Here’s a breakdown of the Black population in the U.S. In 2023, approximately 14.4% of the United States population identified as Black, as per data analyzed by WHAT.EDU.VN. This article will delve into the demographic, geographic, and economic characteristics of the Black population in the U.S., offering a comprehensive overview. Explore the intricacies of Black demographics, including racial and ethnic diversity, on WHAT.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding the Black Population in the U.S.
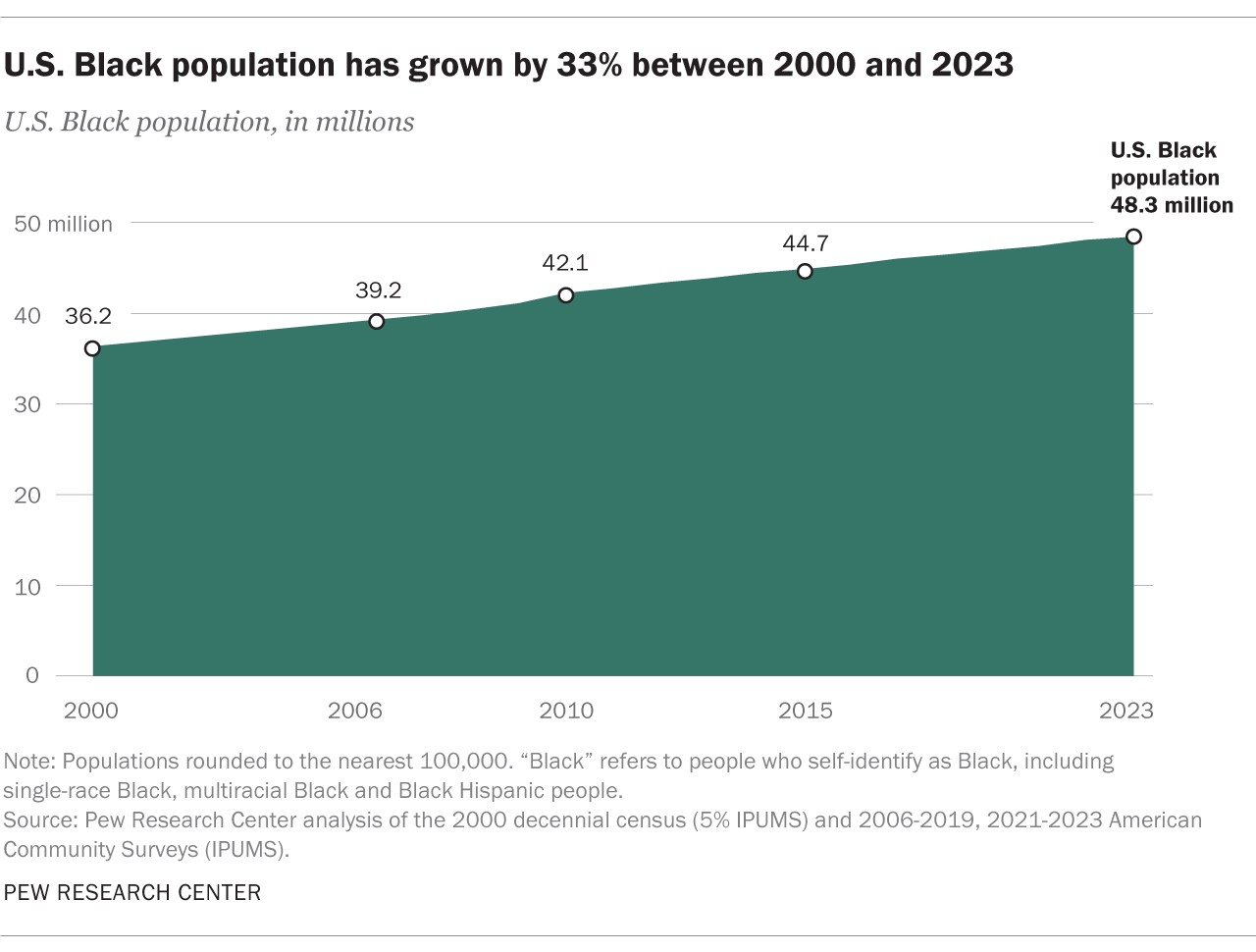
What percentage of the US population is Black? In 2023, approximately 14.4% of the United States population identified as Black. This accounts for an estimated 48.3 million people who self-identify as Black, either alone or in combination with other races. To fully understand the Black demographic in the U.S., it’s essential to consider the nuances within this group, including variations in racial and ethnic identities, immigration status, and socioeconomic factors.
1.1. Defining the Black Population
The term “Black population” encompasses a diverse group of individuals with varied racial and ethnic identities. According to the Pew Research Center, the Black population includes:
- Individuals who identify their race as Black, either alone or in combination with other racial backgrounds.
- Hispanics who identify their race as Black.
- Both U.S. born and foreign born individuals.
Understanding these nuances is essential for accurately interpreting demographic data and formulating inclusive policies.
1.2. Growth and Diversity
The Black population in the U.S. has experienced significant growth over the past few decades. Since 2000, the Black population has increased by 33%, from 36.2 million to 48.3 million in 2023. This growth is attributed to factors such as:
- Natural increase (births exceeding deaths).
- Immigration from African countries, the Caribbean, and other parts of the world.
- An increase in individuals identifying as multiracial.
This growth underscores the increasing diversity within the Black community, with individuals tracing their roots to various countries and cultures.
1.3. Subgroups within the Black Population
To provide a more detailed analysis, the Black population can be further divided into subgroups based on racial and ethnic identities:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: Individuals who identify only as Black and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: Individuals who identify with two or more races and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino.
- Black Hispanic: Individuals who identify as Hispanic or Latino and as Black, either alone or in combination with other races.
Analyzing these subgroups separately provides insights into the unique characteristics and experiences of each group, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the Black population in the U.S.
2. Population Growth Trends
2.1. Overall Growth
The Black population in the U.S. has experienced substantial growth since 2000, increasing from 36.2 million to 48.3 million in 2023. This represents a 33% increase over roughly two decades. Understanding the factors driving this growth is crucial for anticipating future demographic trends and addressing the needs of the Black community.
2.2. Growth of Foreign-Born Black Population
The foreign-born Black population has also experienced significant growth, increasing from 2.4 million in 2000 to over 5 million in 2023. This represents an increase from 7% to 11% of the total Black population. Factors contributing to this growth include:
- Immigration policies and opportunities in the U.S.
- Economic and political conditions in countries of origin.
- Family reunification.
It is important to note that recent data indicates that immigrants are underrepresented in official population estimates used for the 2023 ACS, so these numbers may be slightly smaller than indicated by new Census Bureau estimates.
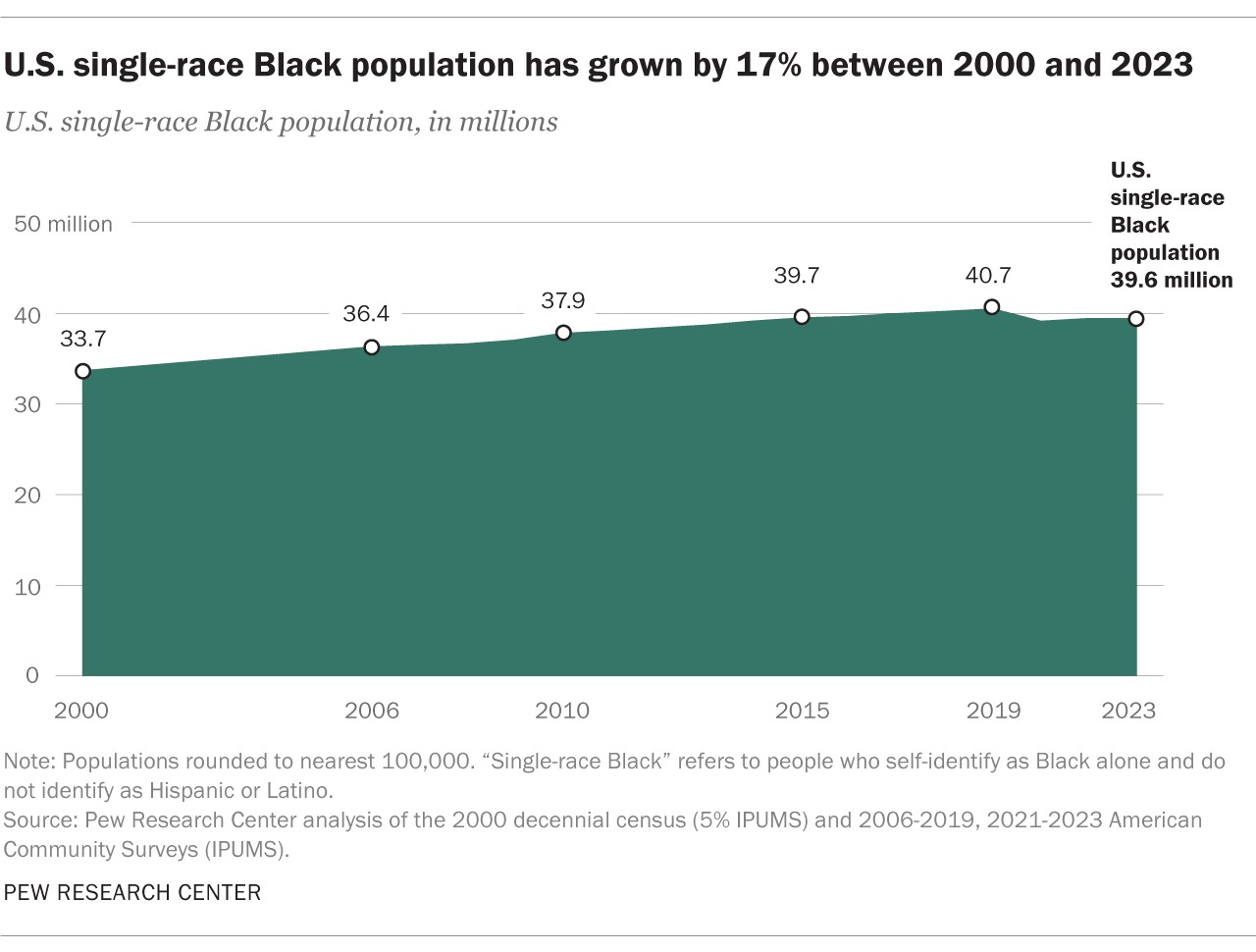
2.3. Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black Population Growth
The single-race, non-Hispanic Black population remains the largest demographic subgroup within the Black population, numbering 39.6 million in 2023. This group has grown by 17% since 2000, when the population was 33.7 million. This growth is primarily driven by natural increase (births exceeding deaths).
2.4. Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black Population Growth
The multiracial, non-Hispanic Black population has experienced the most rapid growth among all subgroups, increasing from 1.5 million in 2000 to 5.6 million in 2023. This represents a 269% increase. Factors contributing to this growth include:
- Increased acceptance and recognition of multiracial identities.
- Changes in census methodology, allowing individuals to identify with multiple races.
- Intermarriage and increasing diversity in family structures.
This rapid growth highlights the increasing complexity of racial identity in the U.S. and the need for inclusive policies that recognize and support multiracial individuals.
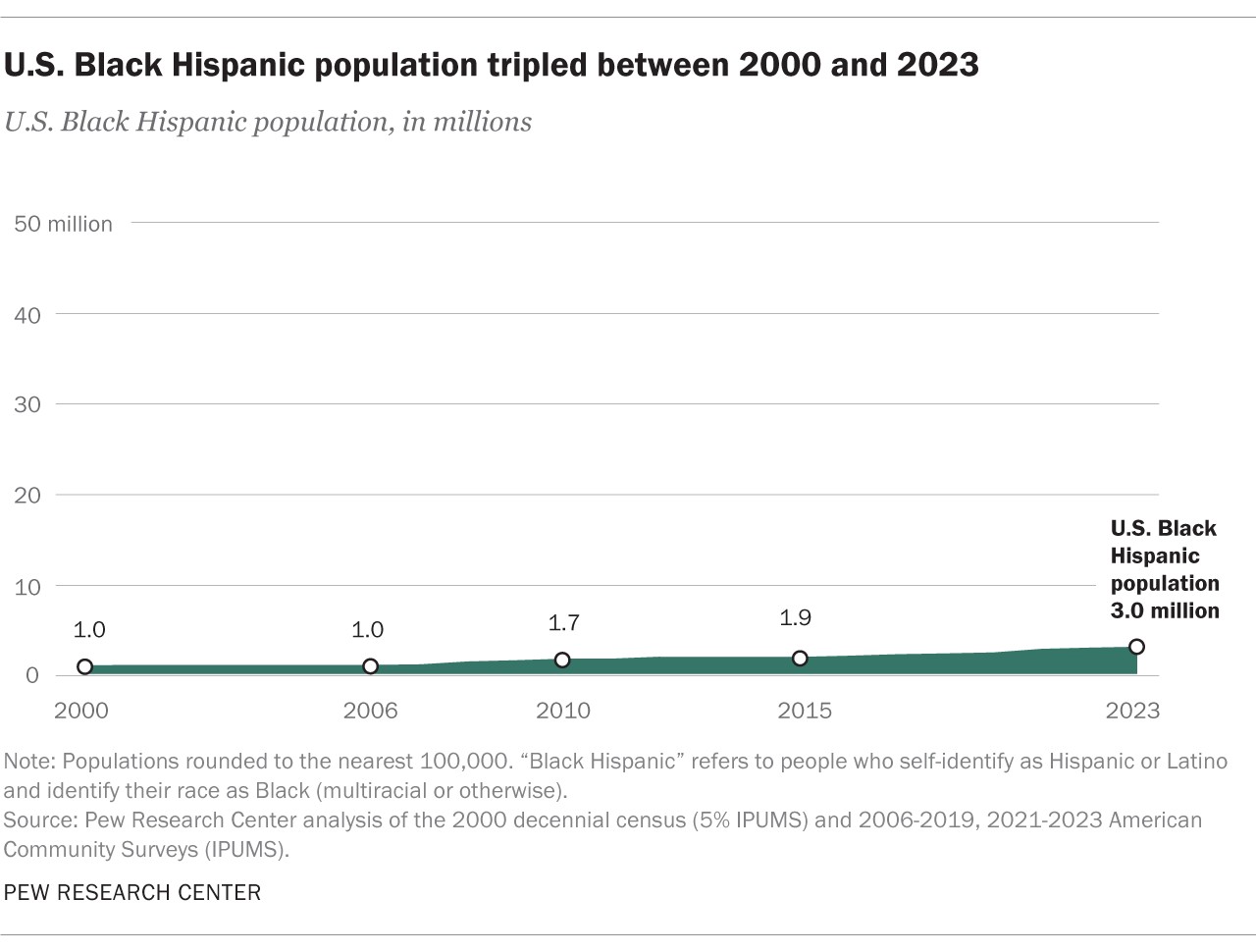
2.5. Black Hispanic Population Growth
The Black Hispanic population has also experienced substantial growth, increasing from 980,000 in 2000 to 3.0 million in 2023. This represents a 210% increase. Factors contributing to this growth include:
- Immigration from Latin American countries with significant Black populations.
- Increasing numbers of individuals identifying with both Black and Hispanic identities.
- Intermarriage and increasing diversity in family structures.
It is important to note that the Black Hispanic population is not necessarily the same as the nation’s Afro-Latino population, as not all Black Hispanics identify as Afro-Latino, and not all Afro-Latinos self-identify as Black or Hispanic.
3. Age Structure and Fertility
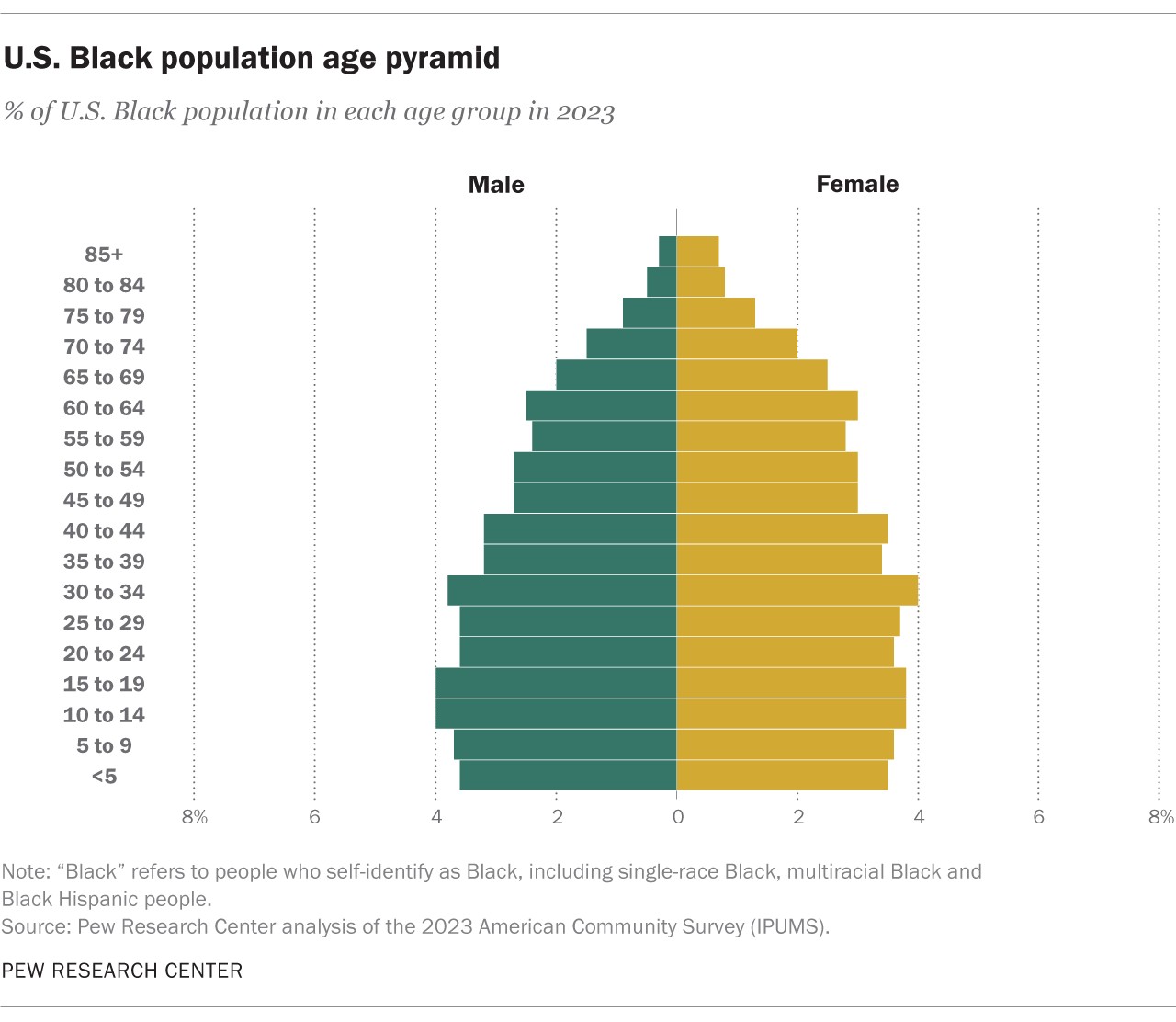
3.1. Median Age
The Black population in the U.S. is relatively young, with a median age of 32.6 years in 2023. This is about six years younger than the median age of the overall U.S. population, which is 38.2 years. This younger age structure has implications for various social and economic factors, including:
- Labor force participation.
- Educational attainment.
- Healthcare needs.
- Social Security and retirement planning.
3.2. Age Distribution
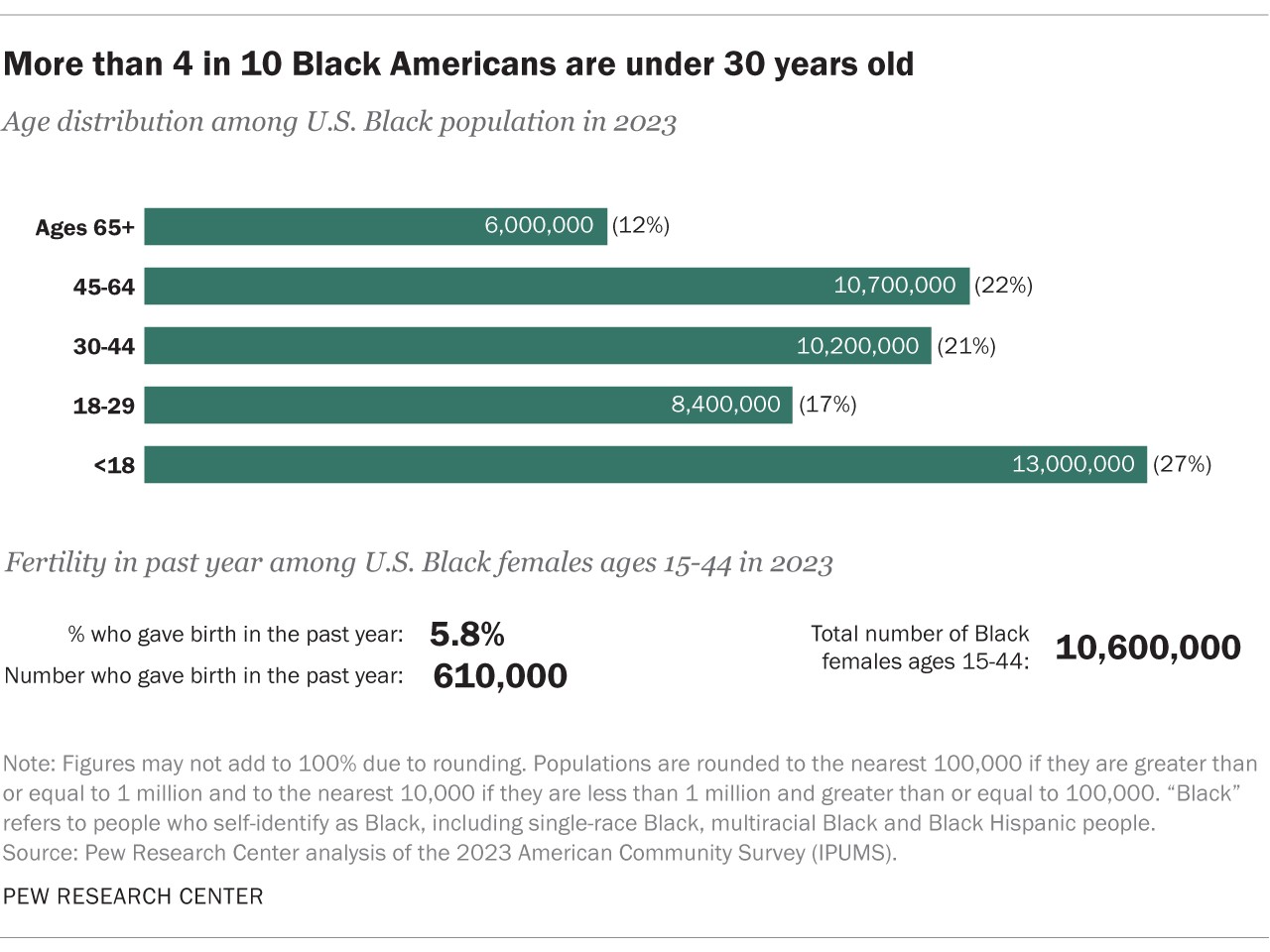
In 2023, approximately 30% of the Black population was under the age of 20, while 12% were 65 or older. This age distribution highlights the importance of investing in education, healthcare, and social services for both young people and seniors within the Black community.
3.3. Share of Population Under 30 and Under 18
Nearly half (44%) of Black Americans were younger than 30 in 2023, and more than a quarter (27%) were under 18. These statistics underscore the potential for future growth and development within the Black community, as well as the need for targeted programs and initiatives to support young people and families.
3.4. Fertility Rate
The general fertility rate among Black females ages 15 to 44 was 5.8% in 2023. This means that 5.8% of females in this age group had a birth in the previous 12 months. This fertility rate is influenced by various factors, including:
- Socioeconomic conditions.
- Access to healthcare and family planning services.
- Cultural norms and values.
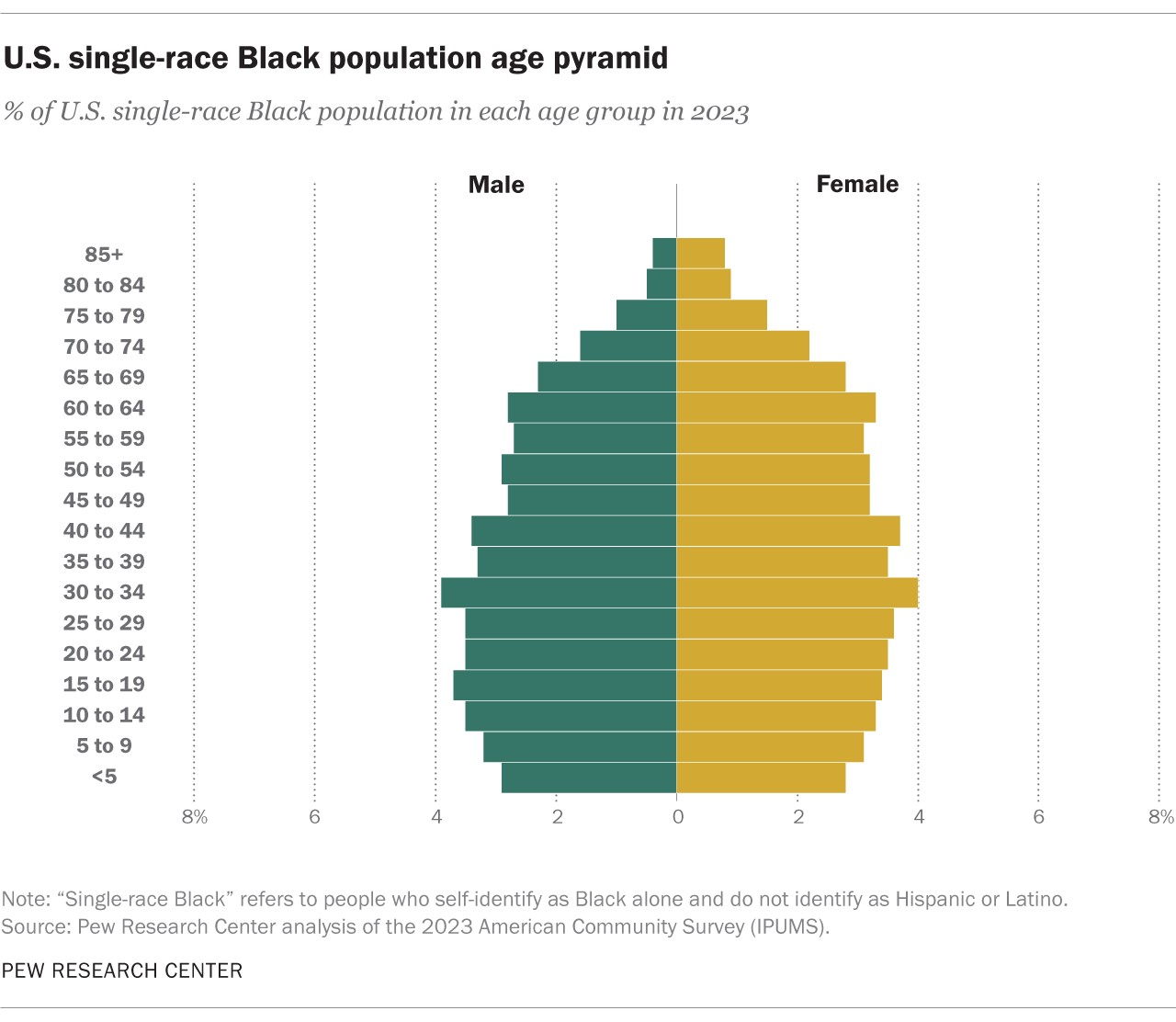
3.5. Age Structure of Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black Population
The single-race, non-Hispanic Black population also has a relatively young age structure, with a median age of 35.4 years in 2023. Approximately 26% of this group was under the age of 20, and 14% were 65 or older.
3.6. Age Structure of Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black Population
The multiracial, non-Hispanic Black population is the youngest subgroup within the Black population, with a median age of 19.5 years in 2023. Nearly half (49%) of this group was under the age of 20, and only 5% were 65 or older. This young age structure has significant implications for the future growth and development of the multiracial Black community.
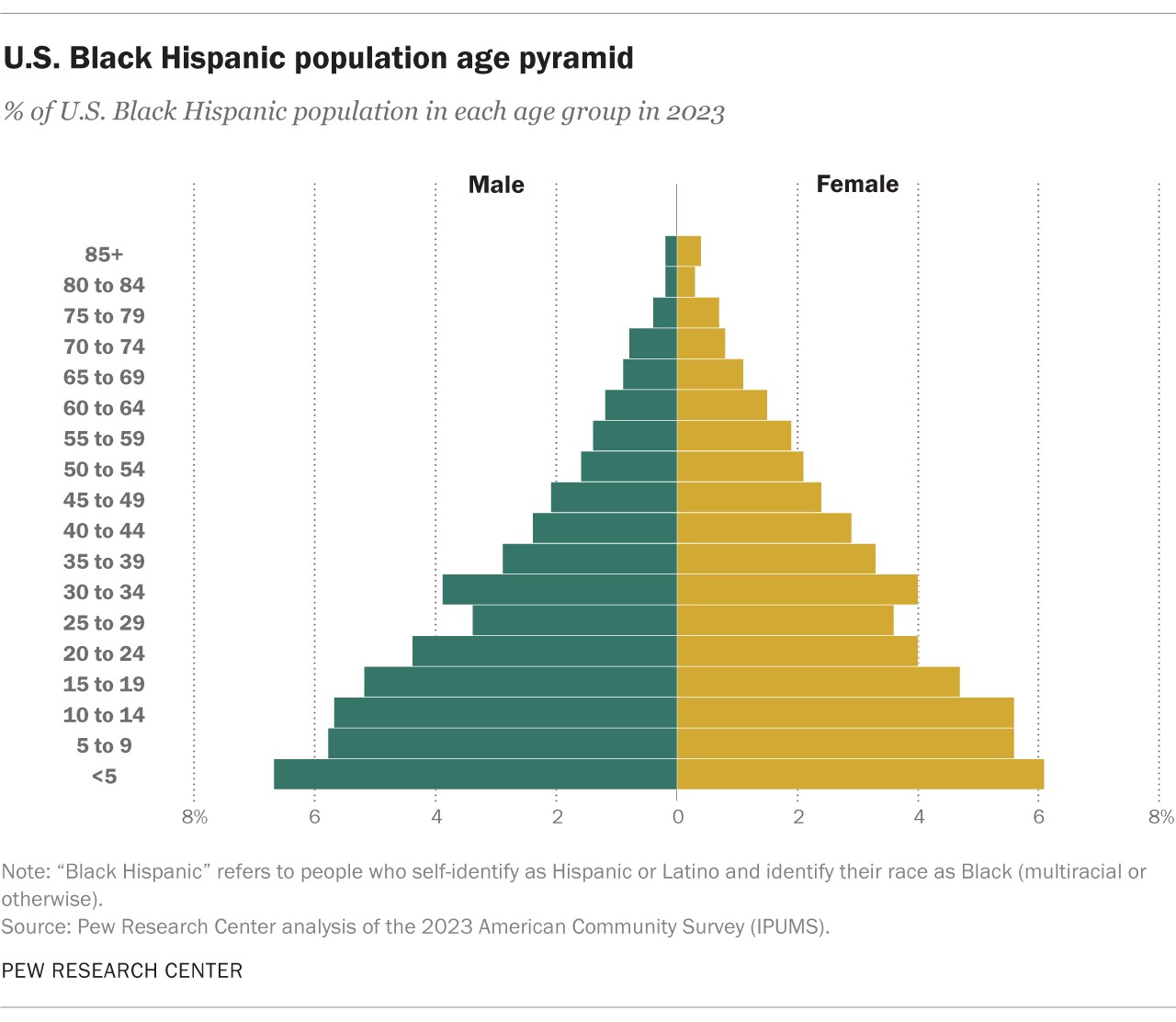
3.7. Age Structure of Black Hispanic Population
The Black Hispanic population is also relatively young, with a median age of 21.7 years in 2023. Almost half (45%) of this group was under the age of 20, and only 6% were 65 or older. This young age structure highlights the potential for future growth and development within the Black Hispanic community, as well as the need for targeted programs and initiatives to support young people and families.
4. Language Use
4.1. English Proficiency
The vast majority of the Black population in the U.S. is proficient in English. As of 2023, 96% of the Black population either speaks only English (88%) or speaks another language at home and reports speaking English very well (8%). This high level of English proficiency facilitates communication, education, and economic opportunities for Black individuals and communities.
4.2. Other Languages Spoken
In addition to English, other languages spoken at home by the Black population include:
- Spanish (4%)
- French or Haitian Creole (3%)
- Niger-Congo languages (1%)
- Amharic and other Ethiopian languages (1%)
The prevalence of these languages reflects the diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds within the Black community, and highlights the importance of providing language access services to those who need them.
4.3. Language Use Among Subgroups
Language use patterns vary among the subgroups within the Black population:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: The vast majority (97%) either speaks only English (90%) or speaks another language at home and reports speaking English very well (7%).
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: The vast majority (98%) either speaks only English (92%) or speaks another language at home and reports speaking English very well (6%).
- Black Hispanic: A substantial majority (82%) either speaks only English (52%) or speaks another language at home and reports speaking English very well (30%).
These variations in language use highlight the importance of culturally and linguistically appropriate services and resources for each subgroup within the Black population.
5. Geographic Distribution
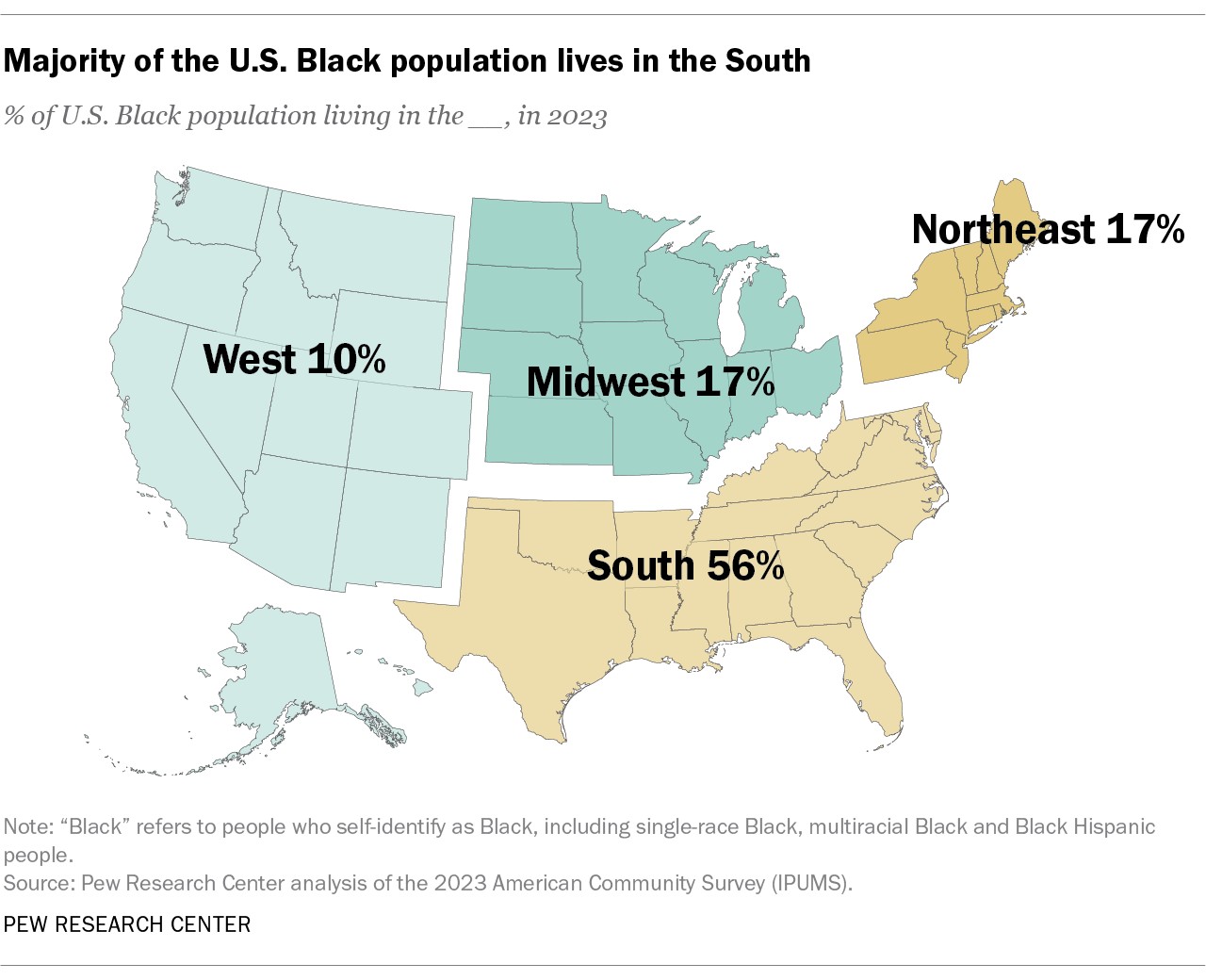
5.1. Regional Distribution
More than half (56%) of the Black population in the U.S. lives in the South as of 2023. Another 17% each live in the Midwest and Northeast, and 10% live in the West. This geographic concentration in the South reflects historical patterns of migration and settlement, as well as ongoing economic and social factors.
5.2. Top States of Residence
Texas is home to the largest Black population of any state, with approximately 4.3 million residents. Florida comes in a close second with 4.0 million, and Georgia comes in third with 3.7 million. These states have historically been centers of Black culture and community, and continue to attract Black residents due to economic opportunities and social networks.
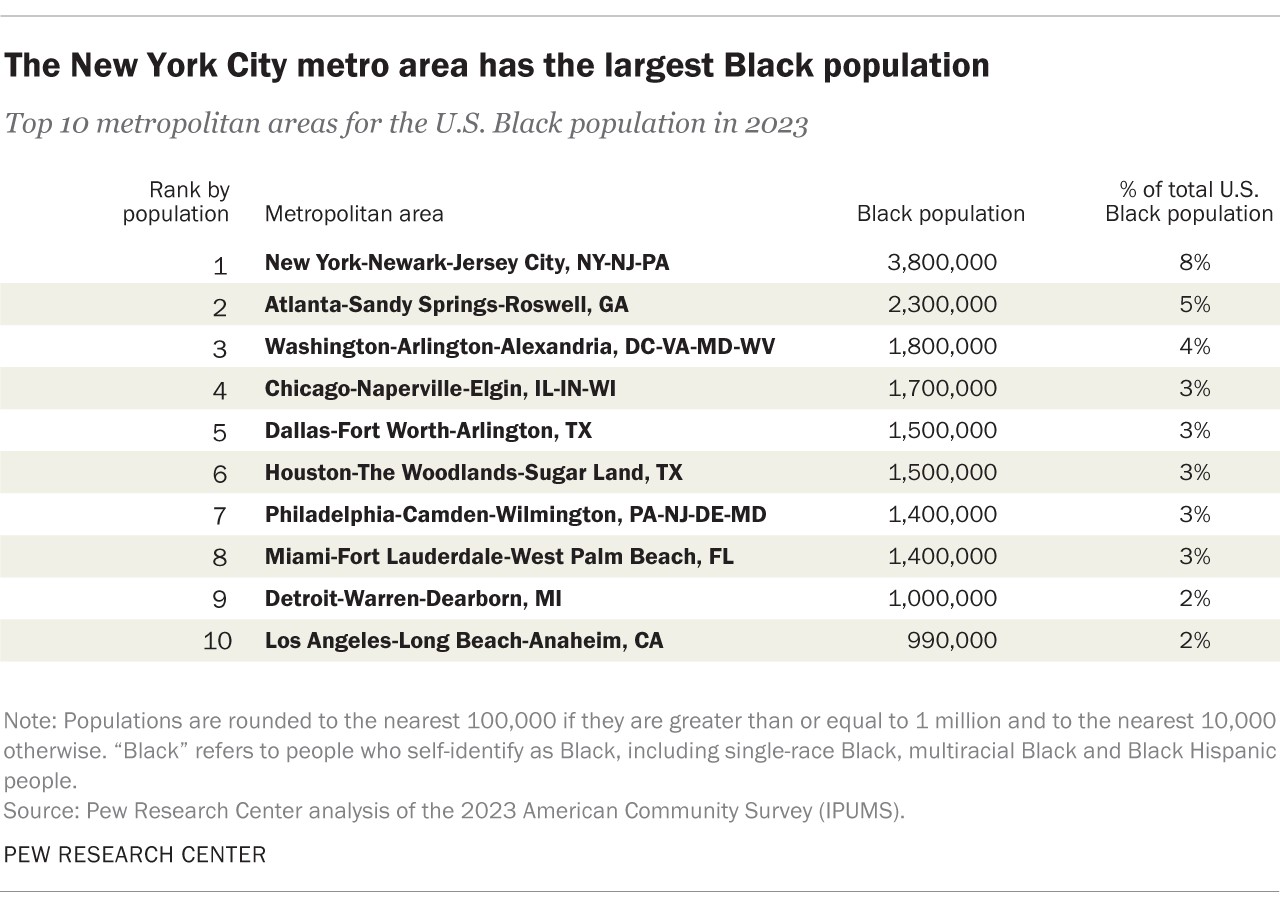
5.3. Metropolitan Areas with Largest Black Populations
The New York City metropolitan area has the greatest number of Black residents (3.8 million). The second-largest Black metro area population is Atlanta with 2.3 million. The Washington, D.C., metro area is third-largest with 1.8 million Black residents. These metropolitan areas offer a range of economic, educational, and cultural opportunities that attract Black residents from across the country and around the world.
5.4. Geographic Distribution of Subgroups
The geographic distribution of subgroups within the Black population varies:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: The South has the highest concentration of single-race, non-Hispanic Black residents, with 59% living there as of 2023.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: The South is home to the highest concentration of the multiracial Black population in the U.S., with 42% of the total as of 2023.
- Black Hispanic: Black Hispanic people are largely concentrated in the Northeast and South (71% combined total).
These variations in geographic distribution reflect the unique histories and experiences of each subgroup, as well as ongoing patterns of migration and settlement.
6. Household Income
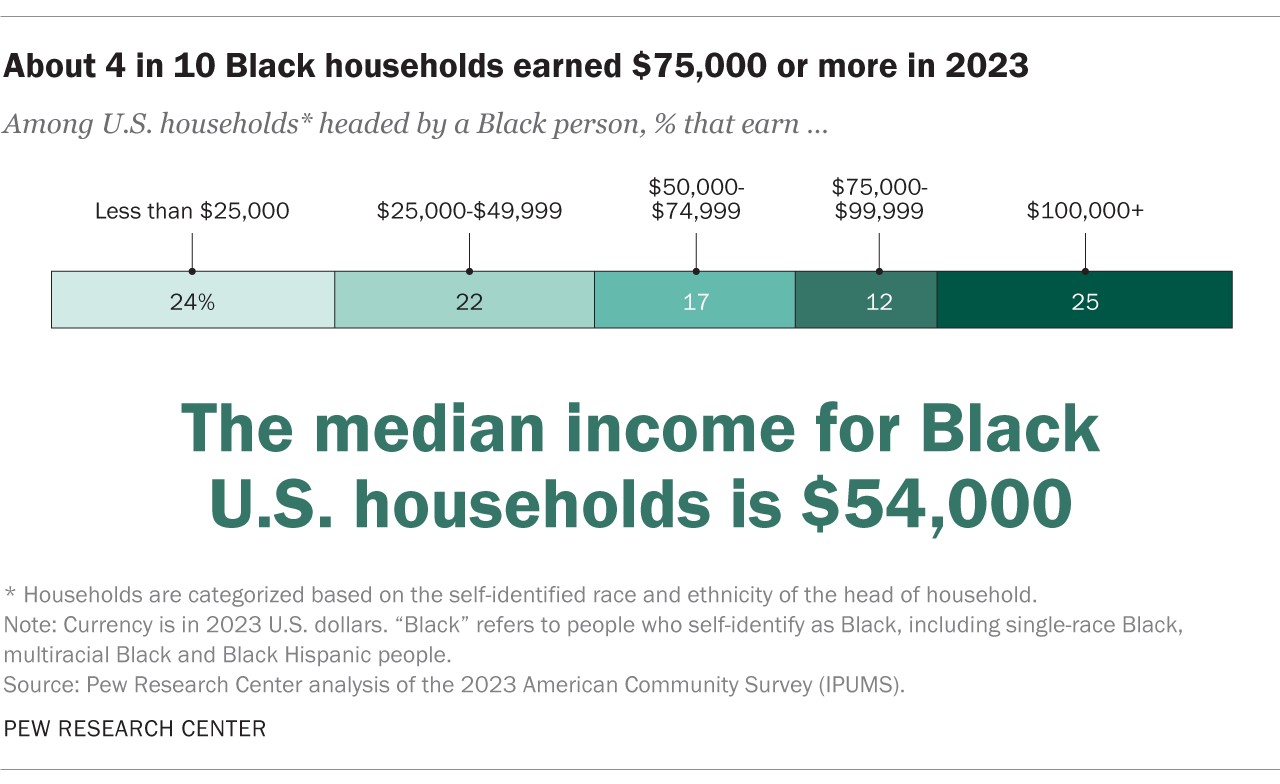
6.1. Median Household Income
Median household income in 2023 for households headed by a Black person was $54,000. This means that half of Black households earned more than that, and half earned less than that. While this represents progress over time, it is still lower than the median household income for White households.
6.2. Income Distribution
Over a third of Black households (37%) earned $75,000 or more in 2023, including 25% that made $100,000 or more. These figures demonstrate the increasing economic diversity within the Black community, as well as the growing number of Black households achieving financial stability.
6.3. Household Income Among Subgroups
Household income varies among the subgroups within the Black population:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: Median household income in 2023 for households headed by a single-race, non-Hispanic Black person was $52,800.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: The median household income for multiracial, non-Hispanic Black U.S. households is $65,800.
- Black Hispanic: The median household income for Black Hispanic U.S. households is $60,000.
These variations in household income reflect the unique economic opportunities and challenges faced by each subgroup, as well as differences in educational attainment, employment patterns, and family structures.
7. Household Type
7.1. Household Composition
About four-in-ten Black people in the U.S. (39%) live in households that are headed by married couples as of 2023. Three-in-ten Black people live in households whose household head is female, and 5% live in male-headed households. Fewer than two-in-ten (17%) are part of nonfamily households.
7.2. Household Type Among Subgroups
Household type varies among the subgroups within the Black population:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: About four-in-ten (38%) live in households that are headed by married couples as of 2023.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: More than four-in-ten (45%) live in households that are headed by married couples as of 2023.
- Black Hispanic: Roughly four-in-ten (43%) live in households headed by married couples in 2023.
These variations in household type reflect the diverse family structures and living arrangements within the Black community, as well as differences in cultural norms, economic conditions, and social support systems.
8. Educational Attainment
8.1. Bachelor’s Degree Attainment
About a quarter (27%) of all Black U.S. adults ages 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree or more education: 16% earned a bachelor’s degree and 11% earned an advanced degree. This represents significant progress over time, as educational attainment has been increasing among Black adults.
8.2. Educational Attainment Levels
As of 2023, about another third (32%) of Black adults have completed some college without obtaining a bachelor’s degree, and 30% have, at most, graduated from high school (or earned an equivalent such as a GED certificate). These figures highlight the ongoing need for efforts to improve educational opportunities and outcomes for Black students at all levels.
8.3. Educational Attainment Among Subgroups
Educational attainment varies among the subgroups within the Black population:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: About a quarter (26%) have earned a bachelor’s degree or higher as of 2023.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: About a third (35%) have earned a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Black Hispanic: Almost three-in-ten (28%) have earned a bachelor’s degree or higher as of 2023.
These variations in educational attainment reflect the unique educational opportunities and challenges faced by each subgroup, as well as differences in socioeconomic status, access to resources, and cultural values.
9. Factors Influencing Black Demographics
Several key factors influence the demographics of the Black population in the U.S.:
- Immigration: Immigration from African countries, the Caribbean, and other parts of the world has contributed to the growth and diversity of the Black population.
- Racial Identity: Changes in how the U.S. Census Bureau asks about racial and ethnic identity have influenced how individuals identify themselves, leading to an increase in the number of people identifying as multiracial.
- Fertility Rates: Fertility rates among Black females have an impact on the age structure and growth of the Black population.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic factors such as income, education, and employment opportunities influence migration patterns, household composition, and overall well-being within the Black community.
10. Implications and Future Trends
Understanding the demographics of the Black population in the U.S. has important implications for:
- Policy Development: Informed policies that address the unique needs and challenges of the Black community.
- Resource Allocation: Equitable distribution of resources to support education, healthcare, and social services within the Black community.
- Community Development: Targeted programs and initiatives to promote economic empowerment, cultural preservation, and community building within the Black community.
Future trends to watch include:
- Continued growth and diversification of the Black population.
- Increasing numbers of individuals identifying as multiracial.
- Shifting geographic distribution patterns.
- Ongoing efforts to address racial disparities in education, income, and health outcomes.
By staying informed about these demographic trends and their implications, policymakers, community leaders, and individuals can work together to create a more equitable and inclusive society for all.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the current percentage of the Black population in the United States? | In 2023, approximately 14.4% of the United States population identified as Black. |
| How has the Black population grown since 2000? | The Black population has grown by 33% since 2000, increasing from 36.2 million to 48.3 million in 2023. |
| What are the major subgroups within the Black population? | The major subgroups include Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black; Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black; and Black Hispanic. |
| Where do most Black Americans live? | More than half (56%) of the Black population lives in the South as of 2023. |
| What is the median household income for Black households? | Median household income in 2023 for households headed by a Black person was $54,000. |
| What is the educational attainment level among Black adults? | About a quarter (27%) of all Black U.S. adults ages 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree or more education. |
| What factors contribute to the growth of the Black population? | Factors include natural increase (births exceeding deaths), immigration, and changes in racial identification. |
| How does language use vary within the Black population? | The vast majority of Black Americans are proficient in English, but other languages spoken include Spanish, French/Haitian Creole, and various African languages. |
| What are some of the key trends to watch in Black demographics? | Key trends include continued growth and diversification, increasing numbers of multiracial individuals, and shifts in geographic distribution. |
| How can understanding Black demographics inform policy and community development? | Understanding Black demographics can inform policies and programs that address the unique needs and challenges of the Black community, promote economic empowerment, and foster community building. |
11.1. Population and Diversity FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the definition of the Black population used in this analysis? | The Black population includes individuals who identify their race as Black, either alone or in combination with other racial backgrounds, and Hispanics who identify their race as Black. |
| How has the foreign-born Black population grown in recent years? | The foreign-born Black population has increased from 2.4 million in 2000 to over 5 million in 2023, representing an increase from 7% to 11% of the total Black population. |
| What factors have contributed to the growth of the Black Hispanic population? | The growth is due to immigration from Latin American countries with significant Black populations, increasing numbers of individuals identifying with both Black and Hispanic identities, and intermarriage. It’s important to note that the Black Hispanic population is not necessarily the same as the nation’s Afro-Latino population, as not all Black Hispanics identify as Afro-Latino. |
11.2. Age and Fertility FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the median age of the Black population in the U.S.? | The median age of the Black population in the U.S. is 32.6 years in 2023, which is younger than the overall U.S. population’s median age of 38.2 years. |
| How does the age structure vary among subgroups of the Black population? | The multiracial, non-Hispanic Black population is the youngest, with a median age of 19.5 years, while the single-race, non-Hispanic Black population has a median age of 35.4 years. |
| What is the general fertility rate among Black females? | The general fertility rate among Black females ages 15 to 44 was 5.8% in 2023. |
11.3. Language and Geography FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What percentage of Black Americans are proficient in English? | The vast majority (96%) of the Black population either speaks only English (88%) or speaks another language at home and reports speaking English very well (8%). |
| Where do most Black Americans live in the U.S.? | More than half (56%) of the Black population lives in the South as of 2023. Texas has the largest Black population of any state, with approximately 4.3 million residents, followed by Florida and Georgia. The New York City metropolitan area has the greatest number of Black residents (3.8 million), followed by Atlanta and Washington, D.C. |
11.4. Income and Education FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the median household income for households headed by a Black person? | Median household income in 2023 for households headed by a Black person was $54,000. |
| What percentage of Black adults have a bachelor’s degree or higher? | About a quarter (27%) of all Black U.S. adults ages 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree or more education. |
| How does household income and educational attainment vary among subgroups of the Black population? | There are variations in household income and educational attainment among subgroups within the Black population, reflecting the unique economic opportunities and challenges faced by each group. The median household income for multiracial, non-Hispanic Black U.S. households is higher than for single-race, non-Hispanic Black U.S. households. |
12. Need Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN
Do you have more questions about demographics, statistics, or any other topic? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a free platform for you to ask any question and receive quick, accurate answers. Our goal is to connect you with a community of knowledgeable individuals who can help you find the information you need.
12.1. Why Use WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free to Use: Ask as many questions as you like without any cost.
- Quick Answers: Get timely responses from experts and community members.
- Easy to Understand: Receive clear and concise explanations tailored to your needs.
- Community Support: Connect with others who share your interests and can offer valuable insights.
12.2. How to Get Started
- Visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN.
- Create a free account.
- Post your question in the appropriate category.
- Receive answers from our community of experts.
12.3. Contact Information
If you have any questions or need assistance, feel free to contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Join what.edu.vn today and experience the convenience of having your questions answered quickly and easily!