SAP software is a powerful suite of tools that helps businesses manage their operations effectively. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear, concise answers to all your questions about SAP and its applications. This guide will explore what SAP software is, its components, benefits, and how it can transform your business processes with related keywords, business solutions and enterprise applications.
1. What Does SAP Software Mean?
SAP software refers to a range of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems developed by the German company SAP SE. ERP software integrates various functions of an organization’s core business processes into a unified system. This integration helps businesses manage and automate essential functions.
SAP software provides a centralized platform where different departments can access and share real-time data. This includes areas like finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, and customer relationship management (CRM). By consolidating these functions, SAP software enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and improves decision-making. SAP systems help organizations streamline their operations, optimize resource allocation, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
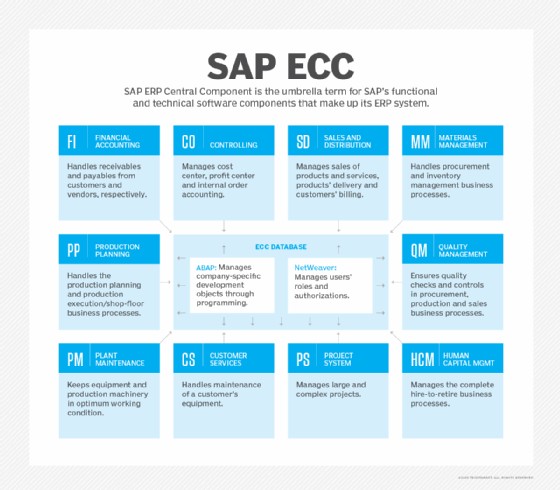 SAP ERP software components chart
SAP ERP software components chart
2. What Does SAP Stand For?
SAP originally stood for System Analysis Program Development. In its full corporate name, SAP SE, the “SE” stands for Societas Europaea, similar to “Inc.” in the U.S.
SAP is a leading multinational software vendor in the ERP market, serving over 180 countries. They offer on-premises, cloud, and hybrid deployment models, focusing on cloud computing. SAP’s ERP products help customers manage their business processes in an integrated environment.
3. What Are the Key SAP ERP Modules?
SAP ERP systems consist of various modules that focus on essential business functions. These modules integrate data from different departments into a central database. The functional modules include:
3.1. Financial Accounting and Controlling (SAP FICO)
SAP FICO manages financial transactions and reporting. It handles general ledger accounting, accounts payable, accounts receivable, asset accounting, and cost controlling. This module helps companies comply with financial regulations and gain insights into their financial performance. SAP FICO is essential for maintaining accurate financial records and supporting strategic decision-making.
3.2. Sales and Distribution (SAP SD)
SAP SD manages sales orders, pricing, shipping, and billing. It ensures efficient order processing and delivery. SAP SD is crucial for managing customer relationships and optimizing sales strategies.
3.3. Materials Management (SAP MM)
SAP MM manages procurement, inventory, and warehouse operations. It ensures the availability of materials for production and sales. This module optimizes the supply chain and reduces costs.
3.4. Production Planning (SAP PP)
SAP PP plans and controls the manufacturing process. It manages production orders, bills of materials, and capacity planning. This module optimizes production schedules and ensures timely delivery of products.
3.5. Quality Management (SAP QM)
SAP QM ensures product quality throughout the manufacturing process. It manages quality inspections, testing, and certifications. This module helps companies meet quality standards and improve customer satisfaction.
3.6. Plant Maintenance (SAP PM)
SAP PM manages the maintenance of equipment and machinery. It plans maintenance schedules, tracks maintenance costs, and ensures equipment reliability. This module minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of assets.
3.7. Project System (SAP PS)
SAP PS manages projects from start to finish. It plans project timelines, budgets, and resources. This module ensures projects are completed on time and within budget.
3.8. Customer Service (SAP CS)
SAP CS manages customer service operations, including service requests, warranties, and repairs. It enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3.9. Human Capital Management (SAP HCM)
SAP HCM manages employee information, payroll, benefits, and training. It ensures compliance with labor laws and optimizes workforce management.
4. How Does the SAP ERP System Work?
SAP ERP, like SAP ECC, is often deployed in a three-tier, client-server architecture consisting of presentation, application, and database tiers.
4.1. Presentation Tier
The presentation tier provides the user interface, accessible on computers using Microsoft Windows or macOS. The SAP GUI is the communication point between the user and ECC.
4.2. Application Tier
The application tier is the core of ECC, processing transactions, executing business logic, running reports, monitoring database access, printing documents, and communicating with other applications.
4.3. Database Tier
The database tier stores transaction records and other data. This architecture ensures efficient data processing and accessibility.
5. What Are the Key Features and Capabilities of SAP ERP?
Key features and modules of SAP ERP include:
5.1. Analytics and Reporting
SAP ERP provides real-time data accessibility and analysis, enabling quick, actionable decisions.
5.2. Financial Accounting
SAP ERP manages financial transactions, reporting, and compliance.
5.3. HR Management
SAP ERP handles employee information, payroll, benefits, and training.
5.4. Materials Management
SAP ERP manages procurement, inventory, and warehouse operations.
5.5. Product Planning
SAP ERP plans and controls the manufacturing process.
5.6. Sales and Distribution
SAP ERP manages sales orders, pricing, shipping, and billing.
5.7. Supply Chain Management
SAP ERP optimizes the flow of goods and information from suppliers to customers.
6. What Are the Different SAP Products?
SAP offers various products tailored to different business needs and sizes. Here are some key SAP products:
6.1. SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA is an in-memory ERP platform optimized for the SAP HANA in-memory database. It reduces complexity and replaces SAP ECC.
6.2. SAP S/4HANA Cloud
SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a SaaS version of S/4HANA, providing the advantages of HANA’s in-memory processing and real-time data accessibility within a subscription-based SaaS model.
6.3. SAP Business ByDesign
SAP Business ByDesign is a SaaS ERP system for small and midsize businesses, occupying the midmarket segment of the SAP product line.
6.4. SAP Business One
SAP Business One is geared toward smaller businesses and runs on-premises or in the cloud.
7. What Are the Advantages of SAP ERP?
SAP ERP offers numerous advantages for businesses:
7.1. Standardizes Business Processes
SAP ERP improves consistency across departments, increasing an organization’s efficiency.
7.2. Unified View of the Business
SAP ERP provides an organization with more transparency across departments.
7.3. Customizability
Organizations only use the ERP modules required to run their business.
7.4. Strong Reporting and Analytics Features
SAP ERP provides real-time data accessibility and analysis, enabling quick, actionable decisions. According to a study by Forrester, companies using SAP ERP experienced a 20% improvement in decision-making speed due to better data visibility.
8. What Are the Disadvantages of SAP ERP?
Despite its benefits, SAP ERP also has some downsides:
8.1. High Purchase and Implementation Costs
These costs include buying the software and infrastructure, labor costs of internal IT employees and external consultants, training employees, and software maintenance and upgrades.
8.2. Complexity
Its complex structure means implementations could take several years.
8.3. Customization
SAP ERP can be difficult to customize without the help of a third party or a technical expert. The customization process could also be difficult for organizations that require specific software tailored to their needs.
9. What Are the Use Cases for SAP Software and ERP?
SAP software helps organizations manage nearly every aspect of their business. Business Suite includes applications and industry-specific functionality for CRM, PLM, SCM, and supplier relationship management (SRM).
9.1. Industry-Specific Applications
Here are some industry-specific applications in Business Suite or S/4HANA:
9.1.1. Consumer
- Agribusiness
- Consumer products
- Fashion
- Life sciences
- Retail
- Wholesale distribution
9.1.2. Discrete Manufacturing
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive
- High tech
- Industrial manufacturing
9.1.3. Energy and Natural Resources
- Building products
- Chemicals
- Mill products
- Mining
- Oil, gas, and energy
- Utilities
9.1.4. Financial Services
- Banking
- Insurance
9.1.5. Public Services
- Defense and security
- Federal and national government
- Future cities
- Healthcare
- Higher education and research
- Regional, state, and local government
9.1.6. Services
- Cargo transportation and logistics
- Engineering, construction, and operations
- Media
- Passenger travel and leisure
- Professional services
- Sports and entertainment
- Telecommunications
10. What Is the History of SAP?
SAP was founded in 1972 by five former IBM employees in Mannheim, Germany. The idea was to enable customers to interact with a common corporate database for a comprehensive range of applications in real-time.
10.1. SAP R/1 (1973)
SAP released R/1, a financial accounting system running on IBM servers and disk operating systems. It had a single-tier architecture.
10.2. SAP R/2 (1979)
SAP released R/2, a mainframe system providing real-time data processing across accounting, manufacturing, supply chain, and HR. R/2 used a two-tier architecture and helped SAP grow.
10.3. SAP R/3 (1992)
SAP released R/3, switching from mainframe computing to the client-server model and from a two-tier to a three-tier architecture. R/3 launched SAP onto the world stage.
10.4. SAP NetWeaver (2004)
SAP launched NetWeaver, a web-based, cross-application platform for developing SAP applications. Also, SAP ECC was released as the successor to R/3.
10.5. SAP Business Suite 7 (2009)
SAP Business Suite 7 became available, using a service-oriented architecture.
10.6. SAP HANA (2011)
SAP launched SAP HANA, an in-memory database platform. SAP intends HANA to replace traditional databases for its business applications.
10.7. SAP S/4HANA (2015)
SAP released SAP S/4HANA, a successor to SAP ERP, built entirely off of SAP HANA’s in-memory database. S/4HANA offers better performance, real-time analytics, and simplified processes.
10.8. Recent Developments (2020 Onward)
Since 2020, SAP has focused on a cloud-first strategy, offering products like SAP S/4HANA Cloud and Rise with SAP. In 2023, SAP introduced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies to its services.
11. What Are Some of SAP’s Key Acquisitions?
Since 1996, SAP has made over 60 acquisitions to build its cloud computing capabilities and enable greater mobility. Prominent acquisitions include:
- 2024: WalkMe, digital adoption platforms.
- 2021: Signavio, business process management.
- 2018: Qualtrics, experience management; later spun out by SAP.
- 2018: CallidusCloud, sales team performance management.
- 2014: Concur Technologies, online travel and expense management SaaS.
- 2014: Fieldglass, cloud-based contingent labor and services.
- 2013: Hybris, e-commerce.
- 2012: Ariba, cloud-based B2B marketplace.
- 2011: SuccessFactors, SaaS HCM.
- 2007: BusinessObjects, business intelligence.
12. What Is the Future of SAP?
SAP is focused on moving more customers to the cloud and S/4HANA, using both as platforms to deliver leading-edge technologies like AI, IoT, big data, and advanced analytics. The goal is to help customers build the intelligent enterprise, which leverages AI, networking, and human-centric user experiences to become more adaptive and innovative.
SAP will end support for SAP ECC by 2027, pushing S/4HANA, S/4HANA Cloud, and Rise with SAP instead. Integration with AI and IoT is a trend in ERP, offering benefits to data use in business. AI-powered analytics and data visualization tools may replace ERP dashboards.
SAP will likely continue to promote its cloud-based ERP offerings and integrate technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT into its product offerings.
13. FAQ About SAP Software
13.1. What is the main purpose of SAP?
The main purpose of SAP is to integrate and automate business processes across various departments within an organization. SAP systems provide a centralized platform for managing data and operations, enhancing efficiency and decision-making. According to a survey by Panorama Consulting Solutions, companies using ERP systems like SAP experienced a 15% improvement in operational efficiency.
13.2. How is SAP different from other ERP systems?
SAP stands out due to its comprehensive suite of modules, scalability, and industry-specific solutions. While other ERP systems may offer similar functionalities, SAP’s depth and breadth of features make it suitable for large, complex organizations. SAP’s robust integration capabilities and real-time data processing further differentiate it from competitors.
13.3. Is SAP difficult to learn?
Learning SAP can be challenging due to its complexity and extensive functionality. However, with proper training and hands-on experience, users can become proficient in using SAP modules relevant to their roles. Many online courses, training programs, and SAP certifications are available to help users develop their SAP skills.
13.4. What are the benefits of using SAP for small businesses?
For small businesses, SAP offers solutions like SAP Business One, designed to streamline operations and improve efficiency. The benefits include better inventory management, improved customer relationship management, and enhanced financial control. SAP Business One helps small businesses scale their operations and compete effectively in the market.
13.5. How does SAP support supply chain management?
SAP supports supply chain management through modules like SAP MM and SAP SCM. These modules help businesses manage procurement, inventory, warehouse operations, and logistics. SAP enables companies to optimize their supply chain, reduce costs, and improve delivery times, ensuring a seamless flow of goods from suppliers to customers.
13.6. What is SAP Fiori, and how does it enhance user experience?
SAP Fiori is a design system that provides a modern and intuitive user interface for SAP applications. It enhances user experience by offering a simplified and personalized interface, making it easier for users to access and interact with SAP functionalities. SAP Fiori improves user productivity and satisfaction by providing a more user-friendly experience.
13.7. How does SAP handle data security and compliance?
SAP systems incorporate robust security features to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations. These features include data encryption, access controls, audit trails, and compliance reporting. SAP helps organizations maintain data integrity, prevent data breaches, and comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
13.8. What is SAP’s role in digital transformation?
SAP plays a crucial role in digital transformation by providing the tools and technologies needed to modernize business processes and embrace new digital capabilities. SAP helps organizations leverage data analytics, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence to drive innovation, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge in the digital economy.
13.9. What are the career opportunities for SAP professionals?
SAP professionals are in high demand across various industries. Career opportunities include SAP consultants, SAP developers, SAP analysts, and SAP project managers. These professionals help organizations implement, customize, and manage SAP systems. The demand for SAP skills continues to grow as more companies adopt SAP solutions.
13.10. How can I stay updated with the latest SAP trends and updates?
To stay updated with the latest SAP trends and updates, you can follow SAP blogs, attend SAP conferences, participate in SAP community forums, and subscribe to SAP newsletters. Additionally, you can pursue SAP certifications to enhance your knowledge and skills. Continuous learning is essential for SAP professionals to stay relevant in the industry.
14. Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN for Your SAP Questions?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding reliable and accurate answers to your questions can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive free, expert answers. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
We make it easy for anyone to ask questions and get answers quickly. Our platform is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to everyone, regardless of their technical background.
If you’re struggling to find answers, don’t know who to ask, or are worried about the cost of consulting, WHAT.EDU.VN offers a free solution. Our goal is to provide you with the information you need in a clear, understandable way.
15. Have More Questions? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN Today
Do you still have questions about SAP software or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask us at WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you need, completely free of charge. Visit our website today and experience the convenience of having your questions answered quickly and accurately.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Join what.edu.vn today and get the answers you deserve!