Here at WHAT.EDU.VN, we know you’re looking for clear, concise answers, and understanding the nuances of generational demographics is important. Gen Z Age refers to individuals born from 1997 onward, shaping the landscape of youth culture and influencing trends across various sectors. Let’s dive deeper into understanding this influential generation, exploring their defining characteristics and impact and discover how WHAT.EDU.VN helps you stay informed.
1. Defining Gen Z: The Post-Millennial Generation
What precisely defines Generation Z? It’s a question frequently asked, and here’s a comprehensive answer.
Gen Z, short for Generation Z, refers to the demographic cohort succeeding the Millennials. While generational boundaries aren’t an exact science, Pew Research Center defines Gen Z as individuals born from 1997 onward. This makes the oldest Gen Z members around 27 years old in 2024. They are also known as Zoomers. This generation has grown up in a digital world, heavily influenced by technology and social media.
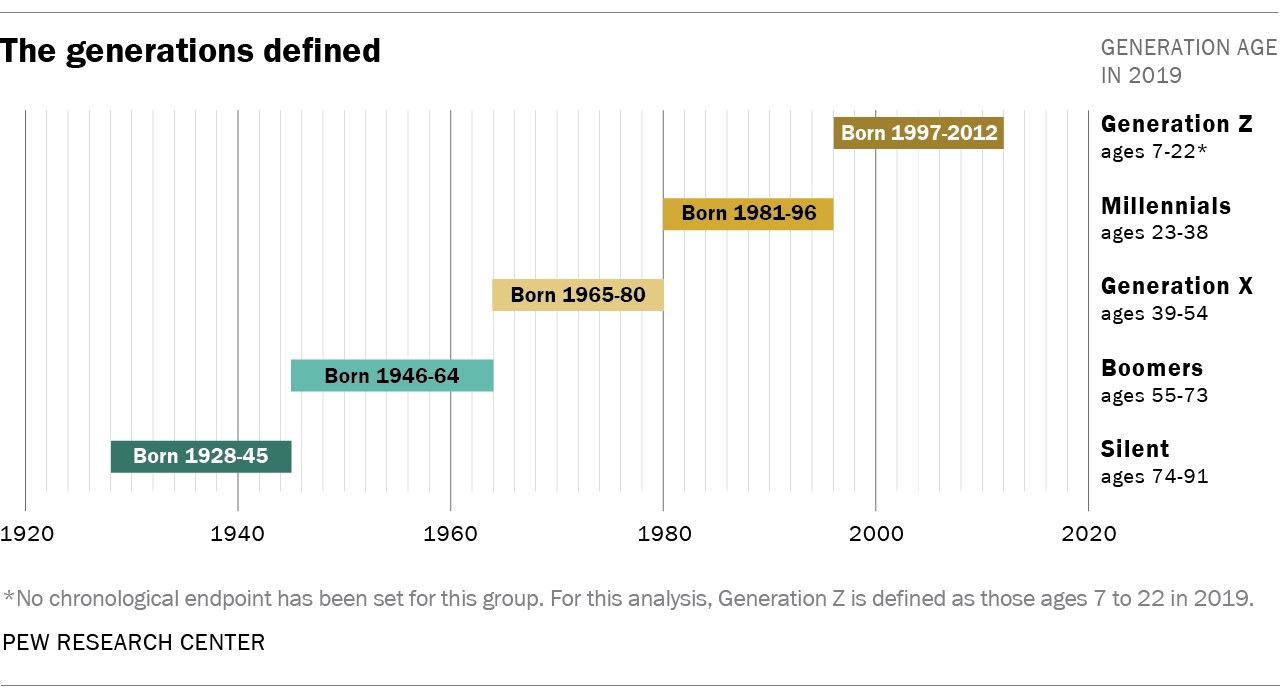 Gen Z graphic showcasing demographic and age range.
Gen Z graphic showcasing demographic and age range.
1.1. What are the Key Characteristics of Gen Z?
Gen Z exhibits distinct characteristics shaped by their unique formative experiences:
- Digital Natives: Growing up with the internet, smartphones, and social media as integral parts of their lives, Gen Z is highly tech-savvy and digitally literate.
- Diverse and Inclusive: Gen Z is the most racially and ethnically diverse generation to date, embracing inclusivity and advocating for social justice.
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: Many Gen Z members display an entrepreneurial spirit, seeking innovative solutions and creating their own opportunities.
- Pragmatic and Realistic: Witnessing economic instability and global challenges, Gen Z tends to be pragmatic, valuing financial security and practical skills.
- Socially Conscious: Gen Z is deeply concerned about social and environmental issues, actively engaging in activism and seeking sustainable solutions.
1.2. How Does Gen Z Differ from Millennials?
While both generations have been shaped by technology, key differences exist between Gen Z and Millennials:
| Feature | Millennials (Born 1981-1996) | Gen Z (Born 1997 onward) |
|---|---|---|
| Defining Events | 9/11 attacks, 2008 Financial Crisis | Rise of social media, climate change awareness |
| Economic Outlook | Entered workforce during recession | Facing economic uncertainties and gig economy |
| Technology Use | Adapted to emerging digital technologies | Grew up as digital natives |
| Social Values | Optimistic and idealistic | Pragmatic and socially conscious |
1.3. What is the significance of the Gen Z age range?
The Gen Z age range is significant because it encapsulates a generation shaped by specific historical, technological, and economic events. Their formative years were marked by the rise of social media, increased awareness of climate change, and economic uncertainties. Understanding this age range provides insights into their behaviors, values, and future impact.
1.4. Where Can I Find More Information About Gen Z?
For more in-depth information, consider exploring resources from Pew Research Center, McKinsey & Company, and other reputable research institutions. WHAT.EDU.VN also offers insights into various aspects of Gen Z, providing a platform for asking questions and gaining knowledge.
2. The Impact of Technology on Gen Z
How has technology shaped the lives of Gen Z? It’s a crucial question to understand their perspective.
Technology has profoundly impacted Gen Z, shaping their communication, learning, and worldview.
2.1. How Has Social Media Influenced Gen Z?
Social media is integral to Gen Z’s identity, influencing their social interactions, self-expression, and access to information. They use platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube to connect with peers, follow trends, and create content. However, concerns exist regarding the impact of social media on mental health, body image, and online privacy.
2.2. What Role Does Mobile Technology Play in Gen Z’s Lives?
Mobile devices are essential tools for Gen Z, enabling constant connectivity and access to information on the go. They use smartphones for communication, entertainment, education, and even financial transactions. Mobile technology has fostered a culture of instant gratification and multitasking among Gen Z members.
2.3. How Has Technology Affected Gen Z’s Education?
Technology has transformed Gen Z’s learning experience, offering access to online resources, virtual classrooms, and interactive learning tools. They are accustomed to personalized learning and prefer engaging and visually appealing content. However, challenges remain in bridging the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to technology for all students.
2.4. How Does Technology Affect Gen Z’s Mental Health?
The constant connectivity and exposure to social media can have both positive and negative effects on Gen Z’s mental health. While technology offers opportunities for connection and support, it can also contribute to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Balancing technology use with offline activities and mental health resources is crucial for Gen Z’s well-being.
2.5. How Is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Shaping Gen Z’s World?
AI is becoming increasingly prevalent in Gen Z’s lives, from personalized recommendations on streaming services to AI-powered chatbots for customer service. They are growing up in a world where AI is integrated into various aspects of daily life, raising questions about the future of work, privacy, and ethical considerations.
3. Gen Z in the Workplace: Skills and Expectations
What does Gen Z bring to the workplace, and what are their expectations? This is a vital question for employers.
Gen Z is entering the workforce with unique skills and expectations, challenging traditional workplace norms.
3.1. What Skills Does Gen Z Bring to the Workplace?
Gen Z possesses valuable skills that align with the demands of the modern workplace:
- Digital Fluency: They are proficient in using digital tools and platforms, adapting quickly to new technologies.
- Creativity and Innovation: Gen Z members are creative thinkers, seeking innovative solutions and bringing fresh perspectives to problem-solving.
- Collaboration and Communication: They excel at collaborating in digital environments, communicating effectively through various online channels.
- Adaptability and Resilience: Growing up in a rapidly changing world, Gen Z is adaptable and resilient, embracing new challenges with a growth mindset.
3.2. What Are Gen Z’s Expectations for the Workplace?
Gen Z has specific expectations for the workplace:
- Meaningful Work: They seek work that aligns with their values and provides a sense of purpose and impact.
- Work-Life Balance: Gen Z prioritizes work-life balance, seeking flexibility and autonomy in their work arrangements.
- Opportunities for Growth: They desire opportunities for continuous learning and development, seeking mentorship and career advancement.
- Inclusive Culture: Gen Z values diversity and inclusivity, expecting a workplace that embraces different perspectives and backgrounds.
- Technology Integration: They expect technology to be seamlessly integrated into the workplace, enabling efficiency and collaboration.
3.3. How Can Employers Attract and Retain Gen Z Talent?
Employers can attract and retain Gen Z talent by:
- Offering Meaningful Work: Providing opportunities to work on projects that align with their values and make a positive impact.
- Promoting Work-Life Balance: Offering flexible work arrangements, such as remote work and flexible hours.
- Investing in Learning and Development: Providing opportunities for training, mentorship, and career advancement.
- Fostering an Inclusive Culture: Creating a workplace that values diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Leveraging Technology: Integrating technology into the workplace to enhance collaboration and efficiency.
3.4. What Are Some Challenges Employers Face When Working with Gen Z?
Some challenges employers face when working with Gen Z include:
- Managing Expectations: Aligning Gen Z’s expectations with the realities of the workplace, particularly regarding career advancement and compensation.
- Providing Feedback: Offering regular and constructive feedback to help Gen Z members develop their skills and improve performance.
- Fostering Engagement: Keeping Gen Z engaged and motivated in the workplace, particularly in roles that may not align with their passions.
- Addressing Mental Health: Recognizing and addressing the mental health challenges that Gen Z may face, providing resources and support.
3.5. How Is Gen Z Reshaping Leadership?
Gen Z is contributing to a more collaborative, inclusive, and purpose-driven leadership style. They value authenticity, transparency, and empathy in leaders, seeking leaders who inspire and empower them to make a difference.
4. Gen Z and Consumerism: Trends and Preferences
How does Gen Z approach consumerism, and what are their preferences? It’s an important question for businesses.
Gen Z has unique consumer behaviors and preferences, influenced by their digital upbringing and social values.
4.1. What are Gen Z’s Shopping Habits?
Gen Z’s shopping habits differ from previous generations:
- Online Shopping: They prefer online shopping, using mobile devices to browse, compare prices, and make purchases.
- Social Commerce: Gen Z is influenced by social media influencers and often makes purchases directly through social media platforms.
- Sustainability: They are conscious of environmental and social impact, seeking sustainable and ethically sourced products.
- Personalization: Gen Z values personalized experiences, seeking brands that cater to their individual preferences and needs.
4.2. What Brands Appeal to Gen Z?
Brands that resonate with Gen Z:
- Authentic Brands: Brands that are transparent, honest, and true to their values.
- Purpose-Driven Brands: Brands that are committed to social and environmental causes.
- Inclusive Brands: Brands that celebrate diversity and inclusivity.
- Tech-Savvy Brands: Brands that leverage technology to enhance the customer experience.
- Value-Oriented Brands: Brands that offer quality products at affordable prices.
4.3. How Does Gen Z Influence Marketing Strategies?
Gen Z influences marketing strategies by:
- Demanding Authenticity: Requiring brands to be authentic and transparent in their messaging.
- Embracing Influencer Marketing: Leveraging social media influencers to reach Gen Z consumers.
- Creating Engaging Content: Developing engaging and visually appealing content that resonates with Gen Z’s interests.
- Prioritizing Mobile Experience: Optimizing marketing campaigns for mobile devices.
- Focusing on Social Impact: Highlighting the brand’s commitment to social and environmental causes.
4.4. How Is Gen Z Changing the Retail Landscape?
Gen Z is transforming the retail landscape by:
- Driving the Growth of E-commerce: Fueling the growth of online shopping and social commerce.
- Demanding Personalized Experiences: Expecting personalized recommendations and tailored offers.
- Seeking Sustainable Options: Pushing retailers to adopt sustainable practices.
- Blending Online and Offline Experiences: Seeking seamless integration between online and offline shopping experiences.
4.5. How Does Gen Z’s Value System Affect Their Purchasing Decisions?
Gen Z’s value system heavily influences their purchasing decisions, prioritizing:
- Sustainability: Supporting brands that prioritize environmental sustainability.
- Social Justice: Supporting brands that advocate for social justice and equality.
- Ethical Practices: Supporting brands that adhere to ethical labor and manufacturing practices.
- Inclusivity: Supporting brands that embrace diversity and inclusivity.
- Transparency: Supporting brands that are transparent about their practices and values.
5. Gen Z and Social Issues: Activism and Advocacy
How does Gen Z engage with social issues, and what are their priorities? This question is central to understanding their impact on society.
Gen Z is a generation passionate about social issues, actively engaging in activism and advocacy.
5.1. What Social Issues Are Most Important to Gen Z?
Key social issues for Gen Z:
- Climate Change: Addressing climate change and advocating for environmental sustainability.
- Social Justice: Promoting social justice, equality, and human rights.
- Mental Health: Raising awareness about mental health and advocating for access to mental health resources.
- Education Reform: Advocating for education reform and equitable access to quality education.
- Gun Violence Prevention: Working to prevent gun violence and promote gun safety.
5.2. How Does Gen Z Engage in Activism?
Gen Z engages in activism through:
- Social Media Activism: Using social media platforms to raise awareness, organize protests, and advocate for change.
- Political Engagement: Participating in elections, contacting elected officials, and advocating for policy changes.
- Community Organizing: Organizing local events and initiatives to address social issues in their communities.
- Protests and Demonstrations: Participating in protests and demonstrations to raise awareness and demand action.
- Supporting Socially Responsible Businesses: Supporting businesses that align with their values and contribute to social causes.
5.3. What Role Does Social Media Play in Gen Z’s Activism?
Social media is a powerful tool for Gen Z’s activism, enabling them to:
- Raise Awareness: Sharing information and raising awareness about social issues.
- Organize Events: Organizing protests, rallies, and other events.
- Connect with Like-Minded Individuals: Connecting with other activists and building communities.
- Amplify Marginalized Voices: Amplifying the voices of marginalized communities.
- Hold Institutions Accountable: Holding institutions and individuals accountable for their actions.
5.4. How Does Gen Z Influence Political Discourse?
Gen Z influences political discourse by:
- Bringing New Perspectives: Introducing fresh perspectives and challenging traditional political norms.
- Prioritizing Social Issues: Shifting the focus to social issues that are important to them.
- Holding Politicians Accountable: Holding politicians accountable for their actions and promises.
- Driving Political Engagement: Encouraging other young people to get involved in politics.
5.5. How Is Gen Z Shaping the Future of Social Change?
Gen Z is shaping the future of social change by:
- Embracing Digital Activism: Leveraging technology to create social change.
- Promoting Inclusivity: Advocating for inclusivity and social justice for all.
- Demanding Accountability: Holding institutions and individuals accountable for their actions.
- Inspiring Future Generations: Inspiring future generations to get involved in social change.
6. Gen Z and Education: Learning Styles and Preferences
How does Gen Z approach education, and what are their learning preferences? It’s an important consideration for educators.
Gen Z has distinct learning styles and preferences shaped by their digital upbringing.
6.1. What Are Gen Z’s Preferred Learning Styles?
Gen Z’s preferred learning styles include:
- Visual Learning: Preferring visual aids, such as videos, infographics, and presentations.
- Interactive Learning: Engaging in interactive activities, such as group projects, discussions, and simulations.
- Personalized Learning: Seeking personalized learning experiences that cater to their individual needs and interests.
- Technology-Enhanced Learning: Using technology to enhance their learning experience, such as online resources, virtual classrooms, and interactive learning tools.
6.2. How Does Technology Impact Gen Z’s Learning Experience?
Technology impacts Gen Z’s learning experience by:
- Providing Access to Information: Offering access to a vast amount of information online.
- Enabling Personalized Learning: Facilitating personalized learning experiences.
- Promoting Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration and communication among students.
- Enhancing Engagement: Enhancing engagement through interactive and visually appealing content.
6.3. What Are the Challenges in Educating Gen Z?
Challenges in educating Gen Z include:
- Maintaining Attention: Maintaining attention in a world of constant distractions.
- Promoting Critical Thinking: Promoting critical thinking and media literacy skills.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Ensuring equitable access to technology for all students.
- Addressing Mental Health: Addressing the mental health challenges that Gen Z may face.
6.4. How Can Educators Adapt to Gen Z’s Learning Needs?
Educators can adapt to Gen Z’s learning needs by:
- Incorporating Technology: Incorporating technology into the classroom.
- Creating Engaging Content: Developing engaging and visually appealing content.
- Promoting Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration and communication among students.
- Providing Personalized Learning: Offering personalized learning experiences.
- Fostering Critical Thinking: Fostering critical thinking and media literacy skills.
6.5. How Is Gen Z Reshaping Higher Education?
Gen Z is reshaping higher education by:
- Demanding Practical Skills: Seeking practical skills that will prepare them for the workforce.
- Prioritizing Career Development: Prioritizing career development and seeking internships and job opportunities.
- Embracing Online Learning: Embracing online learning and seeking flexible learning options.
- Seeking Personalized Experiences: Seeking personalized learning experiences that cater to their individual needs and interests.
7. Gen Z and the Future: Predictions and Trends
What does the future hold for Gen Z, and what trends can we expect? It’s a question that looks ahead to their continued influence.
Gen Z is poised to shape the future in significant ways, driving trends across various sectors.
7.1. What Are Some Predictions for Gen Z’s Future Impact?
Predictions for Gen Z’s future impact:
- Driving Technological Innovation: Driving technological innovation and shaping the future of technology.
- Transforming the Workplace: Transforming the workplace and challenging traditional workplace norms.
- Reshaping Consumerism: Reshaping consumerism and driving demand for sustainable and ethical products.
- Leading Social Change: Leading social change and advocating for social justice and equality.
- Influencing Political Discourse: Influencing political discourse and shaping the future of politics.
7.2. What Trends Will Define Gen Z’s Future?
Trends that will define Gen Z’s future:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The continued growth and integration of AI into various aspects of daily life.
- Sustainability: Increased focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Mental Health Awareness: Growing awareness and prioritization of mental health and well-being.
- Remote Work: Continued adoption of remote work and flexible work arrangements.
- E-commerce Dominance: Further growth and dominance of e-commerce and online shopping.
7.3. How Will Gen Z Influence the Economy?
Gen Z will influence the economy by:
- Driving Innovation: Driving innovation and creating new industries and job opportunities.
- Shaping Consumer Demand: Shaping consumer demand and influencing the types of products and services that are offered.
- Transforming the Workforce: Transforming the workforce and bringing new skills and perspectives to the workplace.
- Promoting Entrepreneurship: Promoting entrepreneurship and creating new businesses.
7.4. How Will Gen Z Impact Politics?
Gen Z will impact politics by:
- Driving Political Engagement: Driving political engagement among young people.
- Shaping Political Discourse: Shaping political discourse and shifting the focus to social issues.
- Holding Politicians Accountable: Holding politicians accountable for their actions and promises.
- Influencing Elections: Influencing elections and shaping the future of politics.
7.5. What Are Some Challenges Gen Z Will Face in the Future?
Challenges Gen Z will face in the future:
- Economic Uncertainty: Navigating economic uncertainty and job market volatility.
- Climate Change: Addressing the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation.
- Social Inequality: Addressing social inequality and promoting social justice.
- Mental Health Crisis: Addressing the growing mental health crisis among young people.
- Political Polarization: Navigating political polarization and promoting civil discourse.
8. The Diversity Within Gen Z: Subgroups and Identities
Is Gen Z a monolithic group, or are there diverse subgroups and identities within it? This question acknowledges the complexity of the generation.
Gen Z is a diverse generation with various subgroups and identities, reflecting the complexity of modern society.
8.1. What Are Some Key Subgroups Within Gen Z?
Key subgroups within Gen Z:
- Digital Natives: Those who have grown up with technology and are highly tech-savvy.
- Social Activists: Those who are passionate about social issues and actively engage in activism.
- Entrepreneurs: Those who are entrepreneurial and seek to create their own businesses.
- Gamers: Those who are passionate about gaming and actively participate in the gaming community.
- Artists and Creators: Those who are creative and express themselves through art, music, and other forms of creative expression.
8.2. How Does Identity Shape Gen Z’s Experiences?
Identity shapes Gen Z’s experiences by:
- Influencing Social Interactions: Influencing how they interact with others and form relationships.
- Shaping Worldview: Shaping their worldview and perspectives on social issues.
- Affecting Opportunities: Affecting the opportunities they have access to and the challenges they face.
- Impacting Mental Health: Impacting their mental health and well-being.
8.3. How Does Gen Z View Diversity and Inclusion?
Gen Z views diversity and inclusion as:
- Essential: Essential to creating a fair and just society.
- Valuable: Valuable for bringing different perspectives and experiences to the table.
- Something to Celebrate: Something to celebrate and embrace.
- A Source of Strength: A source of strength and resilience.
8.4. How Is Gen Z Redefining Traditional Identities?
Gen Z is redefining traditional identities by:
- Challenging Gender Norms: Challenging traditional gender norms and embracing gender fluidity.
- Redefining Sexuality: Redefining sexuality and embracing LGBTQ+ identities.
- Promoting Racial and Ethnic Diversity: Promoting racial and ethnic diversity and challenging racism and discrimination.
- Celebrating Cultural Heritage: Celebrating cultural heritage and promoting cultural understanding.
8.5. How Can We Ensure Equitable Representation of All Subgroups Within Gen Z?
We can ensure equitable representation of all subgroups within Gen Z by:
- Amplifying Marginalized Voices: Amplifying the voices of marginalized subgroups.
- Promoting Inclusive Policies: Promoting inclusive policies and practices.
- Challenging Bias and Discrimination: Challenging bias and discrimination.
- Creating Safe Spaces: Creating safe spaces for all subgroups to express themselves and connect with others.
9. Addressing Misconceptions About Gen Z
What are some common misconceptions about Gen Z, and how can we address them? It’s important to dispel stereotypes and understand the generation accurately.
Many misconceptions surround Gen Z, often portraying them in inaccurate or overly simplistic ways.
9.1. What Are Some Common Stereotypes About Gen Z?
Common stereotypes about Gen Z:
- Lazy and Entitled: The stereotype that Gen Z is lazy and entitled.
- Addicted to Technology: The stereotype that Gen Z is addicted to technology and social media.
- Lacking in Interpersonal Skills: The stereotype that Gen Z lacks interpersonal skills due to their reliance on technology.
- Easily Distracted: The stereotype that Gen Z is easily distracted and unable to focus.
- Politically Apathetic: The stereotype that Gen Z is politically apathetic and uninterested in civic engagement.
9.2. Why Are These Stereotypes Harmful?
These stereotypes are harmful because they:
- Oversimplify a Complex Generation: Oversimplify a complex and diverse generation.
- Reinforce Negative Biases: Reinforce negative biases and prejudices.
- Limit Opportunities: Limit opportunities for Gen Z members.
- Undermine Their Potential: Undermine their potential and contributions to society.
9.3. What Is the Reality Behind These Stereotypes?
The reality behind these stereotypes:
- Gen Z Is Hardworking: Gen Z is hardworking and entrepreneurial, seeking to create their own opportunities.
- Technology-Savvy, Not Addicted: They are technology-savvy, not addicted, using technology as a tool for learning and communication.
- Adaptable and Collaborative: They are adaptable and collaborative, able to work effectively in both online and offline environments.
- Passionate About Social Issues: They are passionate about social issues and actively engaged in activism.
- Politically Engaged: They are politically engaged and actively participating in the political process.
9.4. How Can We Challenge These Misconceptions?
We can challenge these misconceptions by:
- Educating Ourselves: Educating ourselves about Gen Z and their experiences.
- Listening to Their Voices: Listening to their voices and perspectives.
- Challenging Stereotypes: Challenging stereotypes and biases.
- Recognizing Their Strengths: Recognizing their strengths and contributions.
- Promoting Accurate Representation: Promoting accurate representation of Gen Z in media and popular culture.
9.5. How Can Understanding Gen Z Benefit Society?
Understanding Gen Z can benefit society by:
- Informing Policy Decisions: Informing policy decisions and creating programs that meet their needs.
- Improving Education: Improving education and preparing them for the future.
- Enhancing the Workplace: Enhancing the workplace and leveraging their skills and talents.
- Driving Innovation: Driving innovation and creating new industries and job opportunities.
- Promoting Social Change: Promoting social change and creating a more just and equitable society.
10. Resources for Learning More About Gen Z
Where can I find reliable resources to learn more about Gen Z? This question provides helpful avenues for continued learning.
Numerous resources are available for those seeking to learn more about Gen Z.
10.1. What Are Some Recommended Books About Gen Z?
Recommended books about Gen Z:
- “Gen Z @ Work: How the Next Generation Is Transforming the Workplace” by David Stillman and Jonah Stillman
- “iGen: Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy–and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood” by Jean M. Twenge
- “The Gen Z Effect: The Six Forces Shaping the Future of Business” by Thomas Koulopoulos and Dan Keldsen
- “Marketing to Gen Z: The Rules and Strategies for Reaching the Most Misunderstood Generation of Consumers” by Jeff Fromm and Angie Read
- “Gen Z and the Art of Consumption: Understanding the Next Wave of Consumers” by Ana Andjelic
10.2. What Are Some Reliable Websites and Online Resources?
Reliable websites and online resources:
- Pew Research Center: Offers data and analysis on Gen Z’s demographics, attitudes, and behaviors.
- McKinsey & Company: Provides insights on Gen Z’s consumer trends and workplace expectations.
- Deloitte: Offers research on Gen Z’s values and priorities.
- WHAT.EDU.VN: Offers a platform for asking questions and gaining knowledge about Gen Z.
10.3. What Are Some Reputable Research Institutions Studying Gen Z?
Reputable research institutions studying Gen Z:
- Pew Research Center
- McKinsey & Company
- Deloitte
- Nielsen
- Kantar
10.4. What Are Some Conferences and Events Focused on Gen Z?
Conferences and events focused on Gen Z:
- Gen Z Marketing Conference
- Youth Marketing Strategy Conference
- Social Media Marketing World
- Content Marketing World
10.5. How Can I Stay Up-to-Date on the Latest Gen Z Trends?
Stay up-to-date on the latest Gen Z trends by:
- Following Relevant Social Media Accounts: Following social media accounts that focus on Gen Z trends and insights.
- Subscribing to Industry Newsletters: Subscribing to industry newsletters that cover Gen Z topics.
- Reading Industry Blogs: Reading industry blogs that provide insights on Gen Z’s attitudes and behaviors.
- Attending Industry Events: Attending industry events focused on Gen Z.
- Engaging with Gen Z Members: Engaging with Gen Z members and listening to their perspectives.
Understanding Gen Z is crucial for businesses, educators, and anyone seeking to navigate the future. Their unique perspectives, values, and behaviors are shaping the world around us. Remember, for all your questions, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide answers and connect you with a community of knowledge. Have more questions about Gen Z, or anything else? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today! Our address is 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us on Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890, or visit our website: what.edu.vn. Let’s explore the world together and get free answers to your questions. We can assist you with youth culture insights, digital generation answers and zoomer trends.
