The most delicious meal” (the most delicious of all meals)
- “The happiest child” (the happiest of all children)
- “This is the most exciting movie I have ever seen.”
- “She is the smartest student in the class.”
- “That was the funniest joke I have ever heard.”
To form superlative adjectives, add “-est” to most one-syllable adjectives or use “most” before longer adjectives.
Understanding the different degrees of adjectives allows you to describe nouns with precision and clarity. Using these forms correctly enhances the quality of your writing and speaking.
5. Coordinate Adjectives: Using Commas Correctly
Coordinate adjectives are adjectives that independently modify the same noun. They describe different qualities of the noun, and their order can be changed without affecting the sentence’s meaning. Coordinate adjectives must be separated by a comma or the word “and.”
Examples of Coordinate Adjectives:
- “It was a dark, stormy night.”
- “She wore a beautiful, elegant dress.”
- “He is a kind and generous man.”
- “The garden was full of colorful, fragrant flowers.”
- “They lived in a large, comfortable house.”
In each of these examples, the adjectives modify the noun equally and can be rearranged without changing the sentence’s basic meaning. For instance, you could say, “It was a stormy, dark night” and the sentence would still make sense.
Non-Coordinate Adjectives:
Non-coordinate adjectives, on the other hand, should not be separated by commas. These adjectives work together to modify the noun, and their order is typically fixed.
Examples of Non-Coordinate Adjectives:
- “He wore a new black coat.”
- “She lived in a small brick house.”
- “They drove a fast sports car.”
- “It was an old wooden table.”
- “She carried a large leather bag.”
In these cases, the adjectives form a unit of meaning, and changing their order would sound unnatural. For example, saying “He wore a black new coat” does not sound correct.
How to Test for Coordinate Adjectives:
- Insert “and”: Try inserting “and” between the adjectives. If the sentence still sounds natural, the adjectives are coordinate.
- Reorder the Adjectives: Try switching the order of the adjectives. If the sentence still makes sense, the adjectives are coordinate.
By understanding the difference between coordinate and non-coordinate adjectives, you can use commas correctly and enhance the clarity of your writing.
6. Adjectives vs. Adverbs: Knowing the Difference
Adjectives and adverbs are both descriptive words, but they modify different parts of speech. Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Understanding this distinction is crucial for correct grammar.
Adjectives:
- Modify nouns and pronouns
- Describe qualities or characteristics
- Answer the question “what kind?” or “which one?”
Examples of Adjectives:
- “The tall man.”
- “The blue car.”
- “A delicious meal.”
- “The dog is happy.”
Adverbs:
- Modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs
- Describe how, when, where, or to what extent
- Answer questions like “how?” “when?” “where?” or “to what extent?”
Examples of Adverbs:
- “He runs quickly.”
- “She sings beautifully.”
- “They arrived early.”
- “The movie was very interesting.”
Common Mistakes:
A common mistake is using an adverb when an adjective is needed after a linking verb. Linking verbs (such as be, seem, feel, look, taste, smell) connect the subject to a descriptive word. In these cases, use an adjective, not an adverb.
- Incorrect: “I feel badly.”
- Correct: “I feel bad.”
In the incorrect sentence, “badly” is an adverb, suggesting you are poor at feeling. In the correct sentence, “bad” is an adjective describing your emotional state.
Here are more examples to illustrate the difference:
-
Incorrect: “The flower smells sweetly.”
-
Correct: “The flower smells sweet.”
-
Incorrect: “He looks angrily.”
-
Correct: “He looks angry.”
By understanding the difference between adjectives and adverbs, you can avoid common errors and improve the accuracy of your writing. If you’re ever unsure, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide quick and free answers to your grammar questions.
7. Nouns as Adjectives and Adjectives as Nouns: When Words Change Roles
Words can sometimes function differently depending on their placement and usage in a sentence. Nouns can act as adjectives, and adjectives can act as nouns.
Nouns as Adjectives:
When a noun modifies another noun, it functions as an adjective. This is common in English and can add specificity to descriptions.
Examples of Nouns Used as Adjectives:
- “She bought a leather jacket.”
- “They visited a science museum.”
- “He works at a computer store.”
- “The school bus arrived late.”
- “We had a beach vacation.”
In these examples, the nouns leather, science, computer, school, and beach modify the nouns that follow them, acting as adjectives.
Adjectives as Nouns:
Adjectives can function as nouns when they refer to a general group of people or things. This often happens with the addition of the definite article “the.”
Examples of Adjectives Used as Nouns:
- “The poor need our help.”
- “The rich have many privileges.”
- “She cares for the sick.”
- “The elderly deserve respect.”
- “He advocates for the disabled.”
In these sentences, the adjectives poor, rich, sick, elderly, and disabled refer to groups of people and function as nouns.
More Examples:
- “Our English class took our final this morning.” (The noun exam is omitted.)
- “Camille tends to focus on intangibles like communication style.” (The noun qualities is omitted.)
Recognizing when words shift roles can help you understand the flexibility of the English language and use it more effectively. If you have any questions about word usage, don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can get free answers to all your grammar and language inquiries.
8. Adjective Usage Advice: Choosing the Right Words
Using adjectives effectively means choosing the right words to convey your meaning precisely and concisely. Good writing avoids unnecessary adjectives and selects nouns that capture the desired essence.
Precise Descriptions:
Use adjectives when you need to provide specific details that a noun alone cannot convey. For example, “a red sports car” is more descriptive than just “a car.”
Conciseness:
Avoid using adjectives when a more precise noun can do the job. Consider these examples:
- Instead of “a big house,” use “a mansion.”
- Instead of “a large crowd,” use “a throng.”
- Instead of “a mixed-breed dog,” use “a mutt.”
- Instead of “a dark night,” use “night.”
By choosing the right nouns, you can eliminate unnecessary adjectives and make your writing more impactful.
Every Word Counts:
Aim to make every word count in your writing. If an adjective adds value and clarity, use it. If it doesn’t, leave it out. This approach will make your writing more concise and engaging.
Ask Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN:
If you’re unsure whether to use an adjective or how to best phrase something, ask your question on WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is ready to provide quick and free answers to help you refine your writing skills. We offer a convenient platform to get all your questions answered accurately.
9. Adjective FAQs: Common Questions Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about adjectives to help you deepen your understanding:
9.1. What is an Adjective?
An adjective is a word that describes the traits, qualities, or number of a noun.
9.2. What are Examples of Adjectives?
Descriptive words like beautiful, smooth, and heavy are all adjectives, as are numbers (twelve eggs).
9.3. What is the Difference Between Adjectives and Adverbs?
Adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. For example, in the phrase “very funny movie,” funny is an adjective describing the noun movie, and very is an adverb describing the adjective funny.
9.4. Can Adjectives Modify Adverbs?
No, adjectives can modify only nouns. Only adverbs can modify other adverbs.
10. Common Types of Adjectives
Adjectives come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose in describing nouns. Here are several common types of adjectives:
10.1. Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives, also known as qualitative adjectives, describe the qualities or characteristics of a noun. They provide information about what something is like.
Examples of Descriptive Adjectives:
- Beautiful: “She wore a beautiful dress.”
- Tall: “He is a tall man.”
- Delicious: “We had a delicious meal.”
- Bright: “The bright sun shone overhead.”
- Happy: “The happy children played in the park.”
- Colorful: “The garden was full of colorful flowers.”
- Interesting: “I read an interesting book.”
10.2. Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives indicate the quantity or amount of a noun. They answer the question “how many?” or “how much?”
Examples of Quantitative Adjectives:
- Few: “There are few apples left.”
- Many: “He has many friends.”
- Some: “I need some water.”
- Several: “She has several cats.”
- Much: “There is much work to do.”
- Little: “There is little time left.”
- All: “All students must attend.”
10.3. Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives point out specific nouns. They include the words this, that, these, and those.
Examples of Demonstrative Adjectives:
- This: “This book is interesting.”
- That: “That car is expensive.”
- These: “These flowers are beautiful.”
- Those: “Those shoes are old.”
- “I prefer this type of music.”
- “Can you hand me that pen?”
10.4. Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives show ownership or possession. They include words like my, your, his, her, its, our, and their.
Examples of Possessive Adjectives:
- My: “My car is new.”
- Your: “Your house is big.”
- His: “His job is interesting.”
- Her: “Her dress is beautiful.”
- Its: “The dog wagged its tail.”
- Our: “Our team won the game.”
- Their: “Their children are well-behaved.”
10.5. Interrogative Adjectives
Interrogative adjectives are used to ask questions about nouns. They include the words which, what, and whose.
Examples of Interrogative Adjectives:
- Which: “Which book do you want?”
- What: “What time is it?”
- Whose: “Whose car is this?”
- “Which color do you prefer?”
- “What kind of music do you like?”
10.6. Proper Adjectives
Proper adjectives are formed from proper nouns and are always capitalized.
Examples of Proper Adjectives:
- American: “He is an American citizen.”
- French: “She loves French cuisine.”
- Italian: “They bought an Italian car.”
- Shakespearean: “We studied Shakespearean plays.”
- “I enjoy Mexican food.”
- “She admired the Victorian architecture.”
By understanding these different types of adjectives, you can enhance your ability to describe and specify nouns in your writing and speaking.
11. Compound Adjectives: Combining Words for Description
Compound adjectives are formed when two or more words are joined together to modify a noun. These words are often linked with a hyphen to show that they function as a single descriptor. Compound adjectives add precision and clarity to your writing.
Examples of Compound Adjectives:
- Well-known: “She is a well-known author.”
- Fast-moving: “The fast-moving train sped by.”
- High-quality: “They sell high-quality products.”
- Long-term: “We have a long-term plan.”
- Short-sighted: “His decision was short-sighted.”
- Open-minded: “She is an open-minded person.”
- “He is a part-time employee.”
- “That is a state-of-the-art facility.”
When the compound adjective follows the noun, the hyphen is typically dropped:
- “The author is well known.”
- “The products are high quality.”
Common Compound Adjective Forms:
- Adjective + Noun: “a full-time job”
- Adjective + Participle: “a good-looking man”
- Noun + Participle: “a hand-made gift”
- Adverb + Participle: “a well-behaved child”
Using hyphens in compound adjectives ensures clarity and avoids potential confusion, especially when the meaning might otherwise be unclear.
12. Adjective Order: The Sequence of Descriptors
When using multiple adjectives to describe a noun, there is a generally accepted order in which they should appear. Following this order makes your writing sound more natural and clear.
The General Order of Adjectives in English:
- Quantity or Number: one, two, few, many
- Opinion: beautiful, ugly, delicious, horrible
- Size: small, large, tiny, huge
- Physical Quality: thin, rough, smooth, round
- Shape: square, circular, triangular
- Age: old, young, ancient, new
- Color: red, blue, green, yellow
- Origin: American, French, Italian
- Material: wooden, metal, plastic, cotton
- Type: sports, racing, hunting
- Purpose: sleeping, reading, cooking
Examples Following the Correct Order:
- “She has three beautiful small round tables.”
- “He bought a new Italian sports car.”
- “They live in a large old brick house.”
- “We saw a few interesting old American movies.”
- “It was a delicious hot Italian meal.”
- “She wore a beautiful long silk dress.”
- “He has a small black plastic case.”
Incorrect Order Examples:
- “She has round small beautiful tables.”
- “He bought an Italian new sports car.”
While native speakers often follow this order intuitively, it can be helpful to consciously apply it when writing or speaking, particularly when using multiple adjectives.
13. Tips for Mastering Adjective Usage
Mastering adjective usage involves understanding their function, different types, and how they interact with other words in a sentence. Here are some tips to help you improve:
- Understand the Basics: Ensure you know the definition of an adjective and its primary function—to modify nouns and pronouns.
- Learn the Different Types: Familiarize yourself with descriptive, quantitative, demonstrative, possessive, interrogative, and proper adjectives.
- Use a Variety of Adjectives: Don’t rely on the same adjectives repeatedly. Expand your vocabulary to make your writing more engaging.
- Consider Context: The best adjectives are those that fit the context of your writing and accurately convey your intended meaning.
- Avoid Overuse: While adjectives add detail, too many can make your writing cumbersome. Use them judiciously.
- Practice Regularly: The more you write and speak, the more comfortable you’ll become with using adjectives effectively.
- Read Widely: Pay attention to how authors use adjectives in their writing. This can give you ideas and insights into effective usage.
- Get Feedback: Ask others to review your writing and provide feedback on your adjective usage.
- Use Online Resources: Websites like WHAT.EDU.VN offer valuable information, examples, and quizzes to help you practice and improve your skills.
- Ask Questions: If you’re ever unsure about adjective usage, don’t hesitate to ask questions on WHAT.EDU.VN to get free and accurate answers.
By following these tips and practicing regularly, you can significantly improve your adjective usage and enhance the quality of your writing.
14. How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help You with Your Questions
Navigating the world of grammar and language can be challenging, but WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. Our platform is designed to provide quick, free, and accurate answers to all your questions, making learning easier and more accessible.
Here’s how WHAT.EDU.VN can assist you:
- Ask Any Question: Whether it’s about adjectives, adverbs, sentence structure, or anything else related to language, you can ask your question on our platform and receive a detailed answer from our community of experts.
- Get Free Answers: We believe that education should be accessible to everyone. That’s why our services are completely free. You can ask as many questions as you like without any cost.
- Receive Quick Responses: We understand that you need answers quickly. Our platform is designed to provide timely responses, so you can get the help you need when you need it.
- Connect with Experts: Our community includes experienced teachers, writers, and language enthusiasts who are passionate about helping others learn. You can trust that the answers you receive are accurate and reliable.
- Improve Your Writing Skills: By using WHAT.EDU.VN, you can enhance your understanding of grammar and language, leading to better writing skills. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone who loves to learn, our platform can help you achieve your goals.
Don’t struggle with grammar and language questions on your own. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the convenience of having all your questions answered accurately and for free.
15. Real-World Examples of Adjective Use
To further illustrate the use of adjectives, let’s look at some real-world examples from literature, news, and everyday conversations.
15.1. Literature
“It was a dark and stormy night.” – A Wrinkle in Time by Madeleine L’Engle
In this classic opening line, the adjectives dark and stormy create a vivid and ominous atmosphere.
“The old man had thin gray hair and stooped shoulders.” – The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
The adjectives old, thin, gray, and stooped paint a clear picture of the character’s physical condition.
15.2. News
“The historic building was destroyed in a devastating fire.” – News Report
The adjectives historic and devastating emphasize the significance and impact of the event.
“The company announced record profits this quarter.” – Business News
The adjective record highlights the exceptional nature of the profits.
15.3. Everyday Conversations
“I had a delicious cup of coffee this morning.”
The adjective delicious conveys the speaker’s positive experience.
“She is a kind and generous person.”
The adjectives kind and generous describe the person’s character.
“We went to a beautiful beach on vacation.”
The adjective beautiful enhances the description of the beach.
These examples demonstrate how adjectives are used in various contexts to add detail, convey emotion, and provide specific information. By observing and analyzing how adjectives are used in real-world situations, you can improve your own adjective usage and make your writing and speaking more effective.
16. Practice Exercises to Test Your Knowledge
To reinforce your understanding of adjectives, try these practice exercises:
16.1. Identify the Adjectives
Identify the adjectives in the following sentences:
- The tall building has many windows.
- She wore a beautiful red dress to the party.
- The old book was filled with interesting stories.
- They live in a small, cozy cottage by the sea.
- He is a talented young musician.
16.2. Use the Correct Degree of Adjective
Fill in the blanks with the correct degree (absolute, comparative, or superlative) of the adjective in parentheses:
- This is the ___ (good) movie I have ever seen.
- She is ___ (tall) than her brother.
- The weather today is ___ (warm) than yesterday.
- He is a ___ (brave) soldier.
- This is the ___ (expensive) car in the showroom.
16.3. Correct the Adjective Order
Rewrite the following sentences with the adjectives in the correct order:
- She has a red beautiful long dress.
- He bought a new Italian sports car.
- They live in a large old brick house.
- We saw a few interesting old American movies.
- It was a hot delicious Italian meal.
16.4. Use Compound Adjectives
Combine the words in parentheses to form compound adjectives and complete the sentences:
- She is a ___ (well / known) author.
- The ___ (fast / moving) train sped by.
- They sell ___ (high / quality) products.
- We have a ___ (long / term) plan.
- He is an ___ (open / minded) person.
16.5. Differentiate Between Adjectives and Adverbs
Choose the correct word (adjective or adverb) to complete the sentences:
- She sings ___ (beautiful / beautifully).
- He looks ___ (angry / angrily).
- The flower smells ___ (sweet / sweetly).
- I feel ___ (bad / badly) about what happened.
- He runs ___ (quick / quickly).
Check your answers and review the explanations provided in this guide to reinforce your understanding of adjectives.
17. Ask Your Questions at WHAT.EDU.VN for Free Answers
Are you still unsure about something? Do you need clarification on a particular topic? Don’t hesitate to ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN. We offer a platform where you can get free and accurate answers to all your language and grammar inquiries.
Whether you’re struggling with adjective usage, sentence structure, or any other aspect of the English language, our community of experts is here to help. We provide detailed explanations and examples to ensure you fully understand the concepts.
How to Ask a Question on WHAT.EDU.VN:
- Visit our website: WHAT.EDU.VN
- Navigate to the question submission page.
- Type your question clearly and concisely.
- Provide any relevant context or examples.
- Submit your question and wait for a response from our experts.
We are committed to making learning accessible to everyone. That’s why our services are completely free. You can ask as many questions as you like without any cost.
Contact Information:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let confusion hold you back. Ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and unlock the power of knowledge. Our team is ready and eager to assist you with all your learning needs.
By following this guide, you should now have a solid understanding of what an adjective is, how to use them correctly, and how to avoid common mistakes. If you ever need help or have more questions, remember that what.edu.vn is here to provide you with free and accurate answers.