A ZIP Code is a cornerstone of the United States Postal Service (USPS) mail delivery system. It’s a five-digit numerical code designed to streamline and expedite the sorting and delivery of mail across the United States and its territories. Think of it as a geographical shorthand that helps ensure your letters and packages reach their destination efficiently.
Do you require ZIP Code data for your projects? Contact us to request the data in various formats such as Excel, shapefile, KML, KMZ, or GeoJSON.
It’s important to understand that a ZIP Code primarily functions as a delivery route identifier. The USPS utilizes ZIP Codes to organize mail delivery sequences, rather than defining precise geographical areas. While many ZIP Codes are associated with delivery zones, they are essentially lists of addresses for efficient mail sorting. However, some ZIP Codes do correspond to specific buildings, campuses, or areas with defined boundaries. Approximated boundaries for ZIP Code areas can be created by grouping smaller census areas based on the most frequent ZIP Code within them, but this is an estimation due to overlapping delivery routes and areas without deliverable addresses. ZIP Code boundaries often disregard city, town, county, or state lines.
For mapping purposes, every ZIP Code can be represented as a point. This point is typically located at the main Post Office for that ZIP Code, if one exists. If not, it’s placed at a central location within the ZIP Code’s delivery area. In cases where a ZIP Code represents a building or campus, the point remains central to that location.
Decoding the ZIP Code: A 5-Digit System
The five digits of a ZIP Code are more than just random numbers; they are a hierarchical system that reveals progressively more specific geographical information.
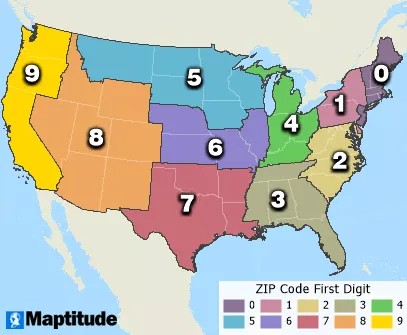
The First Digit: National Areas
The first digit of a ZIP Code divides the United States into ten large geographical areas, ranging from 0 in the Northeast to 9 in the West. This initial digit provides a broad regional classification for mail routing.
The Second Digit: States and Regions
The second digit further refines the location, typically indicating a specific state, a heavily populated portion of a state, or a combination of less populated states. This digit narrows down the general area identified by the first digit.
3-Digit ZIP Codes: Major Areas within States
The first three digits together define a major metropolitan area or a sectional center facility (SCF). An SCF is a central mail processing hub for a group of associated ZIP Codes. For example, all ZIP Codes starting with “165” are part of the “165” 3-digit ZIP Code area, usually representing a large city post office or a major mail concentration point.
It’s interesting to note that some 3-digit ZIP Code areas are not geographically contiguous. For instance, the 3-digit ZIP Codes 683 and 684, when combined, form a contiguous area around Lincoln, Nebraska (ZIP code 685). This is because 683 encompasses ZIP Codes with names starting A-L, and 684 includes those starting M-Z, reflecting an organizational rather than purely geographical logic.
ZIP Codes: Areas or Points?
While ZIP Codes are not officially defined as areas by the USPS, many 5-digit ZIP Codes can be represented as geographical areas. This is particularly true for ZIP Codes covering residential and business addresses, as well as those for institutions with defined property lines. These ZIP Code areas are approximated by grouping smaller census blocks based on the most frequent ZIP Code within each block. Some ZIP Code areas can be as small as a single city block, like 16544.
It’s worth noting the distinction between USPS ZIP Code areas and Census Bureau’s ZIP Code Tabulation Areas (ZCTAs). ZCTAs are statistical areas created by the Census Bureau for data tabulation and are based on census blocks, not USPS delivery routes. Mapping software like Maptitude provides more accurate 5-digit ZIP Code area layers than ZCTAs because they utilize even smaller census units, allowing for boundaries that more closely follow actual deliverable addresses and extend into undeliverable areas to cover the entire USA. These boundaries are also updated annually to reflect USPS ZIP Code changes.
On the other hand, every ZIP Code can also be represented as a point on a map. This point is typically placed at the Post Office serving that ZIP Code or at a central location within the ZIP Code area. ZIP Codes are shown as points when they cannot be represented as areas, such as those for individual businesses, buildings, or PO Boxes (e.g., ZIP Codes 16522, 16530, 16534, 16538, and 16553).
ZIP+4 Codes: Enhanced Precision
For even greater accuracy in mail delivery, the USPS uses ZIP+4 codes. This is an extension to the standard 5-digit ZIP code, adding a hyphen and four extra digits. These additional digits pinpoint a more specific location within a 5-digit ZIP Code, such as a particular building side, a group of apartments, or even specific sides of a street. ZIP+4 codes enhance the efficiency of automated mail sorting and delivery.
Carrier Routes: Efficient Delivery
Within each ZIP Code, the USPS further organizes addresses into carrier routes. A carrier route is a cluster of addresses in close proximity, handled by a single mail carrier. Each carrier route is identified by the 5-digit ZIP code followed by a letter (H for Contract, R for Rural, C for City) and three numbers. Carrier routes are essentially address lists for mail carriers, facilitating organized and efficient delivery within a ZIP Code area. While not defined as areas themselves, carrier routes can be represented on a map by a central point for each address list.
PO Boxes: Postal Convenience
PO Boxes at USPS Post Offices offer a secure way to receive mail, particularly useful when a physical address isn’t suitable or preferred. PO Box ZIP Codes are mapped as 5-digit ZIP Code points, often clustered at the Post Office location they serve.
Leveraging ZIP Codes with Mapping Software
While ZIP Code areas are approximations, software like Maptitude Mapping Software utilizes the most precise ZIP Code data available. Maptitude provides tools, maps, and data to analyze geographical impacts on businesses and organizations.
Maptitude allows users to locate records by ZIP Code, visualize data aggregated by ZIP Codes, create sales territory maps based on ZIP Codes, and analyze Census demographic data at the ZIP Code level.
Learn More about Maptitude | Try Maptitude Free | Free for Students/Teachers
In conclusion, ZIP Codes are an essential component of the US mail system, providing a structured method for organizing and delivering mail efficiently. Understanding the hierarchical structure of ZIP Codes and their applications in mapping software can be valuable for businesses and individuals alike.