Sufism, often described as Islamic mysticism, is a path that helps Muslims draw closer to Allah through direct personal experience. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clarity on complex topics like Sufism, offering a free and accessible platform for all your questions. Explore the depths of Sufism and gain a deeper understanding of Islamic spirituality, mystical traditions, and the Sufi path.
1. What Is Sufism and Its Core Beliefs?
Sufism is often described as the mystical dimension of Islam, focusing on the purification of the heart and the direct experience of God. It emphasizes inner spiritual development and the attainment of divine love and wisdom. According to Annemarie Schimmel, a renowned scholar of Sufism, it is “the attempt to find the divine truth and love through direct experience.”
At its core, Sufism seeks to realize the intimate relationship between the individual and the Divine. This pursuit involves cultivating virtues, shedding egoistic desires, and engaging in practices that facilitate spiritual insight and closeness to God. Key beliefs underpinning Sufism include:
- Tawhid (Oneness of God): Emphasizing the absolute unity of God, Sufis seek to experience this unity in all aspects of life.
- Love as the Path: Love for God and all creation is central. Sufis believe that love is the primary means to attain spiritual enlightenment.
- Inner Purification: Sufism stresses the importance of purifying the heart from negative traits such as pride, envy, and greed.
- Spiritual Guidance: The role of a spiritual guide (Murshid or Sheikh) is considered essential for guiding the seeker on the Sufi path.
- Remembrance of God (Dhikr): Constant remembrance of God through various practices, including chanting, meditation, and prayer, is a cornerstone of Sufi practice.
2. What Is the Origin of the Term “Sufi”?
The term “Sufi” is widely believed to originate from the Arabic word “suf,” referring to the coarse wool garments worn by early Islamic mystics as a symbol of their detachment from worldly comforts. Other theories suggest that the term may derive from “saf,” meaning “pure,” reflecting the Sufi’s focus on purity of heart.
Regardless of its precise etymological origin, the term “Sufi” came to be associated with individuals dedicated to the mystical path within Islam. These individuals sought to transcend the external rituals and legalistic interpretations of religion, focusing instead on the inner experience of divine presence and love. The early Sufis were known for their asceticism, piety, and devotion to God, serving as spiritual guides and exemplars for others seeking to deepen their faith.
3. What Are the Different Sufi Orders (Tariqas)?
Sufi orders, or Tariqas, are distinct schools or lineages within Sufism, each with its own set of practices, teachings, and spiritual masters. These orders serve as frameworks for spiritual development, providing structure and guidance for seekers on the Sufi path. Some of the most well-known Sufi orders include:
- Qadiriyya: Founded by Abdul-Qadir Gilani, this order is one of the oldest and most widespread, emphasizing service to humanity and adherence to Islamic law.
- Rifa’iyya: Known for their ecstatic practices, such as piercing their bodies with skewers, the Rifa’i order emphasizes divine love and self-sacrifice.
- Mevleviyya: Famous for their whirling dervishes, the Mevlevi order, founded by Jalaluddin Rumi, focuses on achieving spiritual union through music, poetry, and dance.
- Naqshbandiyya: This order emphasizes silent dhikr (remembrance of God) and adherence to the Sunnah (practices of the Prophet Muhammad).
- Shadhiliyya: Known for its emphasis on combining worldly responsibilities with spiritual practice, the Shadhili order encourages its followers to live in the world but not be attached to it.
Each Tariqa has its own unique approach to spiritual development, but all share the common goal of attaining closeness to God and realizing the divine presence in all aspects of life.
4. What Is the Role of a Murshid (Spiritual Guide) in Sufism?
The Murshid, or spiritual guide, plays a central role in Sufism, serving as a mentor, teacher, and facilitator for the seeker on the path. The Murshid is considered to be a spiritual doctor, diagnosing the seeker’s spiritual ailments and prescribing remedies to heal them. The role of the Murshid includes:
- Providing Guidance: Offering personalized instruction and direction based on the seeker’s individual needs and capacities.
- Transmitting Blessings: Passing on spiritual blessings (baraka) and insights to the seeker.
- Purifying the Heart: Helping the seeker to identify and overcome negative traits and attachments that hinder spiritual progress.
- Connecting to the Divine: Facilitating the seeker’s connection to the divine presence through practices such as dhikr and meditation.
- Serving as a Role Model: Embodying the virtues and qualities that the seeker aspires to develop.
The relationship between the Murshid and the Murid (student) is considered sacred, based on mutual trust, love, and respect. The Murid submits to the guidance of the Murshid, following their instructions and seeking their blessings in order to progress on the Sufi path.
5. What Are the Key Practices in Sufism?
Sufism involves a variety of practices aimed at purifying the heart, cultivating divine love, and realizing the presence of God in all aspects of life. Some of the key practices include:
- Dhikr (Remembrance of God): Constant remembrance of God through chanting, meditation, and prayer is a central practice in Sufism.
- Muraqaba (Meditation): Sufis engage in various forms of meditation to quiet the mind, cultivate inner awareness, and connect with the divine presence.
- Sama (Listening to Music): Listening to devotional music and poetry is used as a means to stir the heart and evoke spiritual emotions.
- Service to Humanity: Sufis believe that serving others is a form of worship and a way to express divine love.
- Fasting and Prayer: Observing the traditional Islamic practices of fasting and prayer with mindfulness and devotion.
- Self-Reflection: Sufis engage in regular self-reflection to identify and overcome negative traits and attachments that hinder spiritual progress.
These practices are designed to cultivate inner transformation and facilitate the seeker’s journey towards union with the Divine.
6. How Does Sufi Literature Contribute to Spiritual Understanding?
Sufi literature is rich with poetry, stories, and teachings that offer profound insights into the nature of reality, the human condition, and the path to spiritual realization. Some of the most influential Sufi authors and works include:
- Jalaluddin Rumi: His collection of poems, the Masnavi, is considered one of the greatest works of Sufi literature, exploring themes of love, longing, and spiritual union.
- Hafiz: His poems are known for their ecstatic expression of divine love and their celebration of beauty and joy.
- Attar of Nishapur: His Conference of the Birds is an allegorical tale of a group of birds who embark on a journey to find their king, symbolizing the soul’s quest for God.
- Ibn Arabi: His philosophical and mystical writings, such as The Meccan Revelations, explore the nature of existence, the relationship between God and the world, and the path to spiritual knowledge.
Sufi literature uses metaphors, symbols, and allegories to convey complex spiritual concepts in a way that can be understood and experienced by the reader. It serves as a guide for seekers on the path, offering inspiration, wisdom, and practical guidance for cultivating inner transformation.
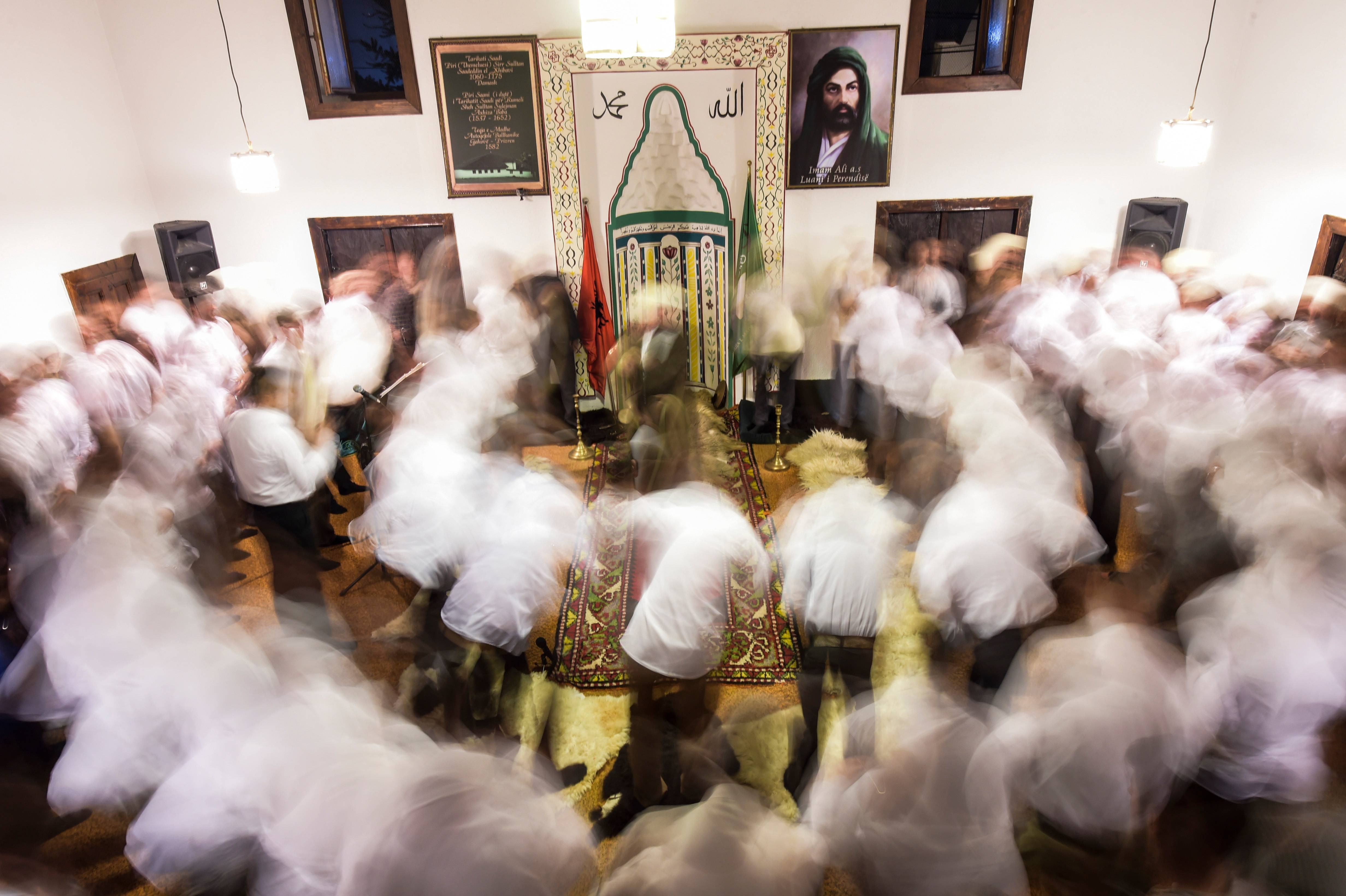 Sufi whirling dervishes performing Sama, a devotional practice.
Sufi whirling dervishes performing Sama, a devotional practice.
Sufi whirling dervishes performing Sama, a devotional practice aimed at achieving spiritual ecstasy.
7. How Does Sufism Differ from Mainstream Islam?
While Sufism is an integral part of Islam, it emphasizes the inner, mystical dimension of the religion, focusing on direct experience of God and cultivation of divine love. Some of the key differences between Sufism and mainstream Islam include:
- Emphasis on Inner Experience: Sufism places greater emphasis on the inner experience of faith, while mainstream Islam often focuses on external rituals and adherence to religious law.
- Role of the Spiritual Guide: Sufism considers the role of a spiritual guide (Murshid or Sheikh) essential for guiding the seeker on the path, while mainstream Islam generally emphasizes individual interpretation of religious texts.
- Practices: Sufism incorporates practices such as dhikr, meditation, and sama, which are not always emphasized in mainstream Islam.
- Interpretation of Religious Texts: Sufis often interpret religious texts allegorically, seeking the inner meaning behind the outer forms, while mainstream Islam typically focuses on the literal interpretation of the texts.
- Focus on Love: Sufism emphasizes love as the primary means to attain spiritual enlightenment, while mainstream Islam often focuses on obedience to God’s commandments.
Despite these differences, Sufism is generally considered to be a complementary aspect of Islam, enriching the faith with its mystical insights and practices.
8. What Criticisms Have Been Leveled Against Sufism?
Sufism has faced criticism from various groups throughout history, including some mainstream Muslims and fundamentalist movements. Some of the common criticisms include:
- Innovation (Bid’ah): Some critics accuse Sufis of introducing innovations into Islam that are not based on the Quran or the Sunnah (practices of the Prophet Muhammad).
- Veneration of Saints: Critics argue that Sufi practices such as visiting the tombs of saints and seeking their intercession are a form of idolatry.
- Pantheism: Some critics accuse Sufis of believing in pantheism, the idea that God is identical with the universe, which is considered to be a deviation from the Islamic concept of Tawhid (Oneness of God).
- Ecstatic Practices: Critics often disapprove of Sufi practices such as whirling, dancing, and singing, considering them to be frivolous and contrary to Islamic piety.
- Relaxation of Religious Law: Some critics argue that Sufis sometimes relax the requirements of Islamic law, prioritizing inner experience over external observance.
These criticisms have often led to persecution and violence against Sufis in some parts of the world.
9. What Is the Significance of Sufism Today?
Despite facing challenges and criticisms, Sufism continues to play a significant role in the contemporary world, offering a spiritual path that emphasizes love, compassion, and inner transformation. Its significance today includes:
- Counteracting Extremism: Sufism’s message of peace, tolerance, and universal love offers a powerful antidote to extremism and violence.
- Promoting Interreligious Dialogue: Sufi teachings emphasize the common ground between different religions, fostering understanding and cooperation.
- Providing Spiritual Guidance: Sufism offers a path for individuals seeking deeper meaning and purpose in life, providing tools and practices for cultivating inner peace and connection to the Divine.
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: Sufi orders have played a vital role in preserving traditional Islamic arts, music, and literature.
- Addressing Social Issues: Sufis are often involved in social activism, working to alleviate poverty, promote education, and address other pressing social issues.
In a world plagued by conflict, division, and materialism, Sufism offers a message of hope, healing, and transformation, reminding us of our shared humanity and our potential for spiritual growth.
10. What Are Some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Sufism?
Here are some frequently asked questions about Sufism, categorized for easier understanding:
Core Beliefs and Practices
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the ultimate goal in Sufism? | The ultimate goal is to achieve union with God (fana) and abide in God (baqa), realizing the divine presence in all aspects of life. |
| How do Sufis view the concept of “self”? | Sufis believe that the ego (nafs) is the main obstacle to spiritual progress and must be purified through self-discipline, remembrance of God, and service to others. |
| What is the role of dreams in Sufism? | Dreams are considered to be a source of spiritual insight and guidance, and Sufis often interpret their dreams to gain a deeper understanding of their spiritual path. |
| How do Sufis balance worldly life with spiritual practice? | Sufis believe that it is possible to live in the world but not be attached to it, fulfilling their worldly responsibilities while remaining focused on their spiritual goals. |
| What is the Sufi view on miracles and supernatural phenomena? | While Sufis acknowledge the possibility of miracles, they emphasize that the true miracle is the transformation of the heart and the attainment of divine love and wisdom. |
Sufi Orders and Teachers
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How does one choose a Sufi order or teacher? | The choice of a Sufi order or teacher is a personal one, based on intuition, attraction, and compatibility. It is important to seek guidance from a qualified and authentic teacher who can provide personalized instruction and support. |
| Are Sufi orders hierarchical? | Yes, most Sufi orders have a hierarchical structure, with the Murshid (spiritual guide) at the top, followed by senior students and then newer members. This structure ensures the continuity of the teachings and the proper guidance of the students. |
| Can women be Sufi teachers? | Yes, there have been many prominent women Sufi teachers throughout history, such as Rabi’a al-Adawiyya, who are revered for their wisdom, piety, and spiritual insight. |
| What are the qualifications of a Sufi teacher? | A Sufi teacher must possess deep spiritual knowledge, practical experience, and the ability to transmit spiritual blessings (baraka) to their students. They must also be of sound character, compassionate, and dedicated to serving others. |
| Is it necessary to travel to meet a Sufi teacher? | While it can be beneficial to meet a Sufi teacher in person, it is not always necessary. With the advent of technology, it is now possible to receive guidance and instruction from a Sufi teacher online or through correspondence. However, personal contact is often considered more effective. |
Criticisms and Misconceptions
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is Sufism a separate religion from Islam? | No, Sufism is an integral part of Islam, representing its mystical dimension. Sufis adhere to the fundamental beliefs and practices of Islam, while also emphasizing the inner experience of faith. |
| Are all Sufis peaceful and tolerant? | While Sufism generally promotes peace and tolerance, there have been instances of Sufis engaging in violence or extremism. However, these instances are rare and do not represent the true spirit of Sufism. |
| Is Sufism only for Muslims? | While Sufism originated within Islam, its teachings and practices can be beneficial to people of all faiths. Many Sufi teachers welcome students from diverse backgrounds and encourage them to explore the spiritual path in accordance with their own beliefs and traditions. |
| Is Sufism a form of escapism? | No, Sufism is not a form of escapism, but rather a path of engagement with the world. Sufis believe that it is possible to live in the world but not be attached to it, using their spiritual insights to address social issues and promote justice and compassion. |
| Is Sufism outdated or irrelevant in the modern world? | No, Sufism is more relevant than ever in the modern world, offering a spiritual path that emphasizes love, compassion, and inner transformation, providing a much-needed antidote to the materialism, violence, and division that plague contemporary society. |
Sufism provides a rich and diverse path for those seeking a deeper connection with the Divine. Whether through poetry, music, meditation, or service to others, Sufism offers a way to cultivate love, compassion, and inner peace in a world that desperately needs it.
Do you have more questions about Sufism or other topics? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can get free answers to all your questions. Our team of experts is here to provide you with the knowledge and guidance you need. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website what.edu.vn today!